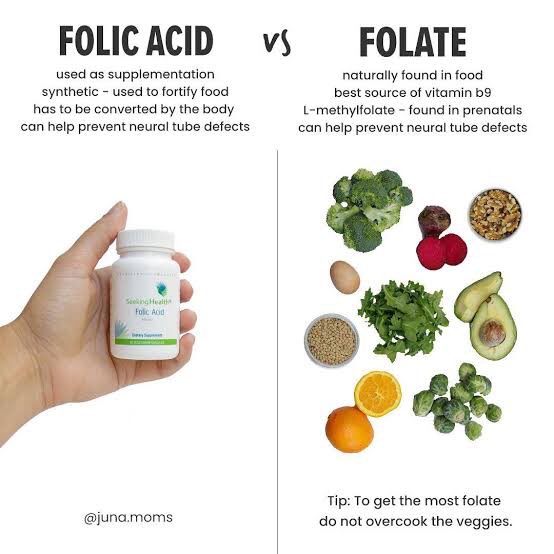
In a lot of health and nutrition talks, especially ones centered around pregnancy and childbirth, it’s possible that you’ve heard Folic Acid or Folate being mentioned. Today, we’re talking about FOLATE as it relates in normal health and pregnancy.
#nutritionfridayswithademi https://twitter.com/ademii__/status/1254760303063072770">https://twitter.com/ademii__/...
#nutritionfridayswithademi https://twitter.com/ademii__/status/1254760303063072770">https://twitter.com/ademii__/...
What is Folate?
Folate (B9) also known as Folic Acid is one of the eight(8) water-soluble B-vitamin complex group.
Let’s set things straight; Folate is what is naturally found in foods while Folic Acid is the commercially synthesised form added to foods or made as supplements.
Folate (B9) also known as Folic Acid is one of the eight(8) water-soluble B-vitamin complex group.
Let’s set things straight; Folate is what is naturally found in foods while Folic Acid is the commercially synthesised form added to foods or made as supplements.
It is one vitamin that is appreciated for its importance beyond normal metabolism, especially in the etiology of chronic diseases and birth defects in infants.
The biochemically active form of folate is Tetrahydrofolic acid (THF).
The biochemically active form of folate is Tetrahydrofolic acid (THF).
Let’s have some facts..
- Folic acid deficiency is an important public health challenge in many parts of the world, especially in places where there’s poverty and malnutrition. It’s also one important cause of anemia.
- Folic acid deficiency is an important public health challenge in many parts of the world, especially in places where there’s poverty and malnutrition. It’s also one important cause of anemia.
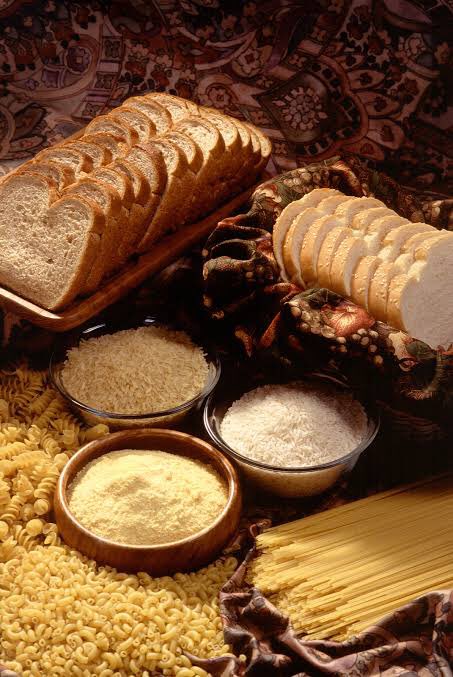
- In 1998, the U.S. FDA mandated that folic acid be added to all enriched cereal grain products (breads, pastas, wheat flours, breakfast cereals, rice) to reduce the prevalence of birth defects called Neural tube defects (NTDs) in infants caused by folic acid deficiency.
So, what does Folate do in the body?
1. Folate is important for normal fetal (foetus) growth and development, especially their brain and spinal cord https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤰🏾" title="Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤰🏾" title="Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">
2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA">
3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine.
1. Folate is important for normal fetal (foetus) growth and development, especially their brain and spinal cord
2. It is required for DNA synthesis
3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine.
Now, let’s talk food. Where can we get folate from?
Folate occurs in a variety of food, both from plant and animal origins.
Liver (chicken and beef liver) is the richest animal sources of folate and honestly the richest source itself.
Folate occurs in a variety of food, both from plant and animal origins.
Liver (chicken and beef liver) is the richest animal sources of folate and honestly the richest source itself.
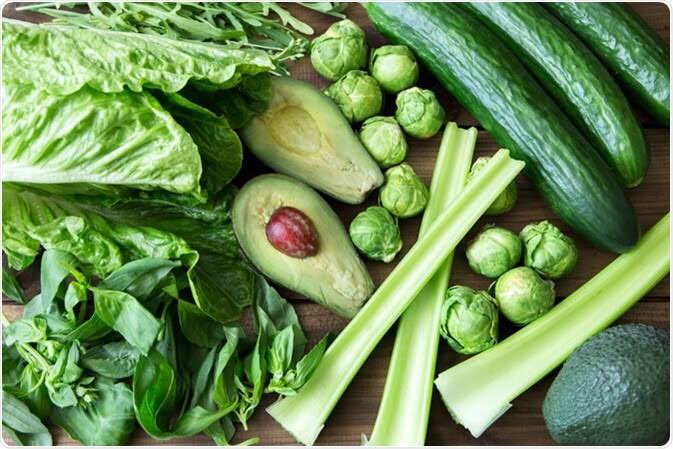
Plant origins include leafy vegetables  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥬" title="Leafy green" aria-label="Emoji: Leafy green"> (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥬" title="Leafy green" aria-label="Emoji: Leafy green"> (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate.
It’s important to note that Folate is an unstable vitamin and >70% is usually lost due to leaching/heating of these vegetables and longer storage as well (3 days or more). So eat fresh veggies and minimally heat them
Folic acid fortification of cereal grains (bread, rice, pasta and breakfast cereal) is also an excellent way to get adequate folate intake. Folic acid supplements are also recommended for women of child-bearing age.
Just to add, Folic Acid has positive and negative interactions with drugs and nutrients.
Negative https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👎🏾" title="Thumbs down (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs down (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)"> interactions with NSAIDS (pain relief drugs) , chemotherapeutic agents and antacids.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👎🏾" title="Thumbs down (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs down (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)"> interactions with NSAIDS (pain relief drugs) , chemotherapeutic agents and antacids.
Positive https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👍🏾" title="Thumbs up (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs up (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">interactions with Vit B6, B-12 and vitamin C. This enhances utilitisation.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👍🏾" title="Thumbs up (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs up (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">interactions with Vit B6, B-12 and vitamin C. This enhances utilitisation.
Negative
Positive
Alright guys, that’s it! Thanks for engaging with me on #nutritionfridayswithademi. I’ve attached a glossary for terms I used in this thread.
Remember, it is important to take Folate and for women, to take Folic Acid long before you get pregnant.
Remember, it is important to take Folate and for women, to take Folic Acid long before you get pregnant.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine." title="So, what does Folate do in the body? 1. Folate is important for normal fetal (foetus) growth and development, especially their brain and spinal cord https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤰🏾" title="Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine.">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine." title="So, what does Folate do in the body? 1. Folate is important for normal fetal (foetus) growth and development, especially their brain and spinal cord https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤰🏾" title="Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine.">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine." title="So, what does Folate do in the body? 1. Folate is important for normal fetal (foetus) growth and development, especially their brain and spinal cord https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤰🏾" title="Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine.">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine." title="So, what does Folate do in the body? 1. Folate is important for normal fetal (foetus) growth and development, especially their brain and spinal cord https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤰🏾" title="Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Schwangere Frau (durchschnittlich dunkler Hautton)">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👶🏽" title="Baby (mittlerer Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Baby (mittlerer Hautton)">2. It is required for DNA synthesis https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> 3. It helps to maintain normal levels of homocysteine.">

 (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate." title="Plant origins include leafy vegetables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥬" title="Leafy green" aria-label="Emoji: Leafy green"> (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate.">
(spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate." title="Plant origins include leafy vegetables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥬" title="Leafy green" aria-label="Emoji: Leafy green"> (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate.">
 (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate." title="Plant origins include leafy vegetables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥬" title="Leafy green" aria-label="Emoji: Leafy green"> (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate.">
(spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate." title="Plant origins include leafy vegetables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥬" title="Leafy green" aria-label="Emoji: Leafy green"> (spinach, okra , broccoli , lettuce, asparagus ), mushrooms https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🍄" title="Pilz" aria-label="Emoji: Pilz"> , legumes, nuts https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥜" title="Erdnüsse" aria-label="Emoji: Erdnüsse"> , and oilseeds e.g., soybeans, sunflower seeds. Baker’s yeast is another rich source of folate.">