Unstructured data will account for 80%
Here is an EASY thread
$MDB MongoDB was initially released in 2009  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> and NoSQL quickly became a good alternative / complement to relational databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> and NoSQL quickly became a good alternative / complement to relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📦" title="Paket" aria-label="Emoji: Paket">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📦" title="Paket" aria-label="Emoji: Paket">
Certainly for the modern web giants https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦄" title="Einhorngesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Einhorngesicht"> that had to deal with increasing amounts of data and real-time web applications
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦄" title="Einhorngesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Einhorngesicht"> that had to deal with increasing amounts of data and real-time web applications  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⏱" title="Stoppuhr" aria-label="Emoji: Stoppuhr">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⏱" title="Stoppuhr" aria-label="Emoji: Stoppuhr">
Certainly for the modern web giants
OK… That isn’t very telling https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> Let’s dive into databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> Let’s dive into databases https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="1️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 1" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 1"> What are relational databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="1️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 1" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 1"> What are relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="2️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 2" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 2"> What are non-relational databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="2️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 2" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 2"> What are non-relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="3️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 3" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 3"> What are the use cases for relational databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="3️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 3" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 3"> What are the use cases for relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏭" title="Fabrik" aria-label="Emoji: Fabrik">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏭" title="Fabrik" aria-label="Emoji: Fabrik">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="4️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 4" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 4"> What are the use cases for non-relational databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="4️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 4" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 4"> What are the use cases for non-relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏭" title="Fabrik" aria-label="Emoji: Fabrik">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏭" title="Fabrik" aria-label="Emoji: Fabrik">
When a system or developer needs information
Storing data on different tables enables for more flexibility  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏗" title="Gebäude im Bau" aria-label="Emoji: Gebäude im Bau"> and less redundancy
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏗" title="Gebäude im Bau" aria-label="Emoji: Gebäude im Bau"> and less redundancy  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👥" title="Silhouette von Büsten" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette von Büsten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👥" title="Silhouette von Büsten" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette von Büsten">
E.g. A shop has information on its customers https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👤" title="Silhouette einer Büste" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette einer Büste"> (Customer ID, name, state, mailing address) and their purchases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👤" title="Silhouette einer Büste" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette einer Büste"> (Customer ID, name, state, mailing address) and their purchases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🛍" title="Einkaufstaschen" aria-label="Emoji: Einkaufstaschen"> (Customer ID, purchases, time of visit)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🛍" title="Einkaufstaschen" aria-label="Emoji: Einkaufstaschen"> (Customer ID, purchases, time of visit)
E.g. A shop has information on its customers
An alternative would have been to create a huge database  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏢" title="Bürogebäude" aria-label="Emoji: Bürogebäude"> with Customer ID, name, state, mailing address, purchases, time of visit
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏢" title="Bürogebäude" aria-label="Emoji: Bürogebäude"> with Customer ID, name, state, mailing address, purchases, time of visit
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> But that would NOT be EFFICIENT
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> But that would NOT be EFFICIENT
A key aspect of relational databases is that data needs to be saved according to a pre-determined model  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧮" title="Abacus" aria-label="Emoji: Abacus">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧮" title="Abacus" aria-label="Emoji: Abacus">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> These make sure that relational databases are consistent
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> These make sure that relational databases are consistent  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧼" title="Soap" aria-label="Emoji: Soap"> Meaning that readers ALWAYS receive the last updated information
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧼" title="Soap" aria-label="Emoji: Soap"> Meaning that readers ALWAYS receive the last updated information  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📋" title="Klemmbrett" aria-label="Emoji: Klemmbrett"> or an error
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📋" title="Klemmbrett" aria-label="Emoji: Klemmbrett"> or an error  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚩" title="Dreieckige Fahne an einem Pfosten" aria-label="Emoji: Dreieckige Fahne an einem Pfosten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚩" title="Dreieckige Fahne an einem Pfosten" aria-label="Emoji: Dreieckige Fahne an einem Pfosten">
Careful UPFRONT design  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📝" title="Memo" aria-label="Emoji: Memo"> is thus required and changes have to be carefully implemented
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📝" title="Memo" aria-label="Emoji: Memo"> is thus required and changes have to be carefully implemented  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧪" title="Test tube" aria-label="Emoji: Test tube"> thereafter (sometimes including downtime)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧪" title="Test tube" aria-label="Emoji: Test tube"> thereafter (sometimes including downtime)
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="‼️" title="Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen"> This is a problem for data where the relationships change often or when the data lacks structure
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="‼️" title="Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen"> This is a problem for data where the relationships change often or when the data lacks structure  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎚" title="Schieberegler" aria-label="Emoji: Schieberegler">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎚" title="Schieberegler" aria-label="Emoji: Schieberegler">
Another key weakness is SCALING  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht">
When the amounts / complexity of the data you handle changes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> What can you do?
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> What can you do?
⇣ VERTICAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more power (CPU, RAM)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more power (CPU, RAM)  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to make your machines faster
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to make your machines faster
⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more machines
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more machines  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
When the amounts / complexity of the data you handle changes
⇣ VERTICAL SCALING
⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING
⇣ VERTICAL SCALING in this case, the data resides in the same node (or database instance - place where the data is saved and can be handled)
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> Costs rise exponentially when adding CPUs and RAM
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> Costs rise exponentially when adding CPUs and RAM  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to ONE machine as complexity rises
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to ONE machine as complexity rises  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf">
E.g. buying one high-performance custom made computer is an order of magnitude more expensive than buying 10 standard and average performance computer
⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING in this case, the data is distributed over several machines  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> Costs are kept under control as more “simple” machines can be used as one machine doesn’t need to execute all of the work
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> Costs are kept under control as more “simple” machines can be used as one machine doesn’t need to execute all of the work  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen">
Hint
These documents (equivalent of the “rows” in relational databases”) can be arranged in “collections” (equivalent of the “tables” in relational databases) inside the database
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> But… Since we can compare documents to rows and collections to tables… isn’t it the same thing?
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> But… Since we can compare documents to rows and collections to tables… isn’t it the same thing?  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">
Well no, the major difference lies in the fact that different documents DO NOT NEED TO SHARE THE SAME STRUCTURE  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="‼️" title="Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen"> This is key difference from relational databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="‼️" title="Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Doppeltes Ausrufezeichen"> This is key difference from relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> where every row has the same fields
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> where every row has the same fields  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf">
Data that is unstructured
Lots of data
Does it also provide HORIZONTAL SCALABILITY
YES  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">
While you cannot in principle split tables (from relational databases) on different nodes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> You CAN DISTRIBUTE documents (from non-relational databases) over several machines
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> You CAN DISTRIBUTE documents (from non-relational databases) over several machines  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> This enables for horizontal scaling
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> This enables for horizontal scaling
While you cannot in principle split tables (from relational databases) on different nodes
But what about these duplicates? From IBM  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
“That means the information you receive from a query may be incorrect by a few seconds—perhaps up to half a minute. On social media sites, this means seeing an old profile picture when the newest one is only a few moments old...
“That means the information you receive from a query may be incorrect by a few seconds—perhaps up to half a minute. On social media sites, this means seeing an old profile picture when the newest one is only a few moments old...
...The alternative could be a timeout or error. On the other hand, in banking and financial transactions, an error and resubmit may be better than old, incorrect information.”
You can see it here  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👀" title="Augen" aria-label="Emoji: Augen"> Non-relational databases are good for some websites
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👀" title="Augen" aria-label="Emoji: Augen"> Non-relational databases are good for some websites  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> But others cannot work with “false information”
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> But others cannot work with “false information”  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⛔️" title="Nicht betreten" aria-label="Emoji: Nicht betreten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⛔️" title="Nicht betreten" aria-label="Emoji: Nicht betreten">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer"> This is why NoSQL is now said to stand for “Not Only SQL”
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer"> This is why NoSQL is now said to stand for “Not Only SQL”  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> Where SQL refers to Structured Query Language (language for relational databases)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> Where SQL refers to Structured Query Language (language for relational databases)
All in all, there are some use cases where relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> are a better fit
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> are a better fit  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙌" title="Raising hands" aria-label="Emoji: Raising hands">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙌" title="Raising hands" aria-label="Emoji: Raising hands">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> And some other use cases where non relational databases work best
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> And some other use cases where non relational databases work best
Relational databases are best used for tasks that fail as whole OR succeed - This can be said of
As you can imagine, a financial transaction needs to succeed or fail
These all have to deal with vast amounts of (un)structured content that often changes such as messages, pictures, comments, live data AND can fail / return an error temporarily
According to http://Scalegrid.io"> http://Scalegrid.io (provides services for non and relational databases)
As we can see  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👀" title="Augen" aria-label="Emoji: Augen"> $MDB is one of the most popular NoSQL databases
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👀" title="Augen" aria-label="Emoji: Augen"> $MDB is one of the most popular NoSQL databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> Is the market served by these databases growing
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> Is the market served by these databases growing  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> In other words, is the market for UNSTRUCTURED
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> In other words, is the market for UNSTRUCTURED  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and LARGE AMOUNTS
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and LARGE AMOUNTS  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎡" title="Riesenrad" aria-label="Emoji: Riesenrad"> of data growing?
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎡" title="Riesenrad" aria-label="Emoji: Riesenrad"> of data growing?
Well, according the IDC the size of worldwide data will reach 175 ZettaBytes by 2025  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📋" title="Klemmbrett" aria-label="Emoji: Klemmbrett">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📋" title="Klemmbrett" aria-label="Emoji: Klemmbrett">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Representing a CAGR of 61% over the 2019 - 2025 period
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Representing a CAGR of 61% over the 2019 - 2025 period
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> 80% of that data will be unstructured
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> 80% of that data will be unstructured  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and 49% of the whole data will be in public clouds
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and 49% of the whole data will be in public clouds  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☁️" title="Wolke" aria-label="Emoji: Wolke">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☁️" title="Wolke" aria-label="Emoji: Wolke">
In terms of market size  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Allied Market Research places the NoSQL market at $ 22B in 2026 - up from $ 2.5B in 2018
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Allied Market Research places the NoSQL market at $ 22B in 2026 - up from $ 2.5B in 2018
Good for a CAGR of 31.4% from 2019 to 2026 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> Driven by increased demand from
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> Driven by increased demand from  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🛍" title="Einkaufstaschen" aria-label="Emoji: Einkaufstaschen"> Ecommerce
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🛍" title="Einkaufstaschen" aria-label="Emoji: Einkaufstaschen"> Ecommerce
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> Web applications
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer"> Web applications
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎮" title="Videospiel" aria-label="Emoji: Videospiel"> Social gaming
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎮" title="Videospiel" aria-label="Emoji: Videospiel"> Social gaming
Good for a CAGR of 31.4% from 2019 to 2026
Let’s look at DB-Engines for historical evolution
When looking at the bigger picture  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🖼" title="Bilderrahmen mit Bild" aria-label="Emoji: Bilderrahmen mit Bild"> we can see that established SQL
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🖼" title="Bilderrahmen mit Bild" aria-label="Emoji: Bilderrahmen mit Bild"> we can see that established SQL  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> databases are not loosing too much ground
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> databases are not loosing too much ground  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏰" title="Europäisches Schloss" aria-label="Emoji: Europäisches Schloss">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏰" title="Europäisches Schloss" aria-label="Emoji: Europäisches Schloss">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> PostgreSQL (relational database) and MongoDB (Non relational database) are both gaining in popularity
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> PostgreSQL (relational database) and MongoDB (Non relational database) are both gaining in popularity
It is clear that $MDB is NOT set to replace relational databases  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> These are still widely used
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> These are still widely used  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑💻" title="Technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Technologist">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑💻" title="Technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Technologist">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> But we have seen that $MDB is leading
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> But we have seen that $MDB is leading  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> the document stores databases by a WIDE margin
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> the document stores databases by a WIDE margin
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔍" title="Nach links zeigende Lupe" aria-label="Emoji: Nach links zeigende Lupe"> And searches for “MongoDB Atlas”
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔍" title="Nach links zeigende Lupe" aria-label="Emoji: Nach links zeigende Lupe"> And searches for “MongoDB Atlas”  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> trend upwards over the last 5 years globally
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> trend upwards over the last 5 years globally  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden">
That is a LOT of information  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> A summary
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> A summary
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> Non-relational databases are better than relational in some cases (when data amounts are huge, changes over time)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> Non-relational databases are better than relational in some cases (when data amounts are huge, changes over time)
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> Non-relational databases SCALE way better and are more flexible to real-life data changes
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> Non-relational databases SCALE way better and are more flexible to real-life data changes
So far so good! Let’s have a look at $MDB itself  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👀" title="Augen" aria-label="Emoji: Augen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👀" title="Augen" aria-label="Emoji: Augen">
$MDB generates sales (total of $ 138m) from 3 main sources https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden"> Atlas related subscriptions ($ 61m and growing 69% YoY)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden"> Atlas related subscriptions ($ 61m and growing 69% YoY)
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📦" title="Paket" aria-label="Emoji: Paket"> Other subscriptions ($ 71m and growing 24% YoY)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📦" title="Paket" aria-label="Emoji: Paket"> Other subscriptions ($ 71m and growing 24% YoY)
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> Services ($ 5m - stable)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> Services ($ 5m - stable)
$MDB generates sales (total of $ 138m) from 3 main sources
The “Other subscription” is basically the “MongoDB Enterprise Advanced”  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏢" title="Bürogebäude" aria-label="Emoji: Bürogebäude"> product offered by $MDB
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏢" title="Bürogebäude" aria-label="Emoji: Bürogebäude"> product offered by $MDB
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> This enables businesses to run $MDB on their own infrastructure and customise it very finely to their needs
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> This enables businesses to run $MDB on their own infrastructure and customise it very finely to their needs
MongoDB Atlas  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⛰" title="Berg" aria-label="Emoji: Berg"> is the one providing the growth behind the $MDB story
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⛰" title="Berg" aria-label="Emoji: Berg"> is the one providing the growth behind the $MDB story  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> It is a cloud Database-As-A-Service that offers a free tier
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> It is a cloud Database-As-A-Service that offers a free tier  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> is fully managed
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> is fully managed  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> provides on-demand scaling
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> provides on-demand scaling  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> and real-time insights
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> and real-time insights  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">
To say that Atlas is an incredible product is an understatement  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🗣" title="Silhouette eines sprechenden Kopfes" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette eines sprechenden Kopfes"> “MongoDB Atlas, which launched in June of 2016, is a battle-tested database-as-a-service platform (DBaaS) artfully designed and built by the same team that created and continues to nurture and grow MongoDB...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🗣" title="Silhouette eines sprechenden Kopfes" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette eines sprechenden Kopfes"> “MongoDB Atlas, which launched in June of 2016, is a battle-tested database-as-a-service platform (DBaaS) artfully designed and built by the same team that created and continues to nurture and grow MongoDB...
...MongoDB Atlas is a true blessing to the development community; it provides all of the features of its database counterpart, without the operation and heavy lifting normally required when building new applications, letting you focus on what you do best.” - Nick Parsons
The full review is right here  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://medium.com/@nparsons08/mongodb-atlas-technical-overview-benefits-9e4cff27a75e">https://medium.com/@nparsons...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://medium.com/@nparsons08/mongodb-atlas-technical-overview-benefits-9e4cff27a75e">https://medium.com/@nparsons...
You know what is good about $MDB Atlas?  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> It is a usage-based service
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> It is a usage-based service
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> Remember the growth in unstructured DATA? Well, $MDB is growing not only by adding more customers
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> Remember the growth in unstructured DATA? Well, $MDB is growing not only by adding more customers  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👥" title="Silhouette von Büsten" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette von Büsten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👥" title="Silhouette von Büsten" aria-label="Emoji: Silhouette von Büsten">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer"> BUT ALSO as its current customers have more data to handle
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer"> BUT ALSO as its current customers have more data to handle  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">
Here is @cameroniadeluca excellent take on the matter  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://twitter.com/cameroniadeluca/status/1204067906503479297?s=20">https://twitter.com/cameronia...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://twitter.com/cameroniadeluca/status/1204067906503479297?s=20">https://twitter.com/cameronia...
Financials check  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen"> Sales grew by 39% YoY
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen"> Sales grew by 39% YoY  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> to $ 138m per quarter
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> to $ 138m per quarter  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⚙️" title="Zahnrad" aria-label="Emoji: Zahnrad"> Gross margins stand at 69%
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⚙️" title="Zahnrad" aria-label="Emoji: Zahnrad"> Gross margins stand at 69%  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📉" title="Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend"> Down from 72% in prev. Q.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📉" title="Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend"> Down from 72% in prev. Q.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏢" title="Bürogebäude" aria-label="Emoji: Bürogebäude"> Loss from operations stood at $50m up from a loss of $ 38m a year earlier
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏢" title="Bürogebäude" aria-label="Emoji: Bürogebäude"> Loss from operations stood at $50m up from a loss of $ 38m a year earlier
Disclaimer - This is not investment advice in any form and investors are responsible for conducting their own research before investing.
Sources
✑ Investor presentation
✑ Company website
✑ SimilarWeb
✑ DB Engines
✑ IDC
✑ Allied Market Research
✑ IBM
✑ Guru99
Sources
✑ Investor presentation
✑ Company website
✑ SimilarWeb
✑ DB Engines
✑ IDC
✑ Allied Market Research
✑ IBM
✑ Guru99
✑ Forbes
✑ High Scalability
✑ InfoWorld
✑ Packt
✑ Dataversity
✑ ScaleGrid
✑ Nick Parsons on Medium
✑ PCMag
✑ High Scalability
✑ InfoWorld
✑ Packt
✑ Dataversity
✑ ScaleGrid
✑ Nick Parsons on Medium
✑ PCMag
Hope you liked this thread!
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> For more content, follow us on Twitter
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> For more content, follow us on Twitter  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔥" title="Feuer" aria-label="Emoji: Feuer">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> Want to get UNDER HYPED companies delivered straight to your inbox
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> Want to get UNDER HYPED companies delivered straight to your inbox  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📩" title="Umschlag mit nach unten zeigendem Pfeil darüber" aria-label="Emoji: Umschlag mit nach unten zeigendem Pfeil darüber"> Don’t MISS IT
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📩" title="Umschlag mit nach unten zeigendem Pfeil darüber" aria-label="Emoji: Umschlag mit nach unten zeigendem Pfeil darüber"> Don’t MISS IT  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://getbenchmark.substack.com"> https://getbenchmark.substack.com
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://getbenchmark.substack.com"> https://getbenchmark.substack.com

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter 120% EXPANSION RATE https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht">Unstructured data will account for 80% https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> of the 175 ZETTABYTES produced by 2025 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> NOW the DEFAULT NoSQL database https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> Share price went from $ 24 to $ 267 in 3 YEARS https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen">Here is an EASY thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht"> 120% EXPANSION RATE https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht">Unstructured data will account for 80% https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> of the 175 ZETTABYTES produced by 2025 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> NOW the DEFAULT NoSQL database https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> Share price went from $ 24 to $ 267 in 3 YEARS https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen">Here is an EASY thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
120% EXPANSION RATE https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht">Unstructured data will account for 80% https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> of the 175 ZETTABYTES produced by 2025 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> NOW the DEFAULT NoSQL database https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> Share price went from $ 24 to $ 267 in 3 YEARS https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen">Here is an EASY thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht"> 120% EXPANSION RATE https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht">Unstructured data will account for 80% https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤯" title="Explodierender Kopf" aria-label="Emoji: Explodierender Kopf"> of the 175 ZETTABYTES produced by 2025 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> NOW the DEFAULT NoSQL database https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> Share price went from $ 24 to $ 267 in 3 YEARS https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💵" title="Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Banknote mit Dollar-Zeichen">Here is an EASY thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 Relational databases organise data into tables that can be linked (also “related”) to each other https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol">When a system or developer needs information https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> It can retrieve it from the different tables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm"> where the data is stored into" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="1️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 1" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 1"> Relational databases organise data into tables that can be linked (also “related”) to each other https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol">When a system or developer needs information https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> It can retrieve it from the different tables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm"> where the data is stored into" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
Relational databases organise data into tables that can be linked (also “related”) to each other https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol">When a system or developer needs information https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> It can retrieve it from the different tables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm"> where the data is stored into" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="1️⃣" title="Tastenkappe Ziffer 1" aria-label="Emoji: Tastenkappe Ziffer 1"> Relational databases organise data into tables that can be linked (also “related”) to each other https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol">When a system or developer needs information https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> It can retrieve it from the different tables https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm"> where the data is stored into" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
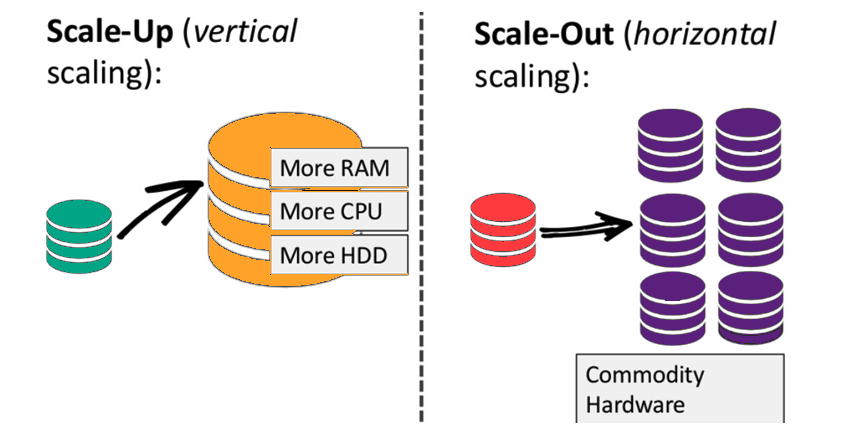 When the amounts / complexity of the data you handle changes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> What can you do?⇣ VERTICAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more power (CPU, RAM) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to make your machines faster ⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more machines https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">" title="Another key weakness is SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht"> When the amounts / complexity of the data you handle changes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> What can you do?⇣ VERTICAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more power (CPU, RAM) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to make your machines faster ⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more machines https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
When the amounts / complexity of the data you handle changes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> What can you do?⇣ VERTICAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more power (CPU, RAM) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to make your machines faster ⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more machines https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">" title="Another key weakness is SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht" aria-label="Emoji: Polizeiautos mit drehendem Licht"> When the amounts / complexity of the data you handle changes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> What can you do?⇣ VERTICAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more power (CPU, RAM) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> to make your machines faster ⇢ HORIZONTAL SCALING https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Add more machines https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💻" title="Computer" aria-label="Emoji: Computer">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
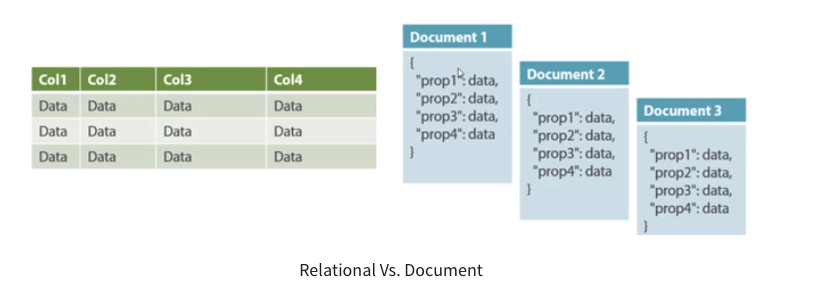 But… Since we can compare documents to rows and collections to tables… isn’t it the same thing? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">" title="These documents (equivalent of the “rows” in relational databases”) can be arranged in “collections” (equivalent of the “tables” in relational databases) inside the databasehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> But… Since we can compare documents to rows and collections to tables… isn’t it the same thing? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
But… Since we can compare documents to rows and collections to tables… isn’t it the same thing? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">" title="These documents (equivalent of the “rows” in relational databases”) can be arranged in “collections” (equivalent of the “tables” in relational databases) inside the databasehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> But… Since we can compare documents to rows and collections to tables… isn’t it the same thing? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
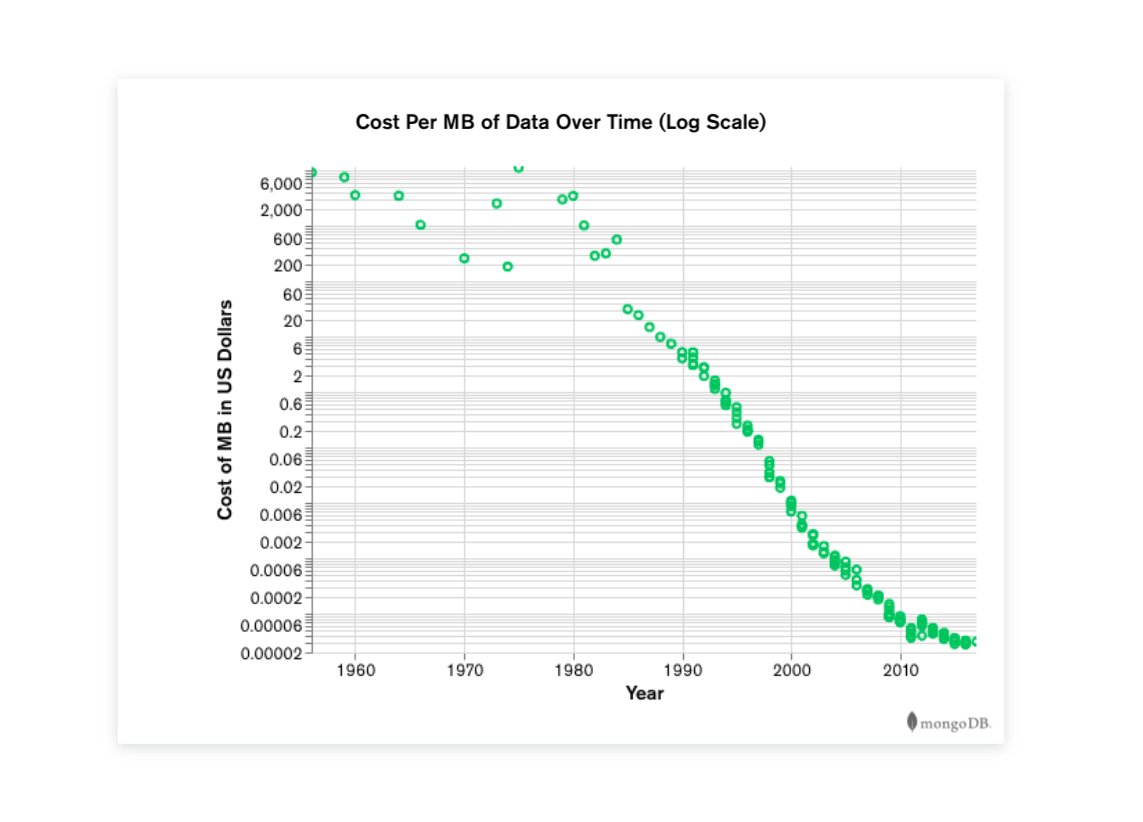 WHY are these seemingly weak advantages, KEY in the modern world https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> First, as the cost of data drastically decreased https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📉" title="Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend"> these last 30 years, the amount of data EXPLODED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👻" title="Geist" aria-label="Emoji: Geist"> AND data came in all shapes and sizes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Structured, semistructured, polymorphic" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> WHY are these seemingly weak advantages, KEY in the modern world https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> First, as the cost of data drastically decreased https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📉" title="Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend"> these last 30 years, the amount of data EXPLODED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👻" title="Geist" aria-label="Emoji: Geist"> AND data came in all shapes and sizes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Structured, semistructured, polymorphic" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
WHY are these seemingly weak advantages, KEY in the modern world https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> First, as the cost of data drastically decreased https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📉" title="Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend"> these last 30 years, the amount of data EXPLODED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👻" title="Geist" aria-label="Emoji: Geist"> AND data came in all shapes and sizes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Structured, semistructured, polymorphic" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen"> WHY are these seemingly weak advantages, KEY in the modern world https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⁉️" title="Ausrufe-Fragezeichen" aria-label="Emoji: Ausrufe-Fragezeichen">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> First, as the cost of data drastically decreased https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📉" title="Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Abwärtstrend"> these last 30 years, the amount of data EXPLODED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👻" title="Geist" aria-label="Emoji: Geist"> AND data came in all shapes and sizes https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> Structured, semistructured, polymorphic" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 MySQL is used most (39%), followed by MongoDB (25%) and then PostgreSQL (17%)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> 44% relied on multiple databases and 75% of these combined SQL and NoSQL to support their products" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> MySQL is used most (39%), followed by MongoDB (25%) and then PostgreSQL (17%)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> 44% relied on multiple databases and 75% of these combined SQL and NoSQL to support their products" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
MySQL is used most (39%), followed by MongoDB (25%) and then PostgreSQL (17%)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> 44% relied on multiple databases and 75% of these combined SQL and NoSQL to support their products" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> MySQL is used most (39%), followed by MongoDB (25%) and then PostgreSQL (17%)https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> 44% relied on multiple databases and 75% of these combined SQL and NoSQL to support their products" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
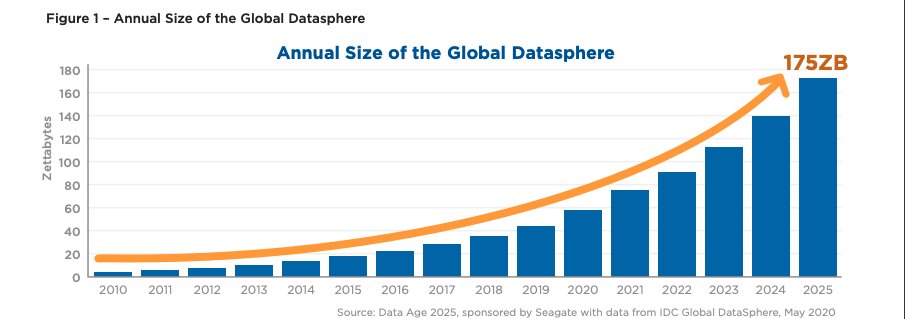 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Representing a CAGR of 61% over the 2019 - 2025 periodhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> 80% of that data will be unstructured https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and 49% of the whole data will be in public clouds https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☁️" title="Wolke" aria-label="Emoji: Wolke">" title="Well, according the IDC the size of worldwide data will reach 175 ZettaBytes by 2025 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📋" title="Klemmbrett" aria-label="Emoji: Klemmbrett">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Representing a CAGR of 61% over the 2019 - 2025 periodhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> 80% of that data will be unstructured https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and 49% of the whole data will be in public clouds https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☁️" title="Wolke" aria-label="Emoji: Wolke">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Representing a CAGR of 61% over the 2019 - 2025 periodhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> 80% of that data will be unstructured https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and 49% of the whole data will be in public clouds https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☁️" title="Wolke" aria-label="Emoji: Wolke">" title="Well, according the IDC the size of worldwide data will reach 175 ZettaBytes by 2025 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📋" title="Klemmbrett" aria-label="Emoji: Klemmbrett">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> Representing a CAGR of 61% over the 2019 - 2025 periodhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts"> 80% of that data will be unstructured https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> and 49% of the whole data will be in public clouds https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☁️" title="Wolke" aria-label="Emoji: Wolke">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
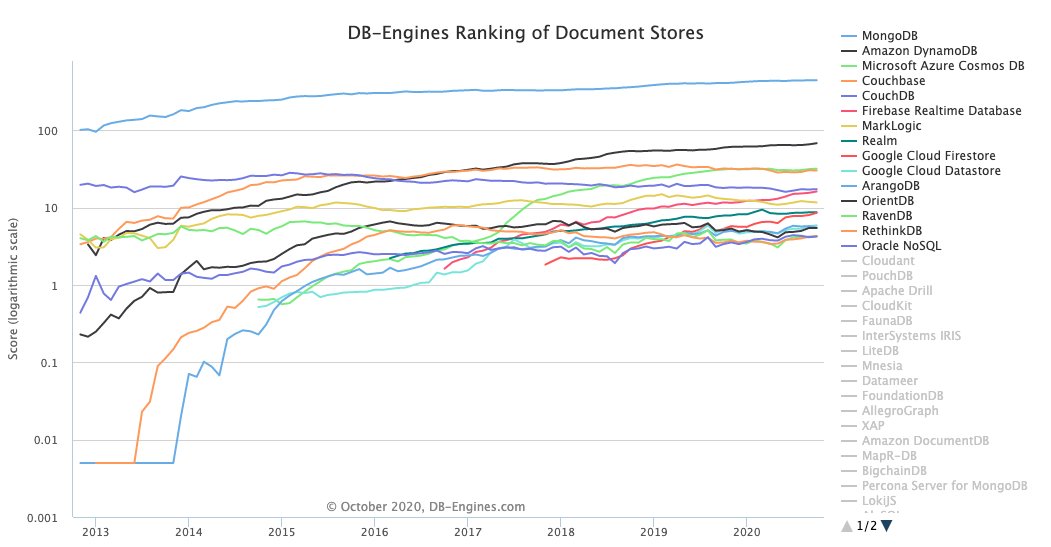 It is leading the pack while other fail to break out e.g. #CouchbaseDB (score of 30) $AMZN (score of 68) and $MSFT (score of 32)" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> It is leading the pack while other fail to break out e.g. #CouchbaseDB (score of 30) $AMZN (score of 68) and $MSFT (score of 32)" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
It is leading the pack while other fail to break out e.g. #CouchbaseDB (score of 30) $AMZN (score of 68) and $MSFT (score of 32)" title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> It is leading the pack while other fail to break out e.g. #CouchbaseDB (score of 30) $AMZN (score of 68) and $MSFT (score of 32)" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 we can see that established SQL https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> databases are not loosing too much ground https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏰" title="Europäisches Schloss" aria-label="Emoji: Europäisches Schloss">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> PostgreSQL (relational database) and MongoDB (Non relational database) are both gaining in popularity" title="When looking at the bigger picture https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🖼" title="Bilderrahmen mit Bild" aria-label="Emoji: Bilderrahmen mit Bild"> we can see that established SQL https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> databases are not loosing too much ground https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏰" title="Europäisches Schloss" aria-label="Emoji: Europäisches Schloss">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> PostgreSQL (relational database) and MongoDB (Non relational database) are both gaining in popularity" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
we can see that established SQL https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> databases are not loosing too much ground https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏰" title="Europäisches Schloss" aria-label="Emoji: Europäisches Schloss">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> PostgreSQL (relational database) and MongoDB (Non relational database) are both gaining in popularity" title="When looking at the bigger picture https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🖼" title="Bilderrahmen mit Bild" aria-label="Emoji: Bilderrahmen mit Bild"> we can see that established SQL https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> databases are not loosing too much ground https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏰" title="Europäisches Schloss" aria-label="Emoji: Europäisches Schloss">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> PostgreSQL (relational database) and MongoDB (Non relational database) are both gaining in popularity" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
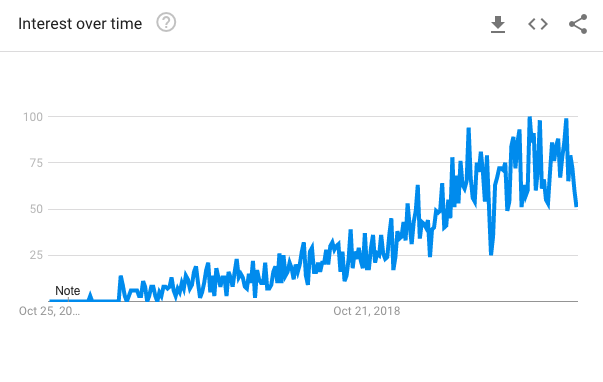 These are still widely used https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑💻" title="Technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Technologist">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> But we have seen that $MDB is leading https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> the document stores databases by a WIDE marginhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔍" title="Nach links zeigende Lupe" aria-label="Emoji: Nach links zeigende Lupe"> And searches for “MongoDB Atlas” https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> trend upwards over the last 5 years globally https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden">" title="It is clear that $MDB is NOT set to replace relational databases https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> These are still widely used https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑💻" title="Technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Technologist">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> But we have seen that $MDB is leading https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> the document stores databases by a WIDE marginhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔍" title="Nach links zeigende Lupe" aria-label="Emoji: Nach links zeigende Lupe"> And searches for “MongoDB Atlas” https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> trend upwards over the last 5 years globally https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
These are still widely used https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑💻" title="Technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Technologist">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> But we have seen that $MDB is leading https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> the document stores databases by a WIDE marginhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔍" title="Nach links zeigende Lupe" aria-label="Emoji: Nach links zeigende Lupe"> And searches for “MongoDB Atlas” https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> trend upwards over the last 5 years globally https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden">" title="It is clear that $MDB is NOT set to replace relational databases https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔗" title="Link Symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Link Symbol"> These are still widely used https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑💻" title="Technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Technologist">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📄" title="Seite mit der Schriftseite oben" aria-label="Emoji: Seite mit der Schriftseite oben"> But we have seen that $MDB is leading https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥇" title="Goldmedaille" aria-label="Emoji: Goldmedaille"> the document stores databases by a WIDE marginhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔍" title="Nach links zeigende Lupe" aria-label="Emoji: Nach links zeigende Lupe"> And searches for “MongoDB Atlas” https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend"> trend upwards over the last 5 years globally https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🌐" title="Weltkugel mit Längengraden" aria-label="Emoji: Weltkugel mit Längengraden">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 is the one providing the growth behind the $MDB story https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> It is a cloud Database-As-A-Service that offers a free tier https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> is fully managed https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> provides on-demand scaling https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> and real-time insights https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">" title="MongoDB Atlas https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⛰" title="Berg" aria-label="Emoji: Berg"> is the one providing the growth behind the $MDB story https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> It is a cloud Database-As-A-Service that offers a free tier https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> is fully managed https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> provides on-demand scaling https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> and real-time insights https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
is the one providing the growth behind the $MDB story https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> It is a cloud Database-As-A-Service that offers a free tier https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> is fully managed https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> provides on-demand scaling https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> and real-time insights https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">" title="MongoDB Atlas https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⛰" title="Berg" aria-label="Emoji: Berg"> is the one providing the growth behind the $MDB story https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📈" title="Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend" aria-label="Emoji: Tabelle mit Aufwärtstrend">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✅" title="Fettes weißes Häkchen" aria-label="Emoji: Fettes weißes Häkchen"> It is a cloud Database-As-A-Service that offers a free tier https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💸" title="Geld mit Flügeln" aria-label="Emoji: Geld mit Flügeln"> is fully managed https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👩💻" title="Woman technologist" aria-label="Emoji: Woman technologist"> provides on-demand scaling https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚀" title="Rakete" aria-label="Emoji: Rakete"> and real-time insights https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📊" title="Balkendiagramm" aria-label="Emoji: Balkendiagramm">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>


