25 powerful methods in JavaScript
⇩
⇩
⬘ Are you learning JavaScript? Even if you are experienced, do you ever feel exhausted by the presence of so many methods?
⬙ The best approach to getting familiar is to know the use cases for these.
Here are 25 methods. Let& #39;s discuss their use cases.
The methods are,
➤ Array.prototype& #39;s
➊ forEach()
➋ map()
➌ reduce()
➍ every()
➎ filter()
➏ find()
➐ slice()
➑ splice()
➒ push()
➓ pop()
➊➊ shift()
➊➋ unshift()
➊➌ indexOf()
➊➍ findIndex()
➊➎ sort()
➤ Array.prototype& #39;s
➊ forEach()
➋ map()
➌ reduce()
➍ every()
➎ filter()
➏ find()
➐ slice()
➑ splice()
➒ push()
➓ pop()
➊➊ shift()
➊➋ unshift()
➊➌ indexOf()
➊➍ findIndex()
➊➎ sort()
➤ String.prototype& #39;s
➊➏ toLowerCase()
➊➐ toUpperCase()
➊➑ substring()
➊➒ indexOf()
20. charAt()
➋➊ trim()
➤ Math& #39;s
➋➋ floor()
➋➌ random()
➤ Global Methods
➋➍ setTimeout()
➋➎ setInterval()
➊➏ toLowerCase()
➊➐ toUpperCase()
➊➑ substring()
➊➒ indexOf()
20. charAt()
➋➊ trim()
➤ Math& #39;s
➋➋ floor()
➋➌ random()
➤ Global Methods
➋➍ setTimeout()
➋➎ setInterval()
➊ Array.prototype.forEach()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the array
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the array
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element
✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value
✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype
➤ Use Case
✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value
✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype
➋ Array.prototype. map()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the array
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the array
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which returns a value
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which returns a value
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Returns a new array with all returned values
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Returns a new array with all returned values
✘ Not suitable if the task doesn& #39;t return any value
➤ Use Case
✘ Not suitable if the task doesn& #39;t return any value
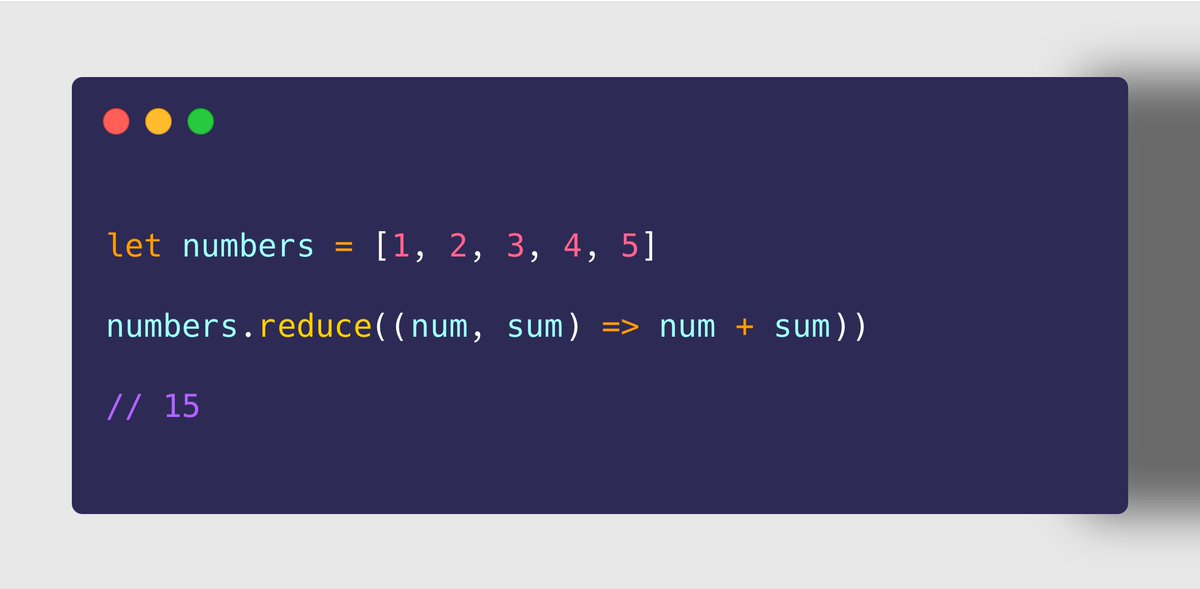
➌ Array.prototype.reduce()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the array
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the array
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value
➤ Example
➀ Sum of all items
➁ Max of all items
➤ Use Case
➤ Example
➀ Sum of all items
➁ Max of all items
➍ Array.prototype.every()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not met
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not met
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The task performed on each element must return a boolean value
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The task performed on each element must return a boolean value
✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it& #39;s not suitable for skipping.
➤ Use Case
✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it& #39;s not suitable for skipping.
➎ Array.prototype.filter()
➏ Array.prototype.find()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find element(s) which match a criteria
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find element(s) which match a criteria
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use find() to find the first matched element
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use find() to find the first matched element
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use filter() to find all matched elements
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use filter() to find all matched elements
✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements
➏ Array.prototype.find()
➤ Use Case
✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements
➐ Array.prototype.slice()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a sub-array from a larger array
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a sub-array from a larger array
✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn& #39;t modify the existing array
➤ Use Case
✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn& #39;t modify the existing array
➑ Array.prototype.splice()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To replace a portion of the array with new elements
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To replace a portion of the array with new elements
✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array
➤ Use Case
✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array
Array.prototype& #39;s
➒ push()
➓ pop()
➊➊ shift()
➊➋ unshift()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.
✩✩ These methods modify the existing array
➒ push()
➓ pop()
➊➊ shift()
➊➋ unshift()
➤ Use Case
✩✩ These methods modify the existing array
Array.prototype& #39;s
➊➌ indexOf()
➊➍ findIndex()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the index of the first matched element
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the index of the first matched element
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> indexOf() does exact match (===)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> indexOf() does exact match (===)
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> findIndex() allows for custom match
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> findIndex() allows for custom match
➊➌ indexOf()
➊➍ findIndex()
➤ Use Case
➊➎ Array.prototype.sort()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To sort all elements of an array in some order
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To sort all elements of an array in some order
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Provide a comparator to define custom order
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Provide a comparator to define custom order
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> By default sorting order is lexical
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> By default sorting order is lexical
✩✩ This method modifies the existing array
➤ Use Case
✩✩ This method modifies the existing array
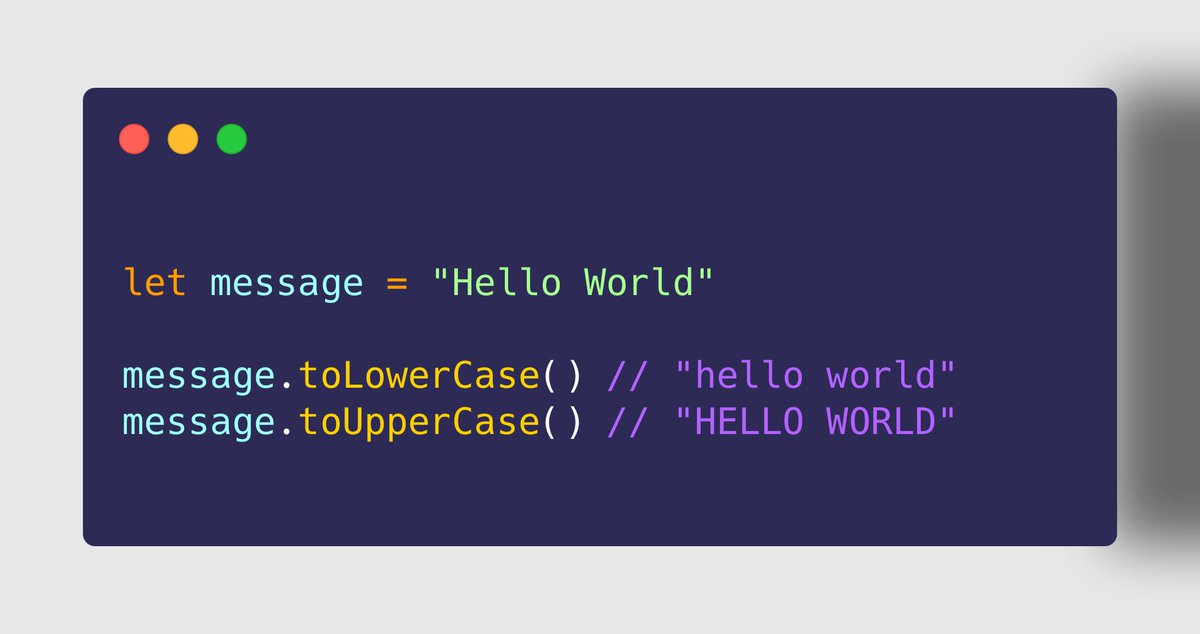
String.prototype& #39;s
➊➏ toLowerCase()
➊➐ toUpperCase()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()
✩✩ These methods returns a new string
➊➏ toLowerCase()
➊➐ toUpperCase()
➤ Use Case
✩✩ These methods returns a new string
➊➑ String.prototype.substring()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes
✩✩ substring() returns a new string
➤ Use Case
✩✩ substring() returns a new string
➊➒ String.prototype.indexOf()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original string
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original string
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked
➤ Use Case
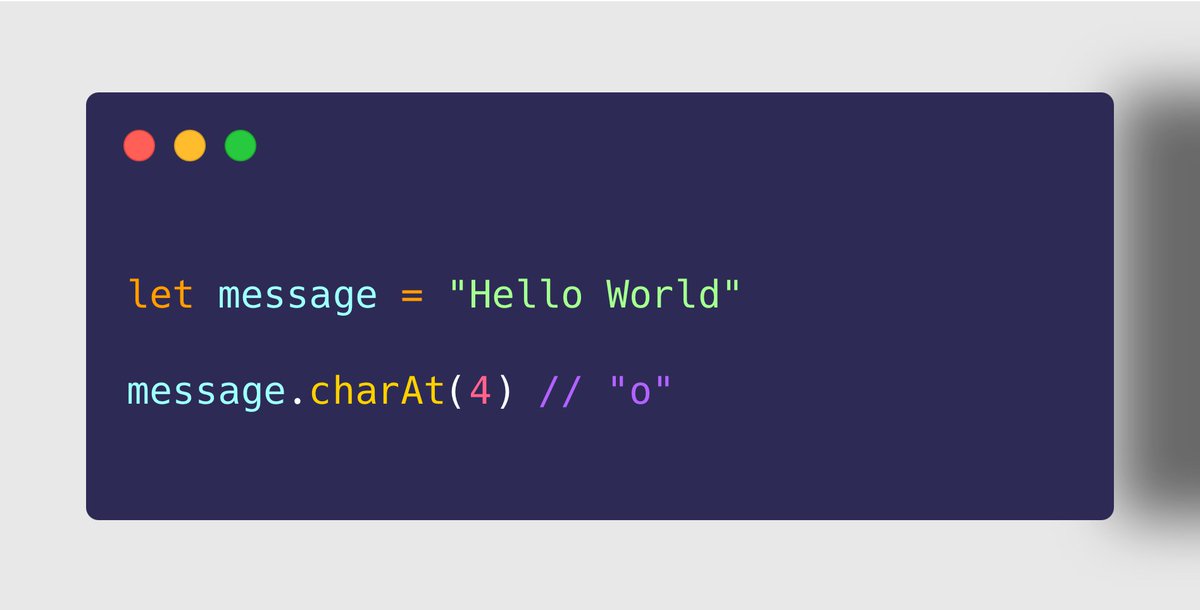
20. String.prototype.charAt()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string.
➤ Use Case
➋➊ String.prototype.trim()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To remove whitespace from both ends of a string
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To remove whitespace from both ends of a string
✩✩ trim() returns a new string
➤ Use Case
✩✩ trim() returns a new string
➋➋ Math.floor()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number
➤ Use Case
➋➌ Math.random()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number
➤ Use Case
➋➍ setTimeout()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expires
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expires
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The code is executed only once.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The code is executed only once.
✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn& #39;t be used where pausing of execution is intended.
➤ Use Case
✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn& #39;t be used where pausing of execution is intended.
➋➎ setInterval()
➤ Use Case
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay
✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.
✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()
➤ Use Case
✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.
✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()
Find use cases of below
➤ String.prototypes& #39;s
❍ startsWith() / endsWith()
❍ fromCharCode()
❍ padStart() / padEnd()
❍ repeat()
❍ match() / matchAll()
❍ replace() / replaceAll()
➤ Math& #39;s
❍ ceil()
❍ trunc()
❍ round()
Hey  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👋" title="Zwaaiende hand" aria-label="Emoji: Zwaaiende hand">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👋" title="Zwaaiende hand" aria-label="Emoji: Zwaaiende hand">
I am a Tech Educator from India https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🇮🇳" title="Vlag van India" aria-label="Emoji: Vlag van India">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🇮🇳" title="Vlag van India" aria-label="Emoji: Vlag van India">
I am sharing Tutorials, Tips, Infographics, Cheat Sheets, Practice Questions, Project Ideas and Roadmaps on Web Development, DSA and, Database.
To never miss anything, Follow Me https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Groot wit vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot wit vinkje">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Groot wit vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot wit vinkje">
I am a Tech Educator from India
I am sharing Tutorials, Tips, Infographics, Cheat Sheets, Practice Questions, Project Ideas and Roadmaps on Web Development, DSA and, Database.
To never miss anything, Follow Me

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter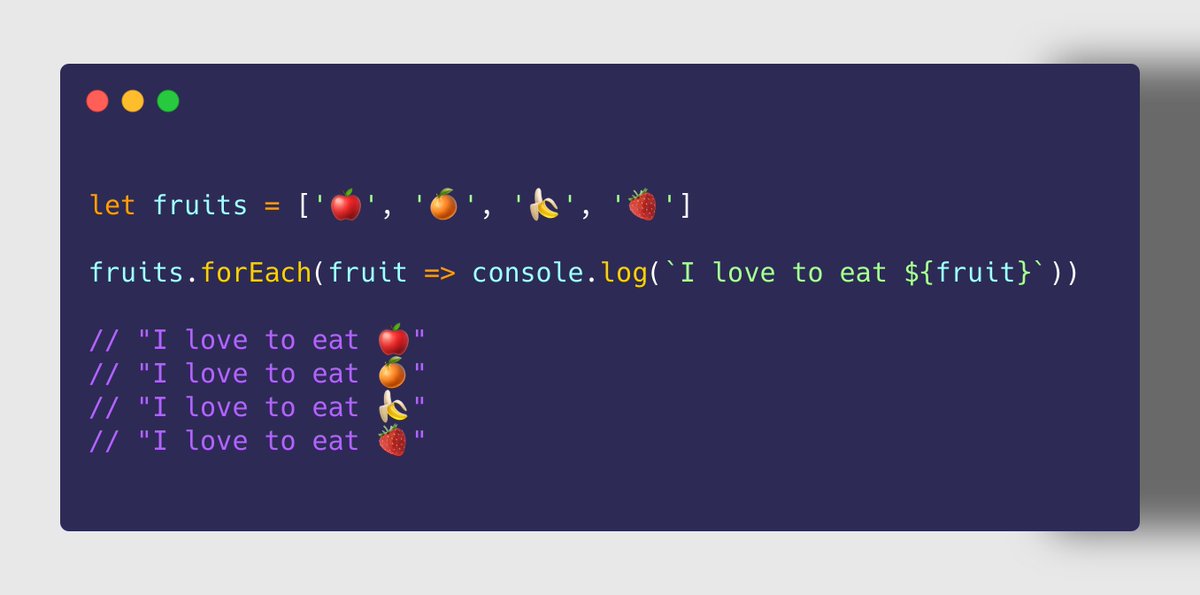 To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype" title="➊ Array.prototype.forEach()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype" title="➊ Array.prototype.forEach()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element✘ Not suitable if the task is supposed to return some value✩✩ forEach() is also available in Set.prototype and Map.prototype" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which returns a valuehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Returns a new array with all returned values✘ Not suitable if the task doesn& #39;t return any value" title="➋ Array.prototype. map()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which returns a valuehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Returns a new array with all returned values✘ Not suitable if the task doesn& #39;t return any value" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which returns a valuehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Returns a new array with all returned values✘ Not suitable if the task doesn& #39;t return any value" title="➋ Array.prototype. map()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which returns a valuehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Returns a new array with all returned values✘ Not suitable if the task doesn& #39;t return any value" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value➤ Example➀ Sum of all items➁ Max of all items" title="➌ Array.prototype.reduce()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value➤ Example➀ Sum of all items➁ Max of all items" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value➤ Example➀ Sum of all items➁ Max of all items" title="➌ Array.prototype.reduce()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through each element in the arrayhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Perform a task on each element which accumulates the previous returned value with current element to return a new value➤ Example➀ Sum of all items➁ Max of all items" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not methttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The task performed on each element must return a boolean value✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it& #39;s not suitable for skipping." title="➍ Array.prototype.every()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not methttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The task performed on each element must return a boolean value✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it& #39;s not suitable for skipping." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not methttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The task performed on each element must return a boolean value✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it& #39;s not suitable for skipping." title="➍ Array.prototype.every()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To iterate through elements in the array until a certain condition is not methttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The task performed on each element must return a boolean value✘ Stops iterating when condition is not met. Hence, it& #39;s not suitable for skipping." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To find element(s) which match a criteriahttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use find() to find the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use filter() to find all matched elements✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements" title="➎ Array.prototype.filter()➏ Array.prototype.find()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find element(s) which match a criteriahttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use find() to find the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use filter() to find all matched elements✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To find element(s) which match a criteriahttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use find() to find the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use filter() to find all matched elements✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements" title="➎ Array.prototype.filter()➏ Array.prototype.find()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find element(s) which match a criteriahttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use find() to find the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use filter() to find all matched elements✩✩ filter() returns a new array of matched elements" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To fetch a sub-array from a larger array✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn& #39;t modify the existing array" title="➐ Array.prototype.slice()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a sub-array from a larger array✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn& #39;t modify the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To fetch a sub-array from a larger array✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn& #39;t modify the existing array" title="➐ Array.prototype.slice()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a sub-array from a larger array✩✩ slice() returns a new array, doesn& #39;t modify the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To replace a portion of the array with new elements✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array" title="➑ Array.prototype.splice()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To replace a portion of the array with new elements✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To replace a portion of the array with new elements✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array" title="➑ Array.prototype.splice()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To replace a portion of the array with new elements✩✩ splice() modifies the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.✩✩ These methods modify the existing array" title="Array.prototype& #39;s➒ push()➓ pop()➊➊ shift()➊➋ unshift()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.✩✩ These methods modify the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.✩✩ These methods modify the existing array" title="Array.prototype& #39;s➒ push()➓ pop()➊➊ shift()➊➋ unshift()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use push() and pop() to insert/remove elements from the end.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Use shift() and unshift() to insert/remove elements from the start.✩✩ These methods modify the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To find the index of the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> indexOf() does exact match (===)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> findIndex() allows for custom match" title="Array.prototype& #39;s➊➌ indexOf()➊➍ findIndex()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the index of the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> indexOf() does exact match (===)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> findIndex() allows for custom match" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To find the index of the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> indexOf() does exact match (===)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> findIndex() allows for custom match" title="Array.prototype& #39;s➊➌ indexOf()➊➍ findIndex()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the index of the first matched elementhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> indexOf() does exact match (===)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> findIndex() allows for custom match" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To sort all elements of an array in some orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Provide a comparator to define custom orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> By default sorting order is lexical✩✩ This method modifies the existing array" title="➊➎ Array.prototype.sort()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To sort all elements of an array in some orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Provide a comparator to define custom orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> By default sorting order is lexical✩✩ This method modifies the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To sort all elements of an array in some orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Provide a comparator to define custom orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> By default sorting order is lexical✩✩ This method modifies the existing array" title="➊➎ Array.prototype.sort()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To sort all elements of an array in some orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> Provide a comparator to define custom orderhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> By default sorting order is lexical✩✩ This method modifies the existing array" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()✩✩ These methods returns a new string" title="String.prototype& #39;s➊➏ toLowerCase()➊➐ toUpperCase()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()✩✩ These methods returns a new string" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()✩✩ These methods returns a new string" title="String.prototype& #39;s➊➏ toLowerCase()➊➐ toUpperCase()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to lowercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To convert entire string to uppercase alphabets, use toLowerCase()✩✩ These methods returns a new string" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes✩✩ substring() returns a new string" title="➊➑ String.prototype.substring()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes✩✩ substring() returns a new string" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes✩✩ substring() returns a new string" title="➊➑ String.prototype.substring()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch a part of the string between 2 indexes✩✩ substring() returns a new string" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original stringhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked" title="➊➒ String.prototype.indexOf()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original stringhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original stringhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked" title="➊➒ String.prototype.indexOf()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To find the very first occurrence of a "substring" in the original stringhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> We can also mention from which index the occurrence should be checked" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string." title="20. String.prototype.charAt()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string." title="20. String.prototype.charAt()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To fetch the character at a specific position of a string.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The character fetched is in UTF-16 and returned as a string." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To remove whitespace from both ends of a string✩✩ trim() returns a new string" title="➋➊ String.prototype.trim()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To remove whitespace from both ends of a string✩✩ trim() returns a new string" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To remove whitespace from both ends of a string✩✩ trim() returns a new string" title="➋➊ String.prototype.trim()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To remove whitespace from both ends of a string✩✩ trim() returns a new string" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
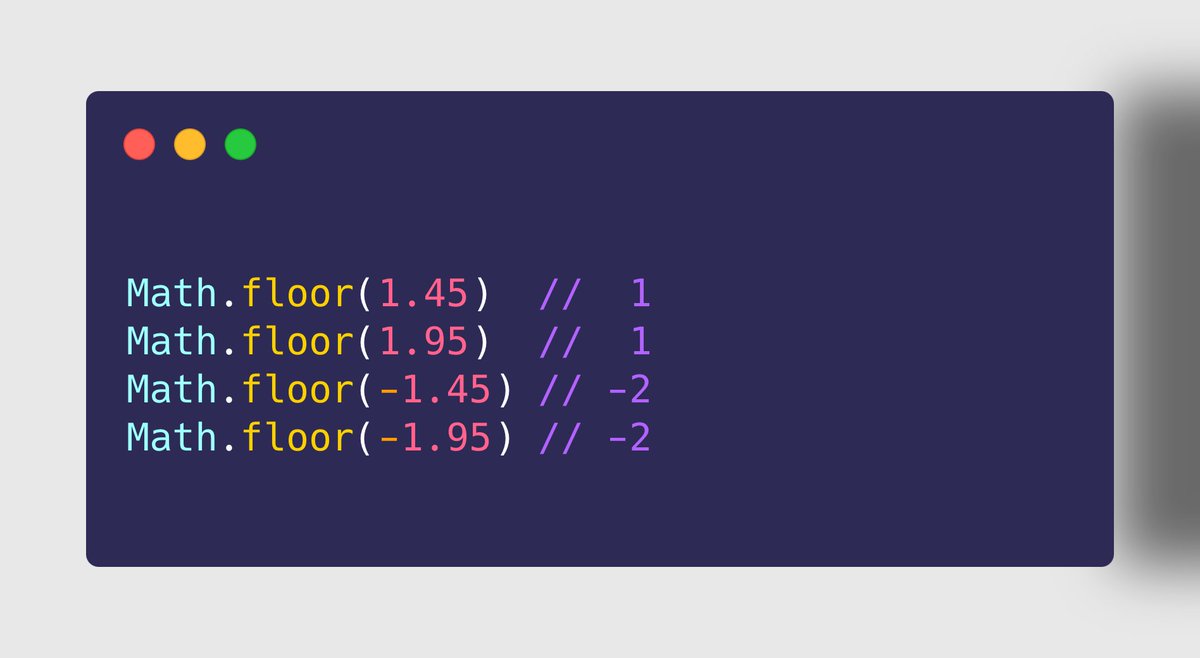 To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number" title="➋➋ Math.floor()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number" title="➋➋ Math.floor()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get the largest integer less than or, equals to the given number" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number" title="➋➌ Math.random()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number" title="➋➌ Math.random()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To get a floating-point pseudo-random number in the range of 0 to less than 1https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> It can be multiplied by any number to make a random number being generated in the range of 0 to less than that number" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expireshttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The code is executed only once.✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn& #39;t be used where pausing of execution is intended." title="➋➍ setTimeout()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expireshttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The code is executed only once.✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn& #39;t be used where pausing of execution is intended." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expireshttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The code is executed only once.✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn& #39;t be used where pausing of execution is intended." title="➋➍ setTimeout()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code after a timer expireshttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> The code is executed only once.✘ It is an asynchronous function. It shouldn& #39;t be used where pausing of execution is intended." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()" title="➋➎ setInterval()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()" title="➋➎ setInterval()➤ Use Casehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✔" title="Groot vinkje" aria-label="Emoji: Groot vinkje"> To execute a function or, piece of code repeatedly with a fix time delay✘ The code is ensured to be executed each time after the time delay. But not "exactly" after the time delay.✩✩ Cancel further execution using clearInterval()" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>


