Web Development Thread #1  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="collectie" aria-label="Emoji: collectie">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="collectie" aria-label="Emoji: collectie">
JavaScript Fundamentals
• Variables
• Comments
• DataTypes
• String
• Number
• ...more
• Operators
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Logical Operators
• Bitwise Operators
A mega thread ↓
JavaScript Fundamentals
• Variables
• Comments
• DataTypes
• String
• Number
• ...more
• Operators
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Logical Operators
• Bitwise Operators
A mega thread ↓
{1/28}
→ What is JavaScript
JavaScript is the most popular programming language and is used on both the client-side and server-side allowing you to make web pages interactive.
→ What is JavaScript
JavaScript is the most popular programming language and is used on both the client-side and server-side allowing you to make web pages interactive.
{2/28}
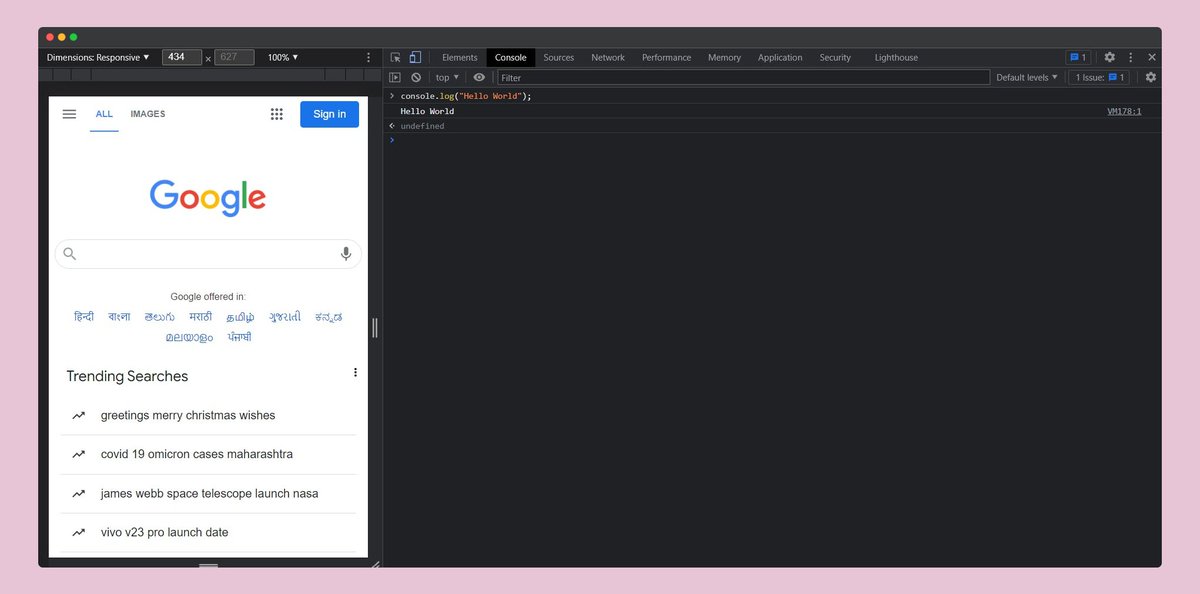
→ Hello World in JavaScript
The first step is to learn how to execute your code, JavaScript doesn& #39;t require any environment setup, You can just use your browser Developer Tools. Click right and select inspect, then go to the console.
→ Hello World in JavaScript
The first step is to learn how to execute your code, JavaScript doesn& #39;t require any environment setup, You can just use your browser Developer Tools. Click right and select inspect, then go to the console.
{3/28}
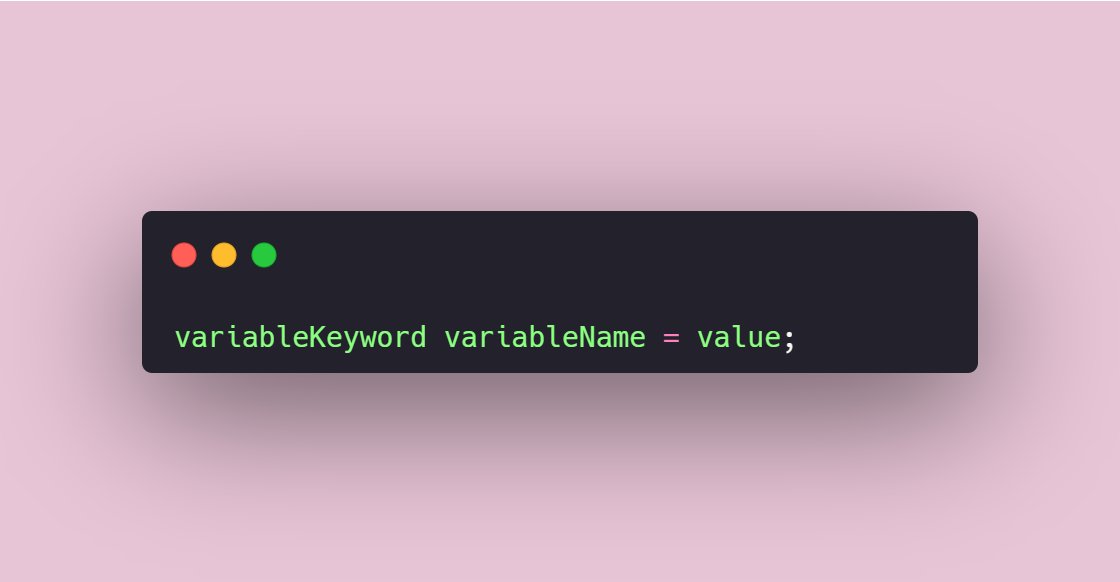
→ Variables
Variables in JavaScript are just a container that stores the value. The variable declaration has the following syntax:
→ Variables
Variables in JavaScript are just a container that stores the value. The variable declaration has the following syntax:
{4/28}
There are three keywords in JavaScript that can be used as a variable keyword (var, let, const). variableName is the name that you give to the variable and the value which will be assigned to the variable means this variable holds this value inside itself.
There are three keywords in JavaScript that can be used as a variable keyword (var, let, const). variableName is the name that you give to the variable and the value which will be assigned to the variable means this variable holds this value inside itself.
{5/28}
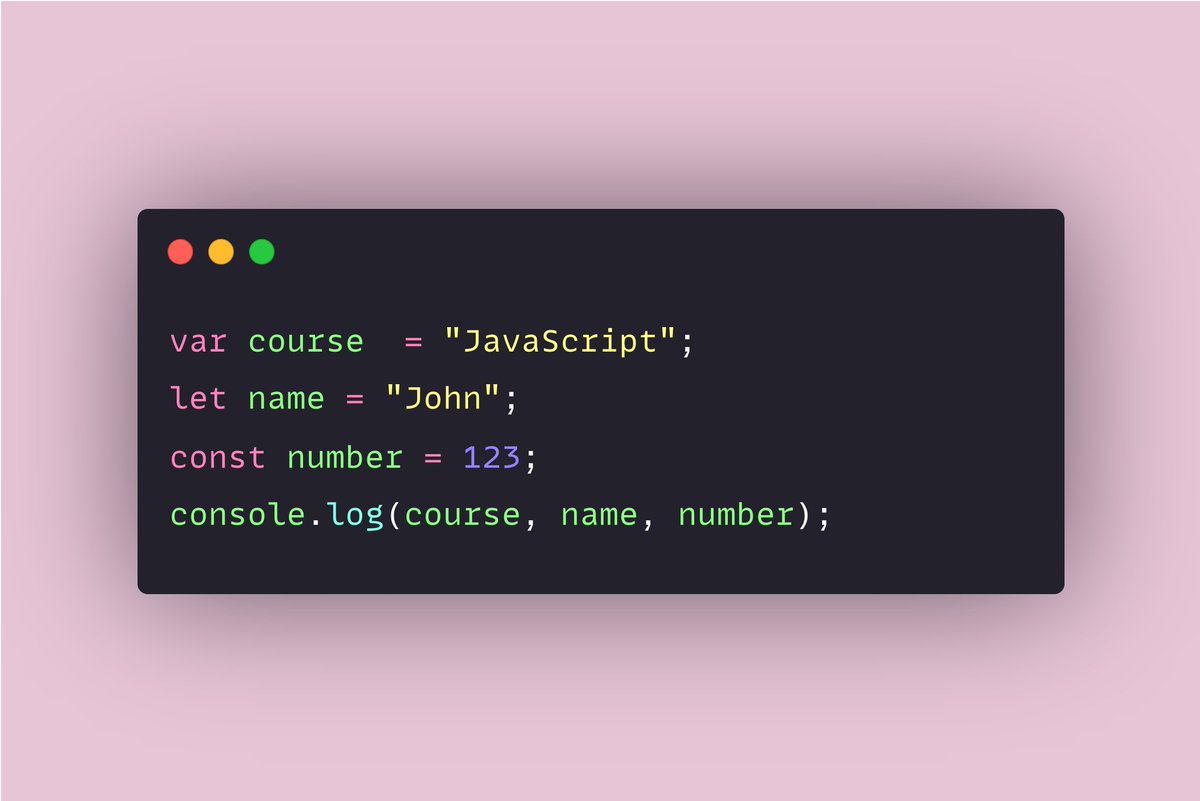
If you paste the below code on the console and click enter the output will be "JavaScript John 123".
It just provided the value of each variable.
If you paste the below code on the console and click enter the output will be "JavaScript John 123".
It just provided the value of each variable.
{6/28}
You can see that (var, let, const) are all doing the same thing, they are all just providing the value of the variable but what is the difference between them?
You can see that (var, let, const) are all doing the same thing, they are all just providing the value of the variable but what is the difference between them?
{7/28}
• var: The variable defined by the var keyword will be accessible in your entire program and you can reassign it.
• Let: When you declare a variable with the let keyword, the variable is only accessible inside that block in which it is declared.
• var: The variable defined by the var keyword will be accessible in your entire program and you can reassign it.
• Let: When you declare a variable with the let keyword, the variable is only accessible inside that block in which it is declared.
{8/28}
• const: The variable which is defined by the const keyword cannot be reassigned. In the above example, you can not reassign the value of the number from 123 to any other value.
• const: The variable which is defined by the const keyword cannot be reassigned. In the above example, you can not reassign the value of the number from 123 to any other value.
{9/28}
→ Comments
Comments are used to write notes or ignore the code without deleting them. This means the code or anything which are commented in your program will not be executed.
→ Comments
Comments are used to write notes or ignore the code without deleting them. This means the code or anything which are commented in your program will not be executed.
{10/28}
There are two ways that you can comment in JavaScript ( Single line using "//") and (multiple lines using "/* your comment */" )
There are two ways that you can comment in JavaScript ( Single line using "//") and (multiple lines using "/* your comment */" )
{11/28}
In the below code, the first line is just a text and it& #39;s just for more clarification. It is just a single-line comment. I have also commented the (console.log(name)) so that the compiler will not execute that line of code.
In the below code, the first line is just a text and it& #39;s just for more clarification. It is just a single-line comment. I have also commented the (console.log(name)) so that the compiler will not execute that line of code.
{12/28}
→ DataTypes
Datatypes are the types of data that you provide for the variables. Do you remember the above variable syntax, here is the value that you assign for a variable that can be any type like a number(123), a string(John), or a boolean(true/false)
→ DataTypes
Datatypes are the types of data that you provide for the variables. Do you remember the above variable syntax, here is the value that you assign for a variable that can be any type like a number(123), a string(John), or a boolean(true/false)
{13/28}
Following are the types of data in JavaScript:
• String
• Number
• Boolean
• Object
• Undefined
• Null
Following are the types of data in JavaScript:
• String
• Number
• Boolean
• Object
• Undefined
• Null
{14/28}
Here is an introduction to the JavaScript datatypes and I will explain each of them and its methods in another thread.
Here is an introduction to the JavaScript datatypes and I will explain each of them and its methods in another thread.
{15/28}
• String: A string is a collection of characters, it can be a name or sentence. If the value of a variable is a string then it should be written inside the single or double-quotes.
• String: A string is a collection of characters, it can be a name or sentence. If the value of a variable is a string then it should be written inside the single or double-quotes.
{16/28}
• Boolean: It is a datatype when the value of a variable is either true or false.
• Object: In JavaScript, an object is an unordered collection of key-value pairs. Each key-value pair is called a property.
• Boolean: It is a datatype when the value of a variable is either true or false.
• Object: In JavaScript, an object is an unordered collection of key-value pairs. Each key-value pair is called a property.
{17/28}
• Number: when a number is the value of the variable then the variable has a number datatype. The number can be with, or without decimals. We will discuss the numbers method in another article.
• Number: when a number is the value of the variable then the variable has a number datatype. The number can be with, or without decimals. We will discuss the numbers method in another article.
{18/28}
• Undefined: When a variable has no value then its datatype is undefined.
• Null: A null means absence of a value. It is declared when the variable does not have any value for now but it will have later on.
• Undefined: When a variable has no value then its datatype is undefined.
• Null: A null means absence of a value. It is declared when the variable does not have any value for now but it will have later on.
{19/28}
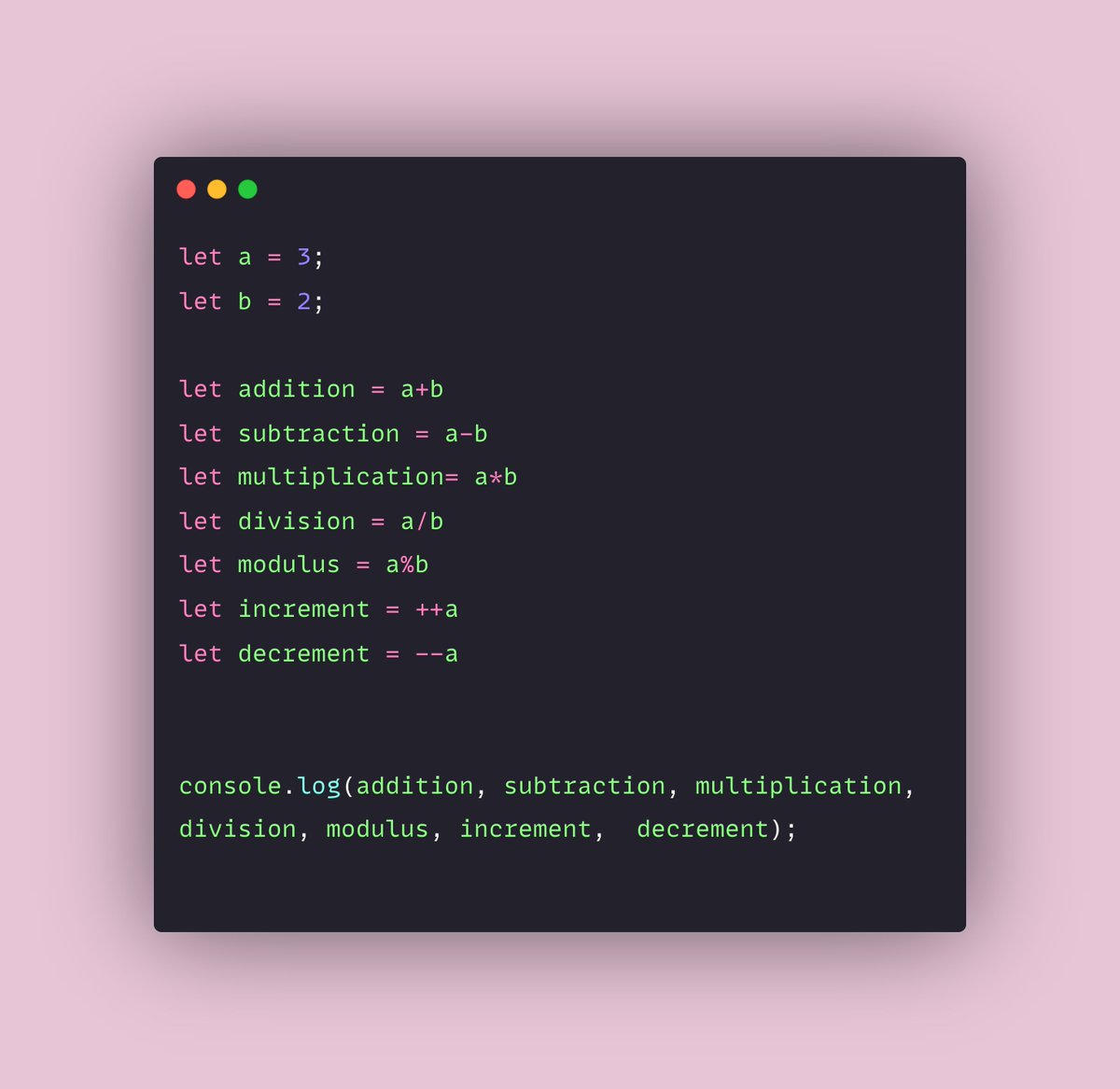
→ Operators
Operators are used to performing specific mathematical and logical computations on operands. Following are the JavaScript operators.
→ Operators
Operators are used to performing specific mathematical and logical computations on operands. Following are the JavaScript operators.
{21/28}
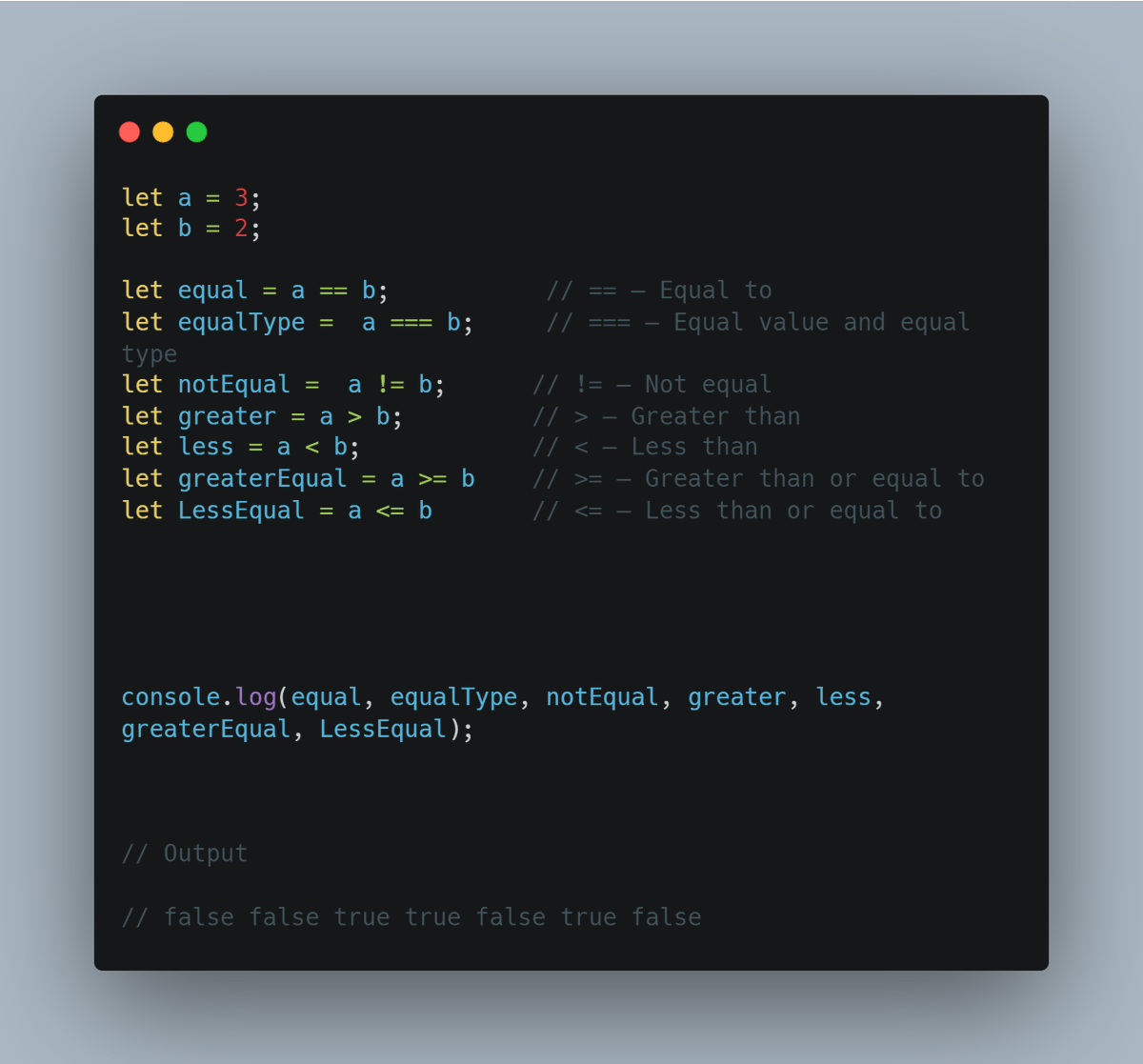
• JavaScript Comparison Operators
Here the output might confuse you, so I am going to explain it.
