Want to understand exclusion from welfare schemes better? This  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread">explains our ‘Glossary of Exclusion’. Find definitions of potential exclusion points across various schemes–starting with a general framework for DBT schemes. See our recent study with @Gram_vaani for more info 1/n
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread">explains our ‘Glossary of Exclusion’. Find definitions of potential exclusion points across various schemes–starting with a general framework for DBT schemes. See our recent study with @Gram_vaani for more info 1/n
Exclusion from Enumeration – Within DBT framework, many schemes depend on BPL and SECC lists for identifying beneficiaries. Being left off these lists can lead to exclusion from schemes such as PMAY. 2/n
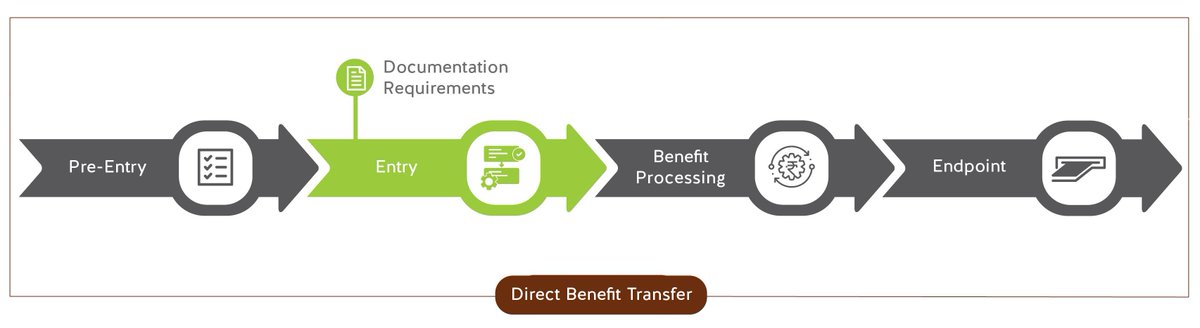
Documentation Requirements – Scheme applicants bear both time and monetary costs in order to procure documents to prove their eligibility, especially under list-based schemes. 3/n
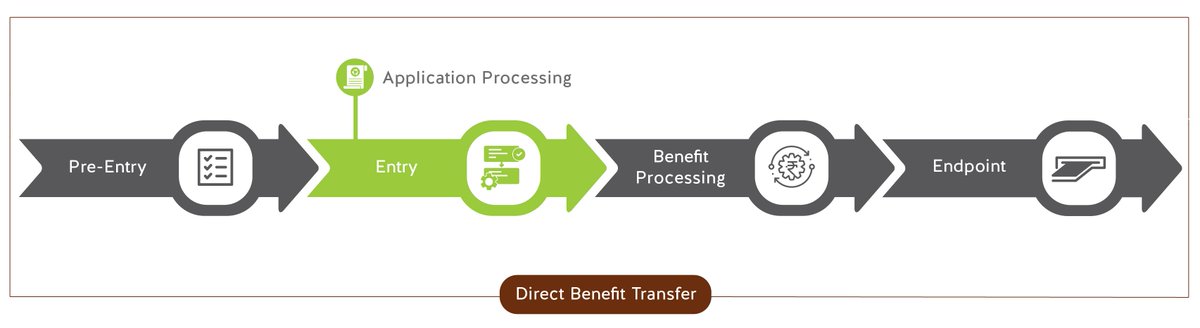
Application Processing – Delays in processing scheme applications have excluded many citizens. General opaqueness, lack of status communication, and weak GRM make welfare transfers inaccessible for many. 4/n
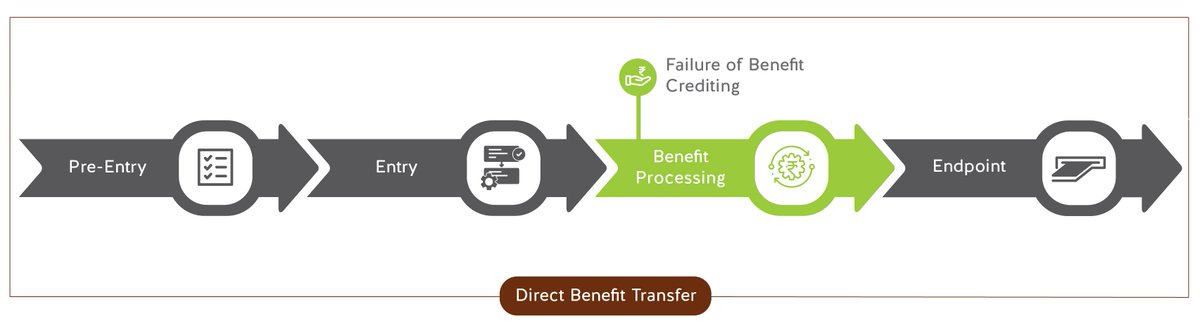
Failure of Benefit Crediting – Failure to receive DBT entitlements in one’s bank accounts. The reasons for failure may vary: improper Aadhaar seeding, database errors, blocked bank accounts, etc. 5/n
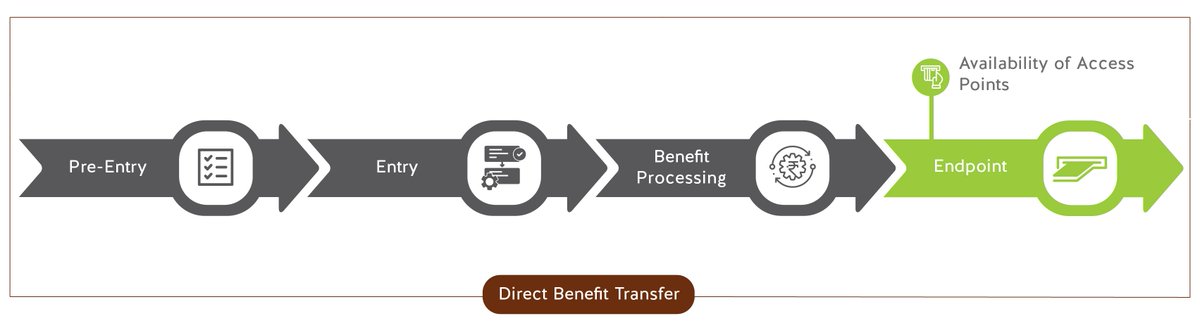
Availability of Access Points – Includes availability of a proximate banking point to withdraw or check the status of DBT entitlements. 6/n
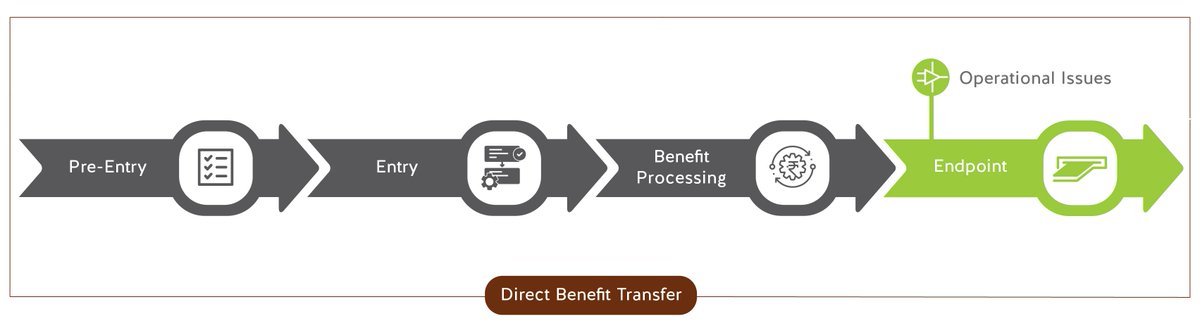
Operational Issues – Includes overcrowding at banks, network failures, cash shortages, biometric authentication failure, PoS glitches, etc. Some of these issues may not lead to exclusion necessarily but result in high costs ( https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⏲️" title="Tischuhr" aria-label="Emoji: Tischuhr">+
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⏲️" title="Tischuhr" aria-label="Emoji: Tischuhr">+ https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💴" title="Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen">) for citizens. 7/n
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💴" title="Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen">) for citizens. 7/n
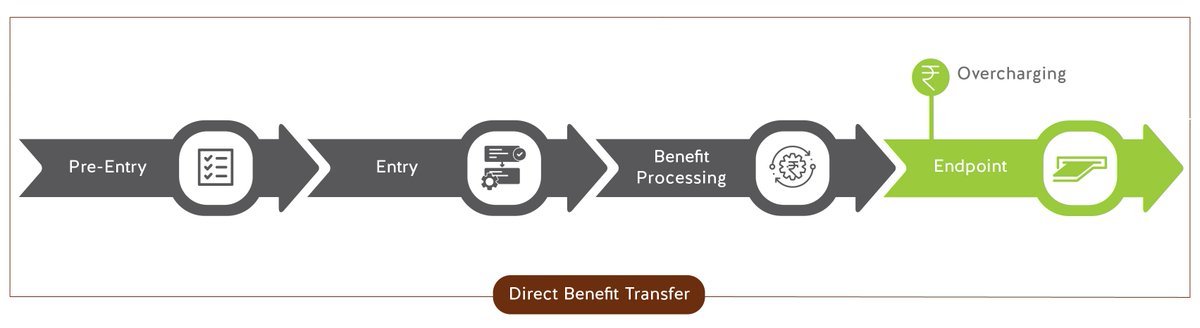
Overcharging – Overcharging for services or holding up delivery of benefits by last-mile agents such as CSC/BC for additional gain, reducing the actual benefit received by citizens. 8/n
Stay tuned for more threads explaining points of exclusion in other schemes! Here is the link to the report: https://www.dvara.com/blog/2021/04/08/delivery-of-social-protection-entitlements-in-india-unpacking-exclusion-grievance-redress-and-the-relevance-of-citizen-assistance-mechanisms/">https://www.dvara.com/blog/2021...

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter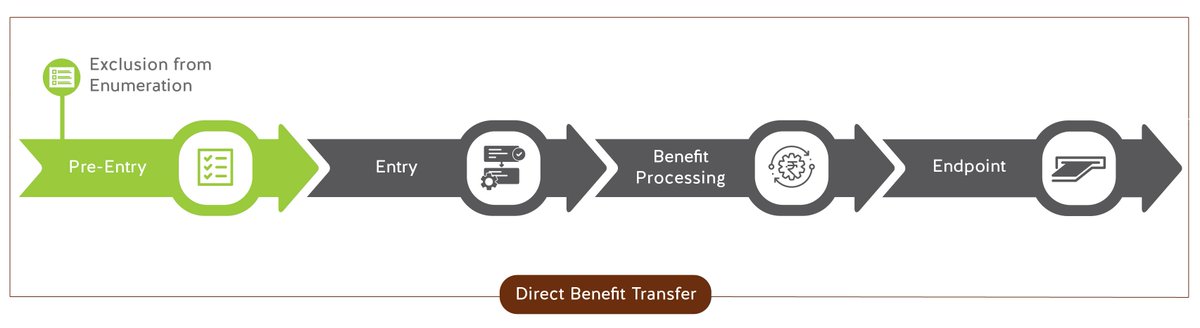
 +https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💴" title="Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen">) for citizens. 7/n" title="Operational Issues – Includes overcrowding at banks, network failures, cash shortages, biometric authentication failure, PoS glitches, etc. Some of these issues may not lead to exclusion necessarily but result in high costs (https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⏲️" title="Tischuhr" aria-label="Emoji: Tischuhr">+https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💴" title="Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen">) for citizens. 7/n" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
+https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💴" title="Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen">) for citizens. 7/n" title="Operational Issues – Includes overcrowding at banks, network failures, cash shortages, biometric authentication failure, PoS glitches, etc. Some of these issues may not lead to exclusion necessarily but result in high costs (https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⏲️" title="Tischuhr" aria-label="Emoji: Tischuhr">+https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💴" title="Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Yen-Zeichen">) for citizens. 7/n" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>