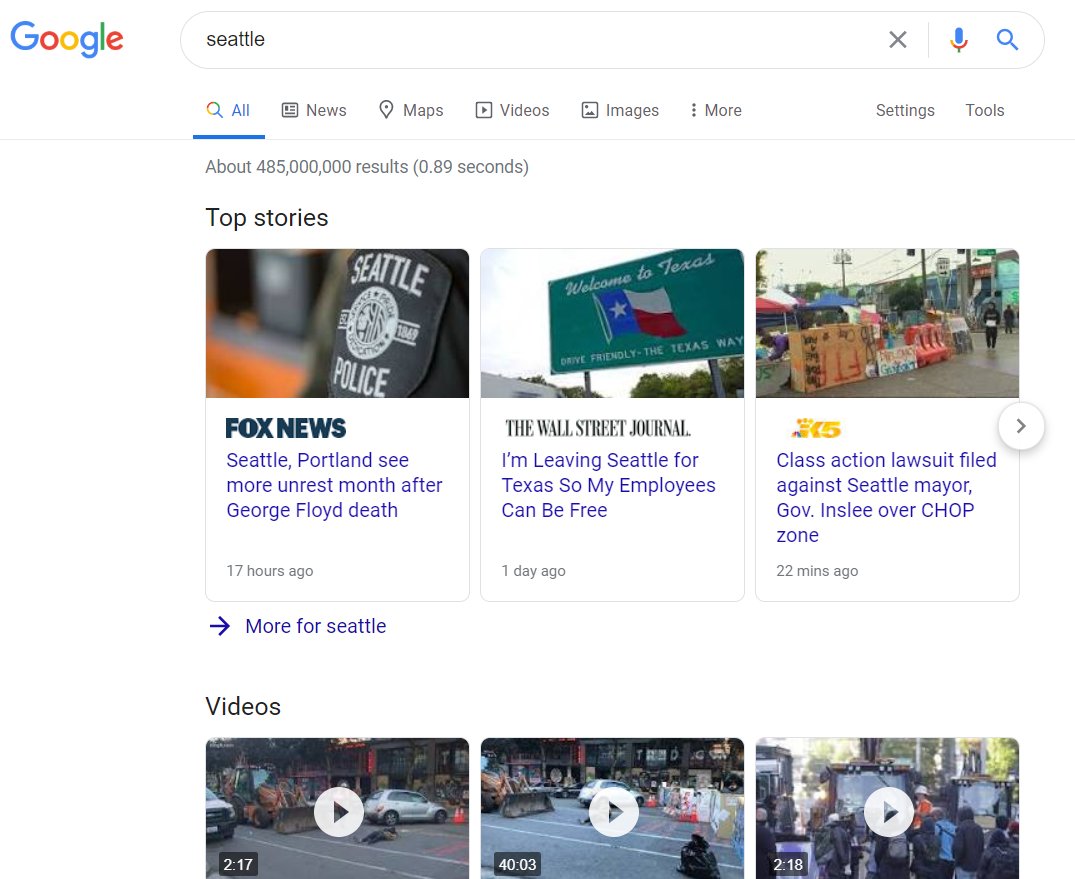
A search for "Seattle" is a superb example of how Google& #39;s algorithm works right now.
- Does the most relevant content rank? No.
- The most well-linked-to? No.
- The best optimized? No.
- The most useful? No.
Google is ranking the most "engaging" content. More details... /1
- Does the most relevant content rank? No.
- The most well-linked-to? No.
- The best optimized? No.
- The most useful? No.
Google is ranking the most "engaging" content. More details... /1
News & videos promoting conservative-media-driven fear about a 6-block area of the city dominate. Fox News, WSJ, YouTube clips, etc.
Why?
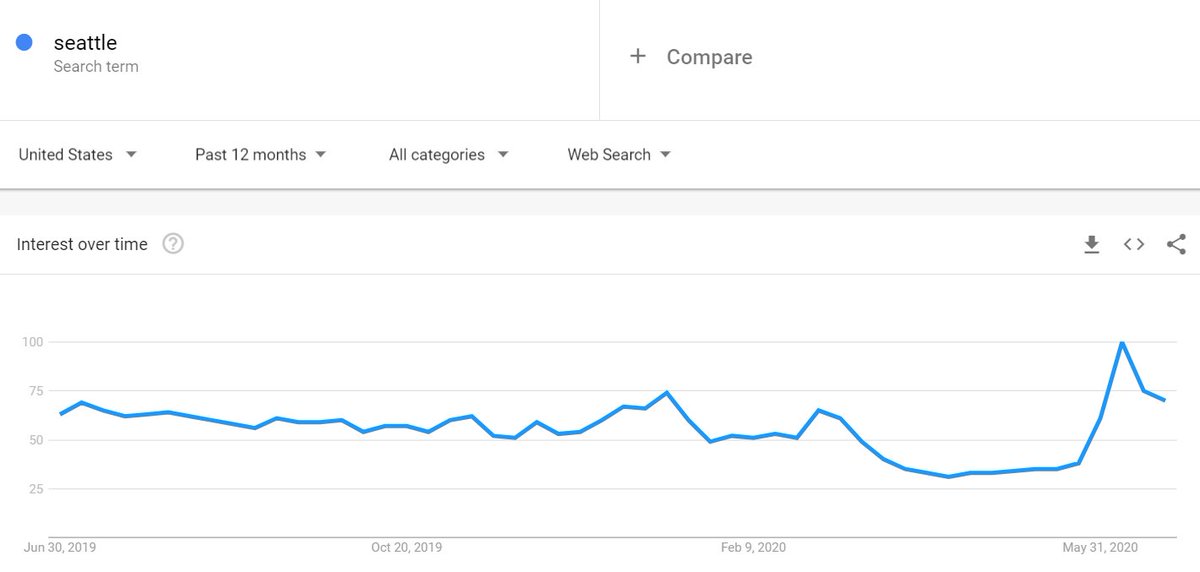
Because searches for Seattle have been spiking as (mostly) right-wing media focuses heavily on the city& #39;s protests. Chart from GG Trends /2
Why?
Because searches for Seattle have been spiking as (mostly) right-wing media focuses heavily on the city& #39;s protests. Chart from GG Trends /2
Those searchers aren& #39;t seeking tourism info, geography, population, or economics. They want articles & videos that reinforce the bias they came with. They& #39;ll scroll until they find it. The ML-algo learns that.
Putting aside politics, this is how Google& #39;s updated QDF works /3
Putting aside politics, this is how Google& #39;s updated QDF works /3
The query *deserves* freshness not only b/c of an increase in volume, but b/c new searchers are querying the keyword with a different purpose.
Google& #39;s algo quickly learns to serve that new purpose, and changes up the types of content that ranks, and the individual pages. /4
Google& #39;s algo quickly learns to serve that new purpose, and changes up the types of content that ranks, and the individual pages. /4
This is one reason SEO in the ~2017-2020 era is so different from SEO in the ten years prior.
The algo learns what searchers will click, and biases to that over what& #39;s relevant or well-optimized (in the classic SEO sense).
That *does not* mean SEO& #39;s impossible, far from it. /5
The algo learns what searchers will click, and biases to that over what& #39;s relevant or well-optimized (in the classic SEO sense).
That *does not* mean SEO& #39;s impossible, far from it. /5
It does, however, require a new kind of SEO.
Build the best "Seattle" resource in the world & you& #39;ll get nowhere.
Craft a biased-to-conservative-media-searchers page that delivers news & scenes of chaos in the CHOP & you might outrank the competition. /6
Build the best "Seattle" resource in the world & you& #39;ll get nowhere.
Craft a biased-to-conservative-media-searchers page that delivers news & scenes of chaos in the CHOP & you might outrank the competition. /6
This is, obviously, more visible in politically-focused searches than other kinds of content, but it happens everywhere.
Want to rank #1 for "New Switch Games"? You& #39;d better have content about games that came out *very* recently. Even a great page about Q1& #39;s games won& #39;t do. /7
Want to rank #1 for "New Switch Games"? You& #39;d better have content about games that came out *very* recently. Even a great page about Q1& #39;s games won& #39;t do. /7
How do you figure out when/whether a search has shifting types of demand? Google Trends can be helpful. Note the "rising" and "related" queries for that "Seattle" example. /8
Note: when I say "clicks," I don& #39;t mean Google& #39;s using *only* raw click data. They& #39;re sophisticated, likely combining signals like:
- Volume patterns
- Pogo-sticking
- Scrolling
- Query refinements
And dozens more. But shorthand, you can think of it as searcher behavior. /9
- Volume patterns
- Pogo-sticking
- Scrolling
- Query refinements
And dozens more. But shorthand, you can think of it as searcher behavior. /9

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter