1/14
Why doesn& #39;t daptomycin treat pneumonia?
The answer also explains why dapto raises serum CK levels.
#medtwitter #tweetorial
Why doesn& #39;t daptomycin treat pneumonia?
The answer also explains why dapto raises serum CK levels.
#medtwitter #tweetorial
2/
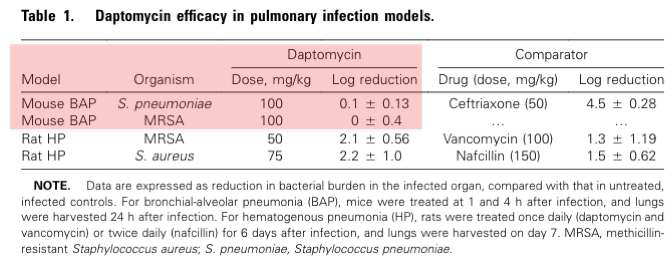
First let& #39;s establish that daptomycin (bactericidal against gram positives) lacks efficacy in treating lung infections.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⚡️" title="Hochspannungszeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Hochspannungszeichen"> In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn& #39;t reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⚡️" title="Hochspannungszeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Hochspannungszeichen"> In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn& #39;t reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/...
First let& #39;s establish that daptomycin (bactericidal against gram positives) lacks efficacy in treating lung infections.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/...
3/
What about lung infections in humans?
Compared to ceftriaxone, daptomycin had lower cure rates for treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18444848/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18444848/...
What about lung infections in humans?
Compared to ceftriaxone, daptomycin had lower cure rates for treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18444848/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18444848/...
4/
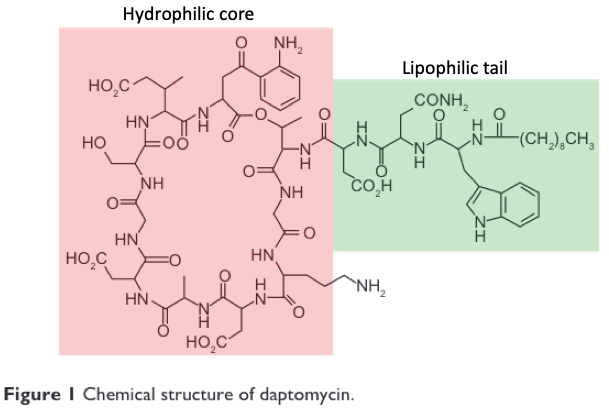
Next we need to review daptomycin& #39;s structure and mechanism of action.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne"> It& #39;s structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne"> It& #39;s structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3108743/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
Next we need to review daptomycin& #39;s structure and mechanism of action.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3108743/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
5/
As a lipopeptide with a fat-soluble tail, daptomycin inserts into bacterial membranes (and cell walls) in the presence of calcium.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC171788/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
As a lipopeptide with a fat-soluble tail, daptomycin inserts into bacterial membranes (and cell walls) in the presence of calcium.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC171788/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
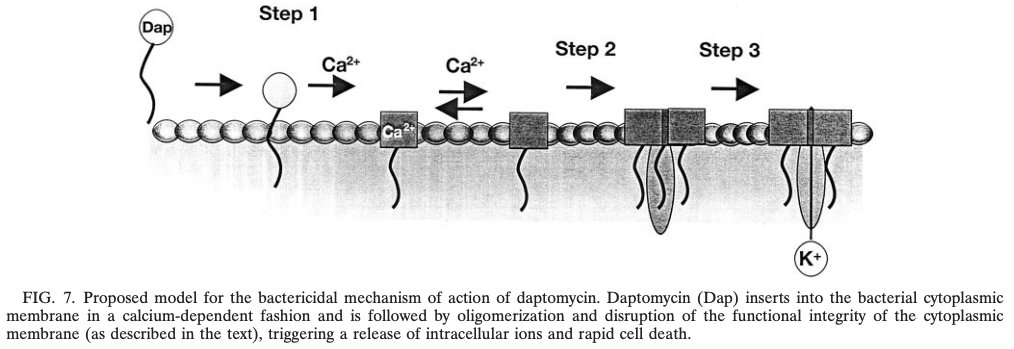
6/
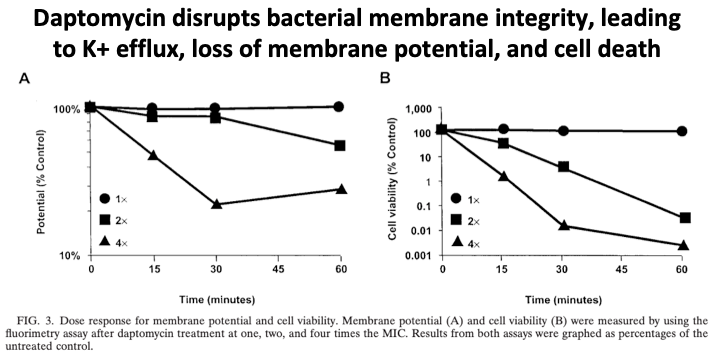
Once inserted into a bacterium& #39;s cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC166110/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
Once inserted into a bacterium& #39;s cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC166110/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
7/
Now that we understand how daptomycin works, let& #39;s learn why it doesn& #39;t work in the lungs.
You may have heard that it has something to do with pulmonary surfactant...
Now that we understand how daptomycin works, let& #39;s learn why it doesn& #39;t work in the lungs.
You may have heard that it has something to do with pulmonary surfactant...
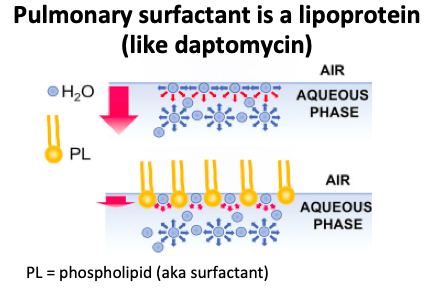
8/
(Very) brief pulmonary surfactant review:
Surfactant, similar to daptomycin, is a lipoprotein with fat and water soluble components. It reduces surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the lung and prevents alveolar collapse.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30552091/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30552091/...
(Very) brief pulmonary surfactant review:
Surfactant, similar to daptomycin, is a lipoprotein with fat and water soluble components. It reduces surface tension at the air-liquid interface in the lung and prevents alveolar collapse.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30552091/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30552091/...
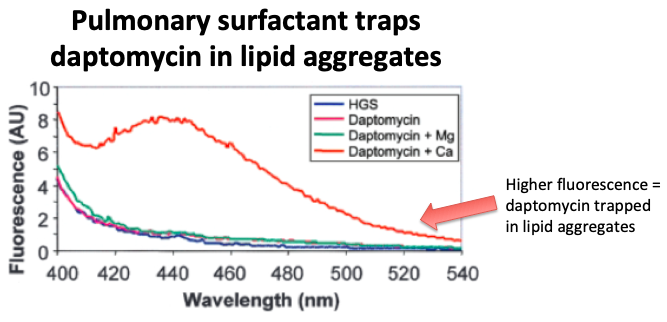
9/
It turns out that adding surfactant to daptomycin in vitro leads to almost immediate loss of antibacterial activity.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/...
It turns out that adding surfactant to daptomycin in vitro leads to almost immediate loss of antibacterial activity.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/...
10/
Why?
Recall that daptomycin has a hydrophobic tail that allows it to insert into/disrupt phospholipid bacterial membranes (tweets 4,5).
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💥" title="Symbol für eine Kollision" aria-label="Emoji: Symbol für eine Kollision"> Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro).
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💥" title="Symbol für eine Kollision" aria-label="Emoji: Symbol für eine Kollision"> Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/...
Why?
Recall that daptomycin has a hydrophobic tail that allows it to insert into/disrupt phospholipid bacterial membranes (tweets 4,5).
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/...
11/
We are left with the mechanism for why daptomycin is ineffective in the lungs:
Pulmonary surfactant sequesters dapto via its hydrophobic tail. This prevents access to bacterial membranes.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> In effect, daptomycin& #39;s very mechanism of action precludes treatment of pneumonia.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> In effect, daptomycin& #39;s very mechanism of action precludes treatment of pneumonia.
We are left with the mechanism for why daptomycin is ineffective in the lungs:
Pulmonary surfactant sequesters dapto via its hydrophobic tail. This prevents access to bacterial membranes.
12/
A final interesting correlate:
Creatine kinase (CK) elevation, and even skeletal muscle myopathy, are known complications of daptomycin therapy.
Can you think of how this might relate to its mechanism of action?
A final interesting correlate:
Creatine kinase (CK) elevation, and even skeletal muscle myopathy, are known complications of daptomycin therapy.
Can you think of how this might relate to its mechanism of action?
13/
While the cause isn& #39;t definitively known, serum CK elevation is thought to result from daptomycin-induced disruption of skeletal muscle membranes.
This is the exact same type of membrane damage that causes bacterial killing.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC101585/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
While the cause isn& #39;t definitively known, serum CK elevation is thought to result from daptomycin-induced disruption of skeletal muscle membranes.
This is the exact same type of membrane damage that causes bacterial killing.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC101585/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
14/
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne">Daptomycin disrupts bacterial membranes via a fat-soluble “tail”
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne">Daptomycin disrupts bacterial membranes via a fat-soluble “tail”
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne">It’s ineffective in lung infections b/c pulmonary surfactant traps it in lipid aggregates
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne">It’s ineffective in lung infections b/c pulmonary surfactant traps it in lipid aggregates
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne">Serum CK elevation likely results from the same mechanism (impacts on integrity of skeletal muscle membranes)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne">Serum CK elevation likely results from the same mechanism (impacts on integrity of skeletal muscle membranes)

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter
 In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn& #39;t reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." title="2/First let& #39;s establish that daptomycin (bactericidal against gram positives) lacks efficacy in treating lung infections. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⚡️" title="Hochspannungszeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Hochspannungszeichen"> In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn& #39;t reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn& #39;t reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." title="2/First let& #39;s establish that daptomycin (bactericidal against gram positives) lacks efficacy in treating lung infections. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⚡️" title="Hochspannungszeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Hochspannungszeichen"> In this study with mouse lungs, daptomycin didn& #39;t reliably kill strep pneumo or MRSA, even at high doses of the drug. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>

 It& #39;s structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." title="4/Next we need to review daptomycin& #39;s structure and mechanism of action.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne"> It& #39;s structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
It& #39;s structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." title="4/Next we need to review daptomycin& #39;s structure and mechanism of action.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💡" title="Elektrische Glühbirne" aria-label="Emoji: Elektrische Glühbirne"> It& #39;s structure consists of a hydrophilic lipoprotein core with a lipophilic, fat-soluble “tail”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>

 This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." title="6/Once inserted into a bacterium& #39;s cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...">
This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." title="6/Once inserted into a bacterium& #39;s cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...">
 This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." title="6/Once inserted into a bacterium& #39;s cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...">
This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic..." title="6/Once inserted into a bacterium& #39;s cellular membrane, daptomycin disrupts its integrity. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔑" title="Schlüssel" aria-label="Emoji: Schlüssel"> This disruption leads to K+ efflux out of the cell and loss of membrane potential, which causes failure of cellular machinery and eventually cell death. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...">

 Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." title="10/Why?Recall that daptomycin has a hydrophobic tail that allows it to insert into/disrupt phospholipid bacterial membranes (tweets 4,5).https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💥" title="Symbol für eine Kollision" aria-label="Emoji: Symbol für eine Kollision"> Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." title="10/Why?Recall that daptomycin has a hydrophobic tail that allows it to insert into/disrupt phospholipid bacterial membranes (tweets 4,5).https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💥" title="Symbol für eine Kollision" aria-label="Emoji: Symbol für eine Kollision"> Pulmonary surfactant instead acts as a decoy for dapto, trapping it in lipid aggregates (at least in vitro). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15898002/..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>



