So many terminologies in Banking!
Confused? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😥" title="Enttäuschtes, aber erleichtertes Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Enttäuschtes, aber erleichtertes Gesicht">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😥" title="Enttäuschtes, aber erleichtertes Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Enttäuschtes, aber erleichtertes Gesicht"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤔" title="Denkendes Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Denkendes Gesicht">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤔" title="Denkendes Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Denkendes Gesicht">
Dont worry.
A thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> on basics of Banking
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> on basics of Banking
Hit "Retweet" to educate Maximum Investors
Lets go https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
(1/20)
Confused?
Dont worry.
A thread
Hit "Retweet" to educate Maximum Investors
Lets go
(1/20)
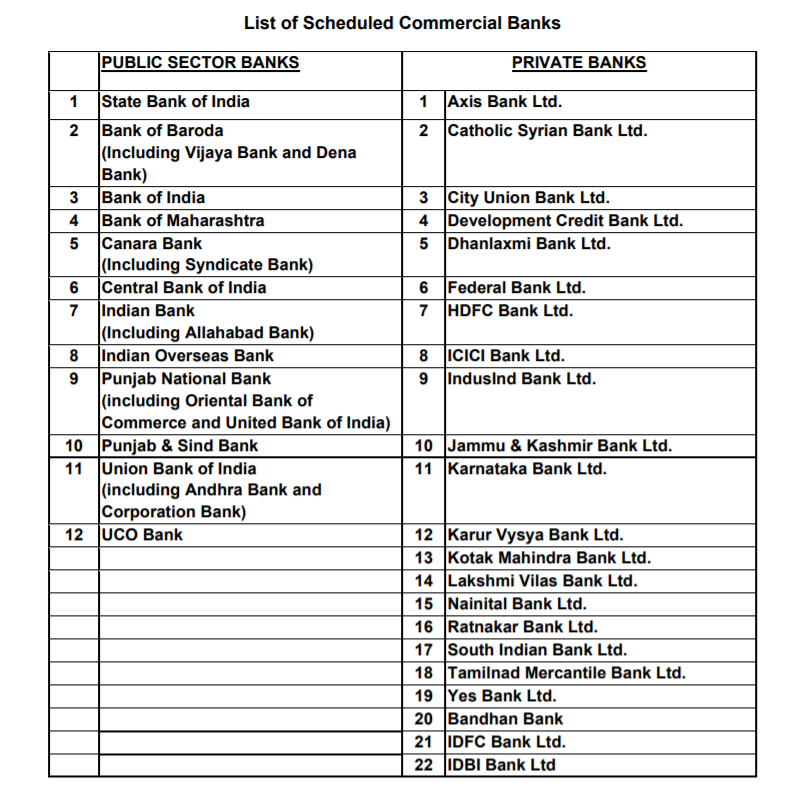
Types of banks:-
Your money should be parked in scheduled commercial Banks
Scheduled Commercial Banks
-PSU Banks
-Private Banks
-Foreign Banks
-Small Finance Banks
Do not park money is Co-operative/Regional Banks
List is shown below
(2/20)
Your money should be parked in scheduled commercial Banks
Scheduled Commercial Banks
-PSU Banks
-Private Banks
-Foreign Banks
-Small Finance Banks
Do not park money is Co-operative/Regional Banks
List is shown below
(2/20)
NPA, NPA, NPA! Kya hain yeh NPA? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤔" title="Denkendes Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Denkendes Gesicht">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤔" title="Denkendes Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Denkendes Gesicht">
Gross NPA (GNPA)-
It is the total loans on which no payment has been paid for 90 days or more.
GNPA % is usually shown in each Bank’s quarterly results. The percentage is basically the GNPA amount as a % of the total advances.
(3/20)
Gross NPA (GNPA)-
It is the total loans on which no payment has been paid for 90 days or more.
GNPA % is usually shown in each Bank’s quarterly results. The percentage is basically the GNPA amount as a % of the total advances.
(3/20)
Net NPA (NNPA)-
The total figure left after deducting provisions made for bad loans from GNPA.
(GNPA – Provisions+upgrades/writeoffs = NNPA)
(4/20)
The total figure left after deducting provisions made for bad loans from GNPA.
(GNPA – Provisions+upgrades/writeoffs = NNPA)
(4/20)
Special Mention Account (SMA) –
SMA-0
SMA-0 is a category in which stress with respect to the principal and interest has remained overdue for a period of 0 to 30 days.
(5/20)
SMA-0
SMA-0 is a category in which stress with respect to the principal and interest has remained overdue for a period of 0 to 30 days.
(5/20)
SMA-1
SMA-1 is a category in which stress with respect to the principal and interest has remained overdue for a period of 30-60 days.
SMA-2
SMA-1 is a category in which stress with respect to the principal and interest has remained overdue for a period of 60-90 days.
(6/20)
SMA-1 is a category in which stress with respect to the principal and interest has remained overdue for a period of 30-60 days.
SMA-2
SMA-1 is a category in which stress with respect to the principal and interest has remained overdue for a period of 60-90 days.
(6/20)
Net Interest Income (NII)-
This is the spread the bank makes on its lending. It is calculated as Interest Income – Interest Expended
(7/20)
This is the spread the bank makes on its lending. It is calculated as Interest Income – Interest Expended
(7/20)
Net Interest Margin (NIM)-
This is the spread the bank makes on its lending. It is the earning which is left after deducting the cost paid to depositors from its yields on Loans. This is denoted in % terms.
The formula is Yield on Loans – Cost of funds
(8/20)
This is the spread the bank makes on its lending. It is the earning which is left after deducting the cost paid to depositors from its yields on Loans. This is denoted in % terms.
The formula is Yield on Loans – Cost of funds
(8/20)
Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR)-
The capital adequacy ratio (CAR) is a measure of a bank& #39;s available capital expressed as a percentage of a bank& #39;s risk-weighted credit exposures.
Basically Capital available to lend
(9/20)
The capital adequacy ratio (CAR) is a measure of a bank& #39;s available capital expressed as a percentage of a bank& #39;s risk-weighted credit exposures.
Basically Capital available to lend
(9/20)
Tier I Capital –
In simple words this capital is freely available with the bank to lend
Tier II Capital-
This is capital tied up somewhere and is less freely available to http://lend.In"> http://lend.In adverse events a bank can use this capital to lend
(10/20)
In simple words this capital is freely available with the bank to lend
Tier II Capital-
This is capital tied up somewhere and is less freely available to http://lend.In"> http://lend.In adverse events a bank can use this capital to lend
(10/20)
Under Basel III norms, a bank’s tier 1+tier 2 capital must be a minimum of 8% of its risk-weighted holdings. The minimum capital adequacy ratio, also including the capital conservation buffer, is 10.5%.
(11/20)
(11/20)
SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) is the money a bank needs to preserve in the form of cash,gold or government Bonds before providing credit customers.
This limitation is added by RBI on banks to make funds available to customers on-demand at your earliest convenience.
(12/20)
This limitation is added by RBI on banks to make funds available to customers on-demand at your earliest convenience.
(12/20)
CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio)-
Banks are required to hold a certain proportion of their deposits in the form of cash.
Banks don’t hold these as cash with themselves, but deposit such amounts with RBI / currency chests.
(13/20)
Banks are required to hold a certain proportion of their deposits in the form of cash.
Banks don’t hold these as cash with themselves, but deposit such amounts with RBI / currency chests.
(13/20)
Repo Rate-
The rate at which the RBI lends short-term money to the banks.
Reverse Repo rate-
The rate at which banks park their short-term excess liquidity with the RBI.
(14/20)
The rate at which the RBI lends short-term money to the banks.
Reverse Repo rate-
The rate at which banks park their short-term excess liquidity with the RBI.
(14/20)
Current Account Saving Account (CASA)-
There is no interest paid on the Current Account and a small interest rate is paid on a savings account. The combination of both is called CASA which shows the number of liabilities that the bank pays relatively less interest on.
(15/20)
There is no interest paid on the Current Account and a small interest rate is paid on a savings account. The combination of both is called CASA which shows the number of liabilities that the bank pays relatively less interest on.
(15/20)
Marginal Cost of fund-based Lending Rate (MCLR)-
A methodology by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for setting the lending rates on loans by commercial banks.
(16/20)
A methodology by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for setting the lending rates on loans by commercial banks.
(16/20)
Provisioning Coverage Ratio (PCR)-
This is the ratio of provisioning to GNPA and indicates the extent of funds a bank has kept aside to cover loan losses. For Instance, a company has GNPAs of Rs 100 and they have set aside 50 Rs, then the PCR is 50%.
(17/20)
This is the ratio of provisioning to GNPA and indicates the extent of funds a bank has kept aside to cover loan losses. For Instance, a company has GNPAs of Rs 100 and they have set aside 50 Rs, then the PCR is 50%.
(17/20)
Credit Costs-
When banks refer to credit costs they are talking about the amount they expect to lose because of standard credit risks.
It is basically the cost of doing business for a bank. NPA/advance is the credit cost
It is usually denoted and guided for in % terms
(18/20)
When banks refer to credit costs they are talking about the amount they expect to lose because of standard credit risks.
It is basically the cost of doing business for a bank. NPA/advance is the credit cost
It is usually denoted and guided for in % terms
(18/20)
Slippages-
Slippages denote the fresh amount of loans that have turned bad in a year
The slippage ratio of a bank is calculated as Fresh accretion of NPAs during the year /Total standard assets at the beginning of the year multiplied by 100.
(19/20)
Slippages denote the fresh amount of loans that have turned bad in a year
The slippage ratio of a bank is calculated as Fresh accretion of NPAs during the year /Total standard assets at the beginning of the year multiplied by 100.
(19/20)
Finally important things to track to analyse a bank
-Management
-Quality of loans
-GNPA/NNPA/PCR
-Slippages
-SMA Book
Banking is all about the Management.....
Dont bet on the Bank
Bet on the leader!
(20/20)
-Management
-Quality of loans
-GNPA/NNPA/PCR
-Slippages
-SMA Book
Banking is all about the Management.....
Dont bet on the Bank
Bet on the leader!
(20/20)

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter