A lot of new data out on treatments for COVID-19. Updating a previous thread with what we know now. Still lots of research ongoing and a few things may change. Much of this world leading research is taking place in the UK, funded and delivered by @NIHRresearch. 1/20
Dexamethasone: A simple steroid drug widely used in many diseases. Shown in @NIHRresearch RECOVERY trial to improve survival for respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (i.e. severe cases only). Probably acts by reducing lung inflammation. 2/20
Hydrocortisone: Another widely used steroid drug. May help systemic (whole body) inflammation in critical (life threatening) illness which some call & #39;cytokine storm& #39;. @NIHRresearch funded @remap_cap trial suggests benefit in ICU patients but weaker signal than dexamethasone. 3/20
Hydroxychloroquine: Used to treat malaria and some types of arthritis. Early studies done during Hong Kong SARS epidemic in 2002. Huge hopes pinned on this drug but @NIHRresearch RECOVERY & @WHO SOLIDARITY trials showed no benefit in COVID-19. Prevention trials ongoing. 4/20
Remdesivir: Anti-viral drug developed for Ebola. Re-tasked for COVID-19. Early trial suggested modest reduction in symptoms but large @WHO SOLIDARITY trial showed no benefit on survival, need for ventilation, etc. We may still use in mild cases. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.10.15.20209817v1.full.pdf">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1... 5/20
Tociluzimab: Used to treat inflammatory arthritis and other immune disorders. Hoped in COVID is suppression of systemic (whole-body) inflammation AKA the & #39;cytokine storm& #39; but small to medium size trials have not shown benefit. Await RECOVERY trial results. Unlikely to work. 6/20
Vitamin D: Good old-fashioned vitamin. Deficiency widespread and linked to poor health. Many believe it could prevent or treat COVID. May help but evidence not there yet (trials ongoing). However, a good thing to supplement in any case and very safe at recommended doses. 7/20
Lopinavir–ritonavir: Anti-viral drug combination used to treat HIV. Re-tasked for COVID-19. An early hope but two major trials ( @NIHRresearch RECOVERY and @WHO SOLIDARITY) have shown no benefit. 8/20
Azithromycin: Antibiotic used to treat bacterial infection but not usually viruses. Early in the pandemic it was thought to have useful anti-inflammatory effects on COVID-19 but COALITION II trial from Brazil showed no benefit. Further results from RECOVERY trial awaited. 9/20
Anticoagulation: Various drugs to prevent blood clots which happen more in COVID-19. Medical terms are deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Latter can be fatal. We are using these blood thinning drugs more in COVID. Trials ongoing but patient care already changed. 10/20
Convalescent plasma: blood with blood cells removed; taken from patients recovered from COVID so contains antibodies to the virus. PLACID trial from India showed no patient benefit despite reducing virus RNA in blood. RECOVERY trial results awaited. https://www.bmj.com/content/371/bmj.m393910/20">https://www.bmj.com/content/3... 11/20
Monoclonal antibodies: Bio-engineered antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 virus given intra-venously to patients. Precision alternative to convalescent plasma. Various trials ongoing including RECOVERY. Some debate amongst doctors about this one but we would all be happy if it works. 12/20
JAK inhibitors: Another powerful anti-inflammatory drug which some hope will prevent the & #39;cytokine storm& #39; of COVID. Emotive term describing the whole-body inflammation we see in critical illness. In decades of research, no drug has prevented this. Clinical trials ongoing. 13/20
Interferon-B: Another anti-inflammatory drug we hoped would control COVID inflammation (cytokine storm) but the large @WHO SOLIDARITY trial showed no benefit on survival, need for ventilation, etc. Not a surprise for ICU docs. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.10.15.20209817v1.full.pdf">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1... 14/20
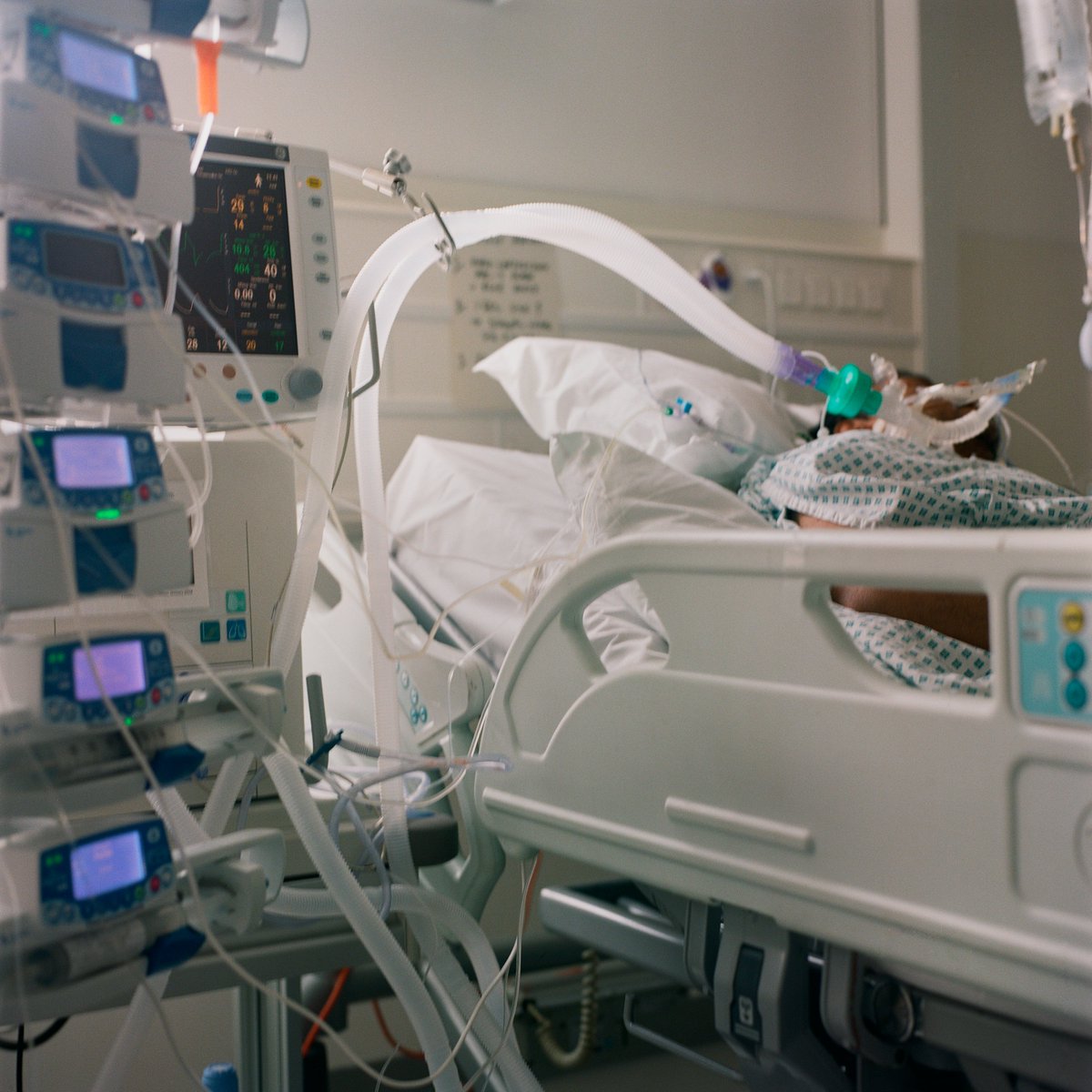
Ventilation: For very severe cases where patients cannot breathe without a machine. Patients are sedated and a tube placed in their windpipe connecting them to a ventilator. High-burden but life sustaining treatment. Needs highly trained nurses. Only used in intensive care. 15/20
CPAP: For severe breathing problems. Awake patients use a tight mask connected to a machine increasing air pressure in their lungs. Needs well trained nurses. Can be life saving. Some docs think CPAP should be used more and ventilation less. No trial data on this yet. 16/20
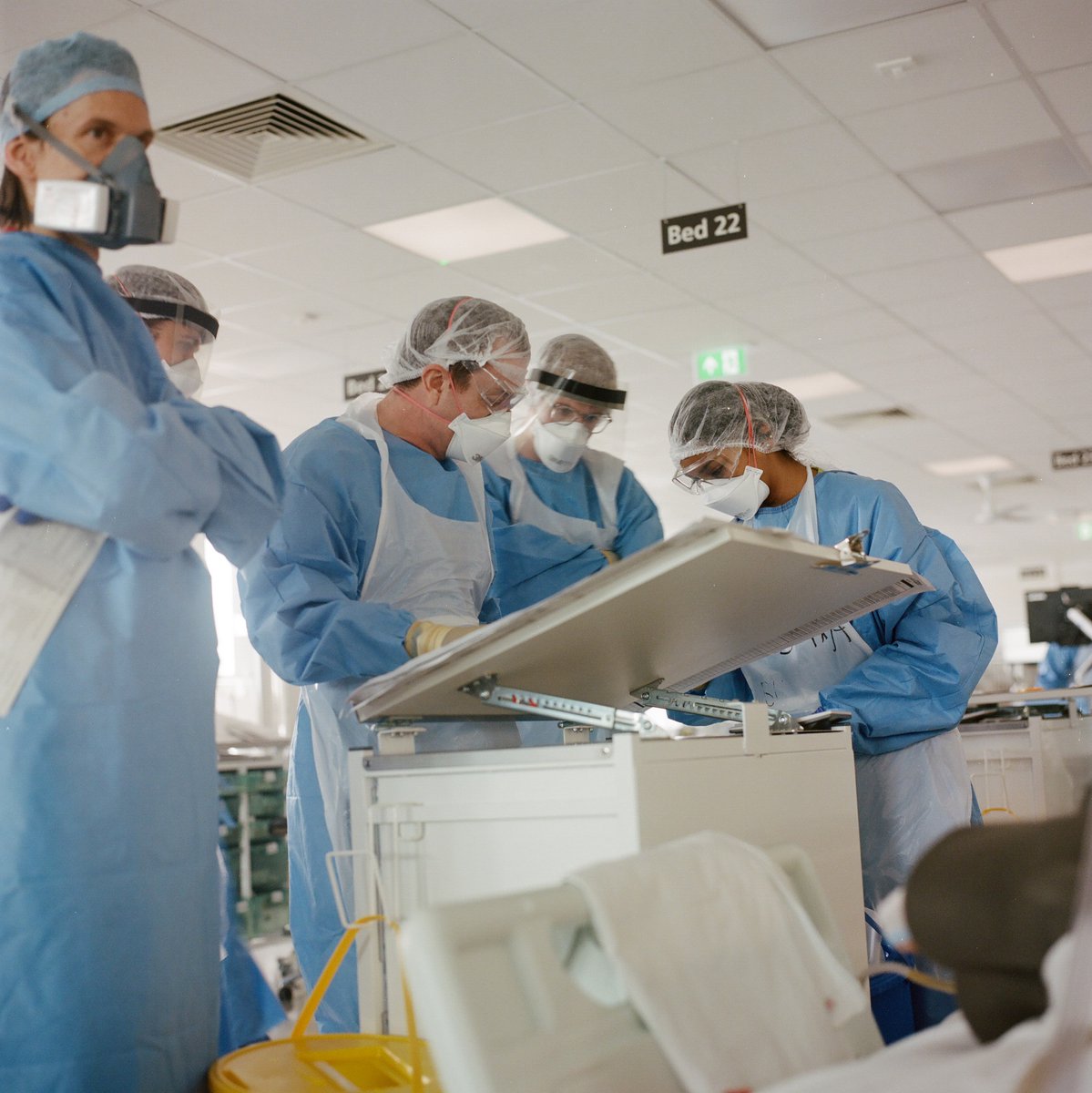
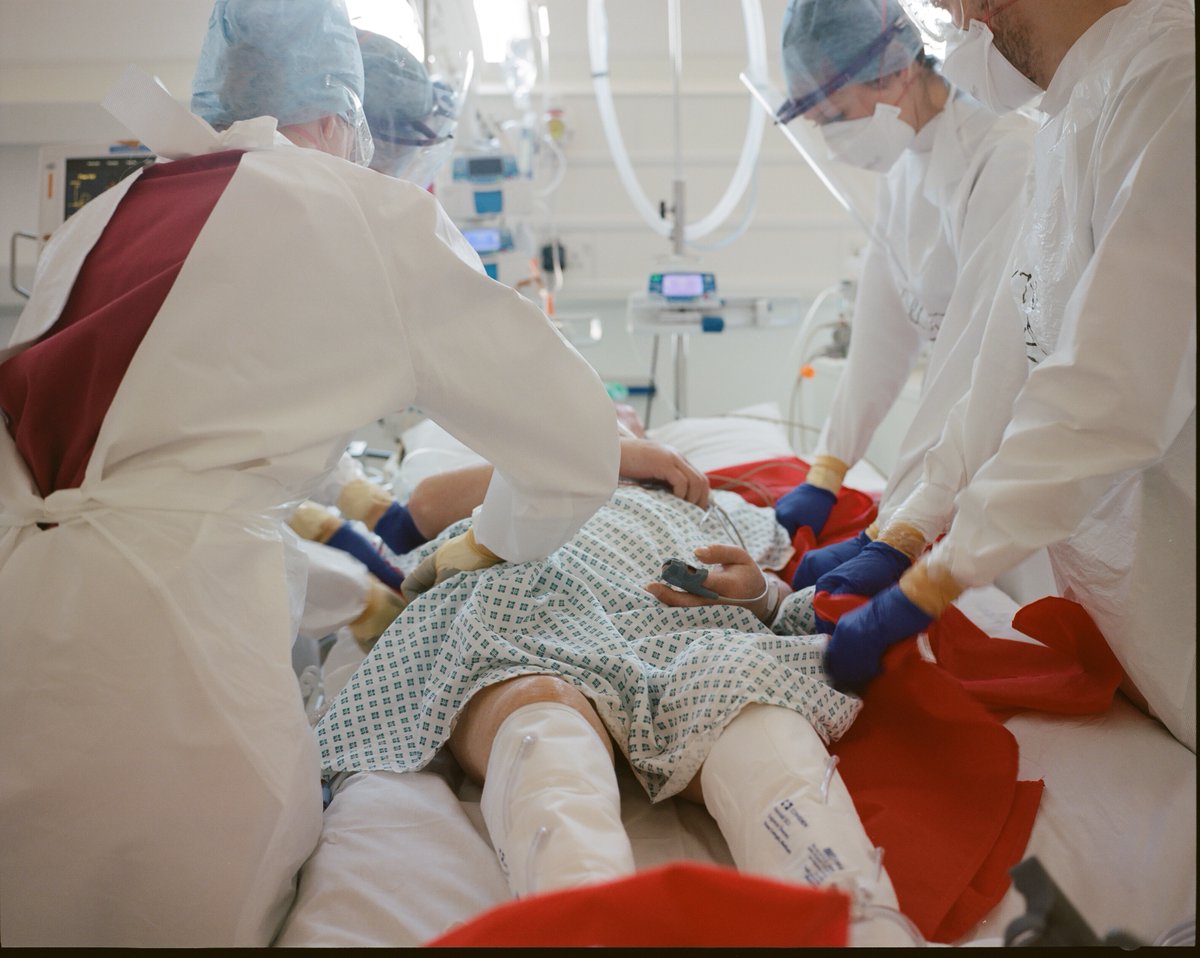
Prone ventilation: For patients with severe breathing problems already on CPAP or ventilation. Quite simply, patients lie (or are turned) on their front, improving lung function & blood oxygen. Useful tool but not always helpful. Needs lots of staff to do safely (photo). 17/20
Vaccines: The end-game. But rumours of a vaccine by Christmas are greatly exaggerated. Lots of clinical trials starting in the UK. Not my field but I hear that coronaviruses are not the easiest pathogen to develop a vaccine against. Beware bold promises. Be patient. 18/20
We shouldn& #39;t be too disappointed with these clinical trials results. All drugs have side-effects so those which don& #39;t work can only do harm. It is good for patients to avoid ineffective treatments. We continue to focus on doing the basics well. This does seem to be working. 19/20
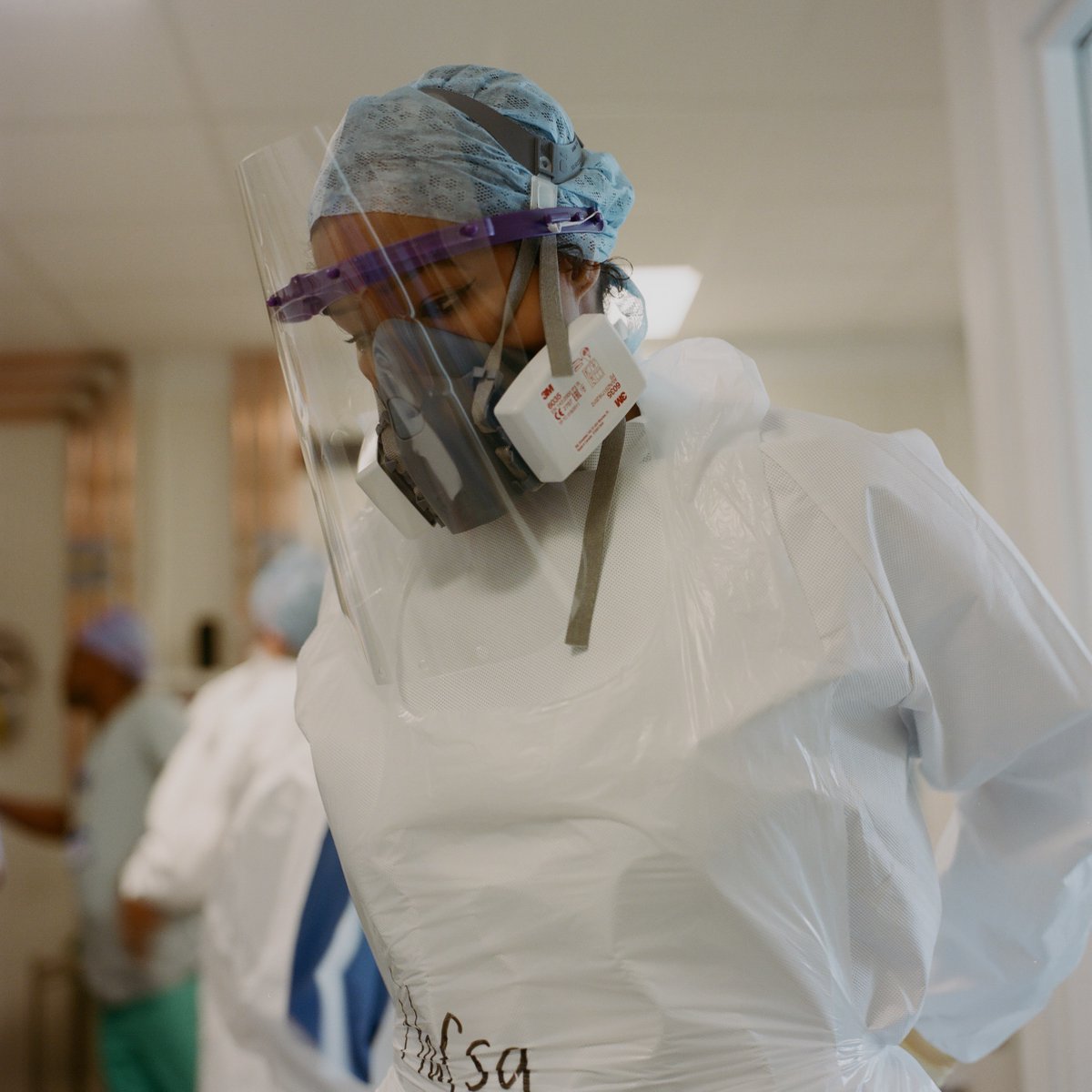
So there is NO cure for COVID-19, just a few drugs which help. The pandemic goes on until we can use widespread vaccination to prevent the virus spreading. Right now, simple things like #HandsFaceSpace will save the most lives by far. Photos of @teamaccu: @jometsonscott 20/20

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter