GraphQL is aggressively becoming the new kid on the block when it comes to writing APi& #39;s.
Partly due to it’s ability to let clients query only the data they need at that moment and in the format that they need it.
A thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread">
Partly due to it’s ability to let clients query only the data they need at that moment and in the format that they need it.
A thread
For a couple of months now, I’ve been digging through GraphQl and the GraphQL schema Definition Language(SDL) which amplify uses, and here’s a breakdown on the basics of what I found out.
The first step in creating a GraphQL API is creating a schema that defines the capabilities of that API.
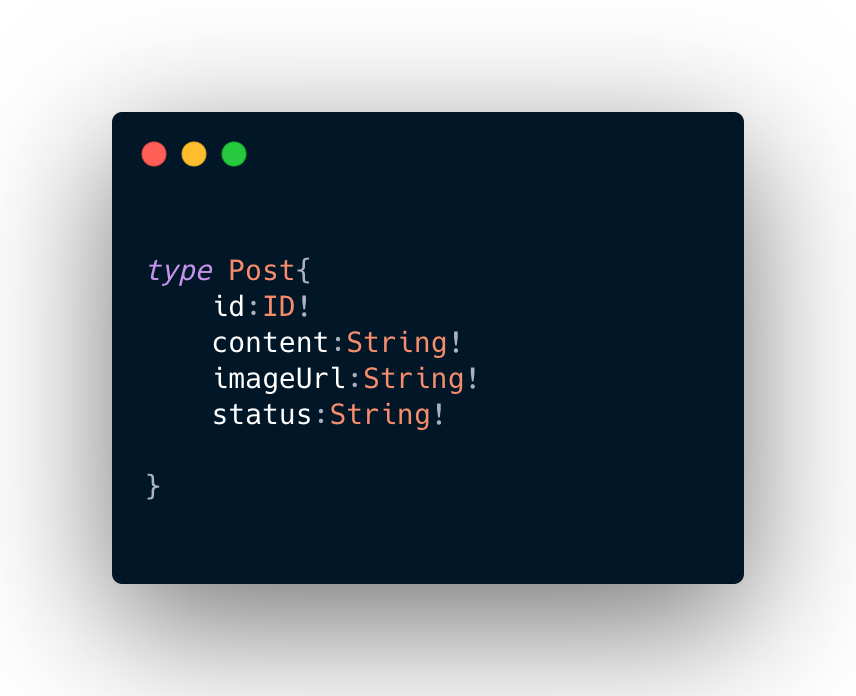
Here’s an example schema that has a user-defined type called Post with values.
The ID and String are known as scalar types.
Here’s an example schema that has a user-defined type called Post with values.
The ID and String are known as scalar types.
There are other scalar types such as Int , Float, Bool etc.
The ! at the end of a scalar type marks that field as non-nullable.
It must always have a value.
A schema is composed of 2 types
1) root type
2) user-defined types.
The ! at the end of a scalar type marks that field as non-nullable.
It must always have a value.
A schema is composed of 2 types
1) root type
2) user-defined types.
We just created a user define type above, let’s take a look at root types.
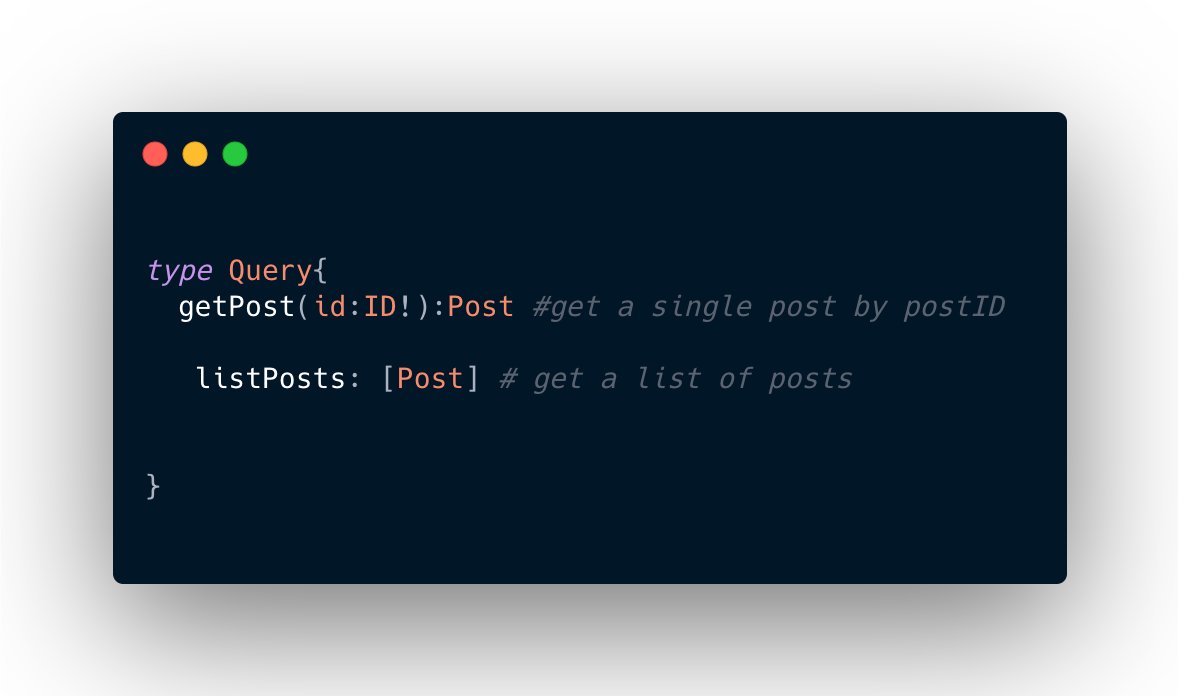
1) Query(Read-only fetch).
Queries are used in fetching data from the data source and nothing else.
1) Query(Read-only fetch).
Queries are used in fetching data from the data source and nothing else.
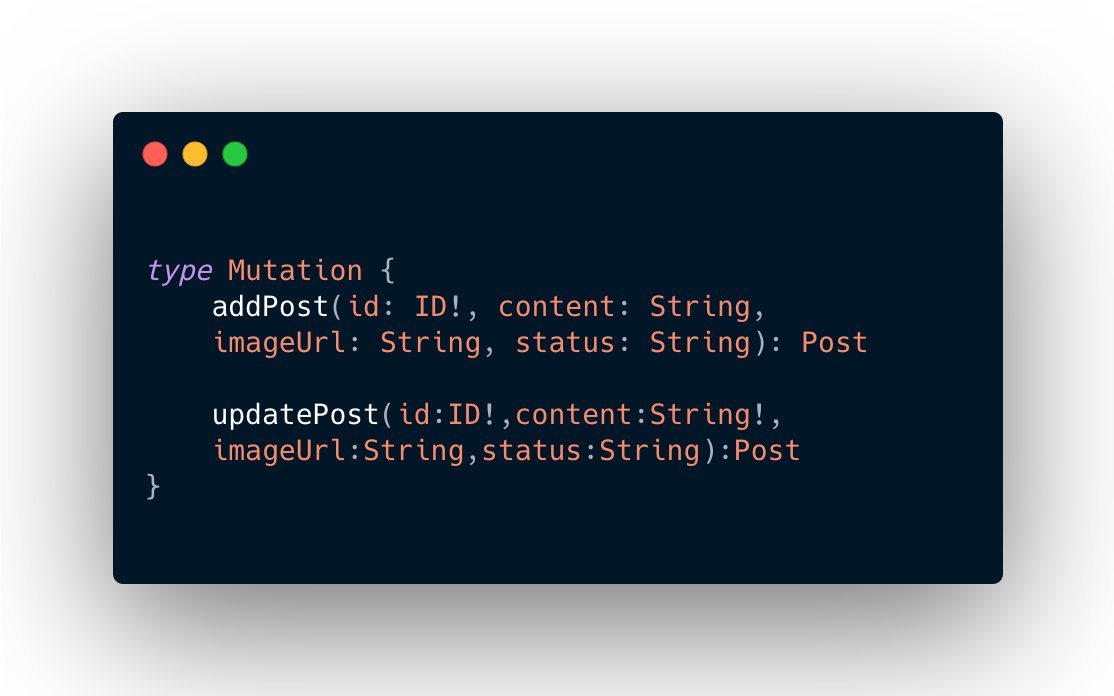
2) Mutation( write, followed by a fetch)
Used in making changes to your database. Returns a value when a change is made.
Used in making changes to your database. Returns a value when a change is made.
Subscription (long-lived connection for receiving data.) Subscriptions in AWS AppSync are invoked as a response to a mutation.
They help provide real-time capabilities to your api.
They help provide real-time capabilities to your api.
Resolvers
One of the concepts in GraphQL that took me a while to comprehend was Resolvers. I don’t know why, but it went over my head.
So here’s a straightforward explanation for it.
One of the concepts in GraphQL that took me a while to comprehend was Resolvers. I don’t know why, but it went over my head.
So here’s a straightforward explanation for it.
We just defined types above. User types and root types . Resolvers simply connects the fields of those types to a data source.
There are multiple data sources you can connect to.
A NoSQL database like DynamoDB, A relational database like Amazon Aurora, lambda functions.
There are multiple data sources you can connect to.
A NoSQL database like DynamoDB, A relational database like Amazon Aurora, lambda functions.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter