1/7 @TJTimberlake asks: "Could you (or another #FireEcology) expert provide some context on the debate regarding beetle-kill affecting fire behavior/severity/extent? Gray stage versus red stage and all that..." Well studied in past 15+ yr; not really a debate in sci. community.
2/7 Short answer: major driver of size of #EastTroublesomeFire = extremely dry fuels + high winds. Mountain pine beetle (MPB) mortality likely affected fire behavior, including tree torching and fire intensity, but TBD if it impact severity - it may not. Here’s the basis:
3/7 Good framework for this Q provided by Jeff Hicke et al., who divide post-MPB stands into 3 categories: red, grey, and old phase. Based on changes in canopy and surface fuels, each phase has diff. expected impacts on  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378112712000746">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378112712000746">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
4/7 Areas of #EastTroublesomeFire (not all) impacted by MBP, up to c. 80% mortality. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">from 2007, looking west towards Grand Lake, from @RockyNPS. This area& #39;s just south of the
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">from 2007, looking west towards Grand Lake, from @RockyNPS. This area& #39;s just south of the  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">, but looking out towards fire-affected areas.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">, but looking out towards fire-affected areas.
5/7 Stands would now be in "Old" phase, suggesting  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Pfeil nach oben" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach oben">surface fire intensity and individual tree torching. Active crown fire potential
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Pfeil nach oben" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach oben">surface fire intensity and individual tree torching. Active crown fire potential  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">– BUT photos, InciWeb & rate of spread indicate extreme
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">– BUT photos, InciWeb & rate of spread indicate extreme  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior: large flame length and rapid spread.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior: large flame length and rapid spread.  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">Andrew Lussie via InciWeb
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">Andrew Lussie via InciWeb
6/7 Overall... high winds + record-setting dry fuels, & everything else becomes less influential. No doubt studies will look at this in depth for #EastTroublesomeFire. @Brian_J_Harvey D. Donato & @MonicaGTurner have a robust study on this Q in N. Rockies: https://www.pnas.org/content/111/42/15120">https://www.pnas.org/content/1...
7/7 Last but not least: @HartsTrees @taniaschoe @ThomasTVeblen T. Chapman: "Contrary to the expectation that an MPB outbreak increases fire risk...[we] show no effect of outbreaks on subsequent area burned during years of extreme burning across the West." https://www.pnas.org/content/112/14/4375">https://www.pnas.org/content/1...

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter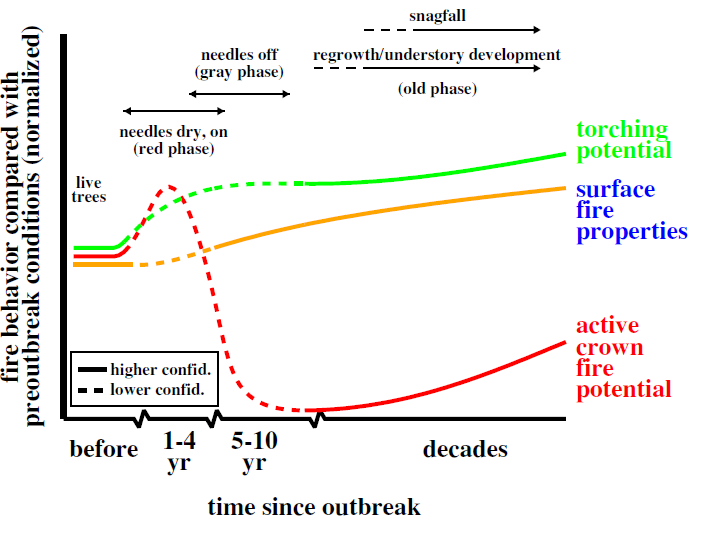 behavior. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." title="3/7 Good framework for this Q provided by Jeff Hicke et al., who divide post-MPB stands into 3 categories: red, grey, and old phase. Based on changes in canopy and surface fuels, each phase has diff. expected impacts on https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
behavior. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." title="3/7 Good framework for this Q provided by Jeff Hicke et al., who divide post-MPB stands into 3 categories: red, grey, and old phase. Based on changes in canopy and surface fuels, each phase has diff. expected impacts on https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 from 2007, looking west towards Grand Lake, from @RockyNPS. This area& #39;s just south of the https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">, but looking out towards fire-affected areas." title="4/7 Areas of #EastTroublesomeFire (not all) impacted by MBP, up to c. 80% mortality.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">from 2007, looking west towards Grand Lake, from @RockyNPS. This area& #39;s just south of the https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">, but looking out towards fire-affected areas." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
from 2007, looking west towards Grand Lake, from @RockyNPS. This area& #39;s just south of the https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">, but looking out towards fire-affected areas." title="4/7 Areas of #EastTroublesomeFire (not all) impacted by MBP, up to c. 80% mortality.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">from 2007, looking west towards Grand Lake, from @RockyNPS. This area& #39;s just south of the https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">, but looking out towards fire-affected areas." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 surface fire intensity and individual tree torching. Active crown fire potential https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">– BUT photos, InciWeb & rate of spread indicate extreme https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior: large flame length and rapid spread. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">Andrew Lussie via InciWeb" title="5/7 Stands would now be in "Old" phase, suggesting https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Pfeil nach oben" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach oben">surface fire intensity and individual tree torching. Active crown fire potential https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">– BUT photos, InciWeb & rate of spread indicate extreme https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior: large flame length and rapid spread. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">Andrew Lussie via InciWeb" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
surface fire intensity and individual tree torching. Active crown fire potential https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">– BUT photos, InciWeb & rate of spread indicate extreme https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior: large flame length and rapid spread. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">Andrew Lussie via InciWeb" title="5/7 Stands would now be in "Old" phase, suggesting https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Pfeil nach oben" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach oben">surface fire intensity and individual tree torching. Active crown fire potential https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">– BUT photos, InciWeb & rate of spread indicate extreme https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">behavior: large flame length and rapid spread. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📷" title="Kamera" aria-label="Emoji: Kamera">Andrew Lussie via InciWeb" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>