• JavaScript Comparison Operators
Here the output might confuse you, so I am going to explain it.
{22/28}
These operators are comparing the operands, the first output is false or the result of the equal operator is false because 3 is not equal to 2. The equalType is also false because it checks both the value and type, the value is not equal because 3 is not equal to 2...
These operators are comparing the operands, the first output is false or the result of the equal operator is false because 3 is not equal to 2. The equalType is also false because it checks both the value and type, the value is not equal because 3 is not equal to 2...
{23/28}
... and checking the types of the two operands means checking their data type, both are numbers so the type is true but because the value is false the result will be false.
... and checking the types of the two operands means checking their data type, both are numbers so the type is true but because the value is false the result will be false.
{24/28}
The third one is true because 3 is not equal to 2, the ! indicates NOT. The greater variable is true because 3 is greater than 2. The less variable is false because 3 is not less than 2. The last two are true and false respectively because their first condition is true.
The third one is true because 3 is not equal to 2, the ! indicates NOT. The greater variable is true because 3 is greater than 2. The less variable is false because 3 is not less than 2. The last two are true and false respectively because their first condition is true.
{25/28}
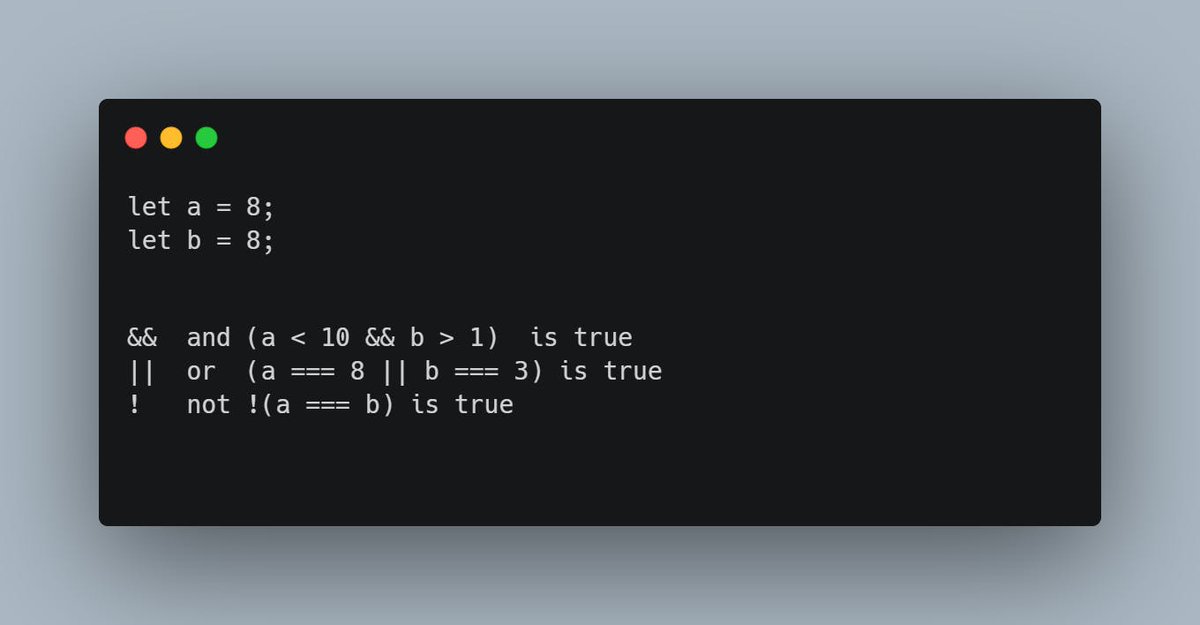
• JavaScript Logical Operators
There are three logical operators in JavaScript (AND, OR, NOT). The & operator returns true if both the conditions are true. In the below example 8 is less than 10 and greater than 1, here both of the conditions are true so result is true
• JavaScript Logical Operators
There are three logical operators in JavaScript (AND, OR, NOT). The & operator returns true if both the conditions are true. In the below example 8 is less than 10 and greater than 1, here both of the conditions are true so result is true
{26/28}
The OR operator is true if both or any one of the conditions are true.
The not operator returns True when the result is False and returns False when the result is True.
The OR operator is true if both or any one of the conditions are true.
The not operator returns True when the result is False and returns False when the result is True.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter