VACCINE EFFICACY 101: A biostatistician& #39;s primer
Ten tweets to cover:
- How is vaccine efficacy calculated?
- Distinguishing between infection, disease, & severe disease.
- Measuring reduced infectiousness.
- Vaccine efficacy vs. effectiveness!
Ten tweets to cover:
- How is vaccine efficacy calculated?
- Distinguishing between infection, disease, & severe disease.
- Measuring reduced infectiousness.
- Vaccine efficacy vs. effectiveness!
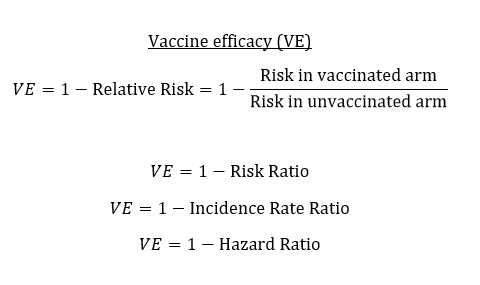
2) Vaccine efficacy (VE) measures the relative reduction in infection/disease for the vaccinated arm versus the unvaccinated arm. A perfect vaccine would eliminate risk entirely, so VE = 1 or 100%. This can be calculated from the risk ratio, incidence rate ratio, or hazard ratio.
3) Vaccine efficacy of 50% roughly means you have a 50% reduced risk of becoming sick compared to an otherwise similar unvaccinated person. Or you have a 50% chance of becoming sick given that you were exposed to enough infectious virus to make an unvaccinated person sick.
4) Though we talk about vaccine efficacy as a single number, there are actually several different types of vaccine efficacy, such as:
- Efficacy to prevent infection (sterilizing immunity)
- Efficacy to prevent disease
- Efficacy to prevent severe disease
- Efficacy to prevent infection (sterilizing immunity)
- Efficacy to prevent disease
- Efficacy to prevent severe disease
5) Most Phase 3 trials are measuring efficacy to prevent disease as the primary analysis, with efficacy against infection and against severe disease as secondary analyses. https://twitter.com/nataliexdean/status/1308474307312594945?s=20">https://twitter.com/nataliexd...
6) Preventing infection entirely is the hardest to achieve. And of course a vaccine that prevents infection will also prevent disease and severe disease. But we can have vaccines where people are still infected but their disease severity is lessened. https://twitter.com/rvenkayya/status/1309932127786610691?s=20">https://twitter.com/rvenkayya...
7) So far I have talked about how well a vaccine directly protects the vaccinated individual. Another important type of vaccine effect is the ability of a vaccine to reduce infectiousness to others. This is known as indirect protection, and is related to herd immunity.
8) A vaccine that prevents infection entirely provides indirect protection to others. If I can& #39;t get infected, I can& #39;t infect you. But it is possible to have a vaccine that prevents disease but individuals can still be infectious. https://twitter.com/florian_krammer/status/1310428768994033664?s=20">https://twitter.com/florian_k...
9) Household studies can be very useful here, where we follow the household contacts of infected vaccinated individuals and infected unvaccinated individuals, and compare how frequently they are infected. Pioneering work from my mentor @betzhallo.
http://courses.washington.edu/b578a/readings/PreziosiHalloranVaccine2003.pdf">https://courses.washington.edu/b578a/rea...
http://courses.washington.edu/b578a/readings/PreziosiHalloranVaccine2003.pdf">https://courses.washington.edu/b578a/rea...
10) Finally, vaccine efficacy vs. effectiveness? We like to reserve "efficacy" for estimates from randomized trials, where everyone receives the vaccine as intended (proper cold chain, no missed doses). We distinguish this idealized measure from real-world "effectiveness." END

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter