Abortion declines in a post-Roe world. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/10/15/upshot/what-happens-if-roe-is-overturned.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti... @qdbui @clairecm
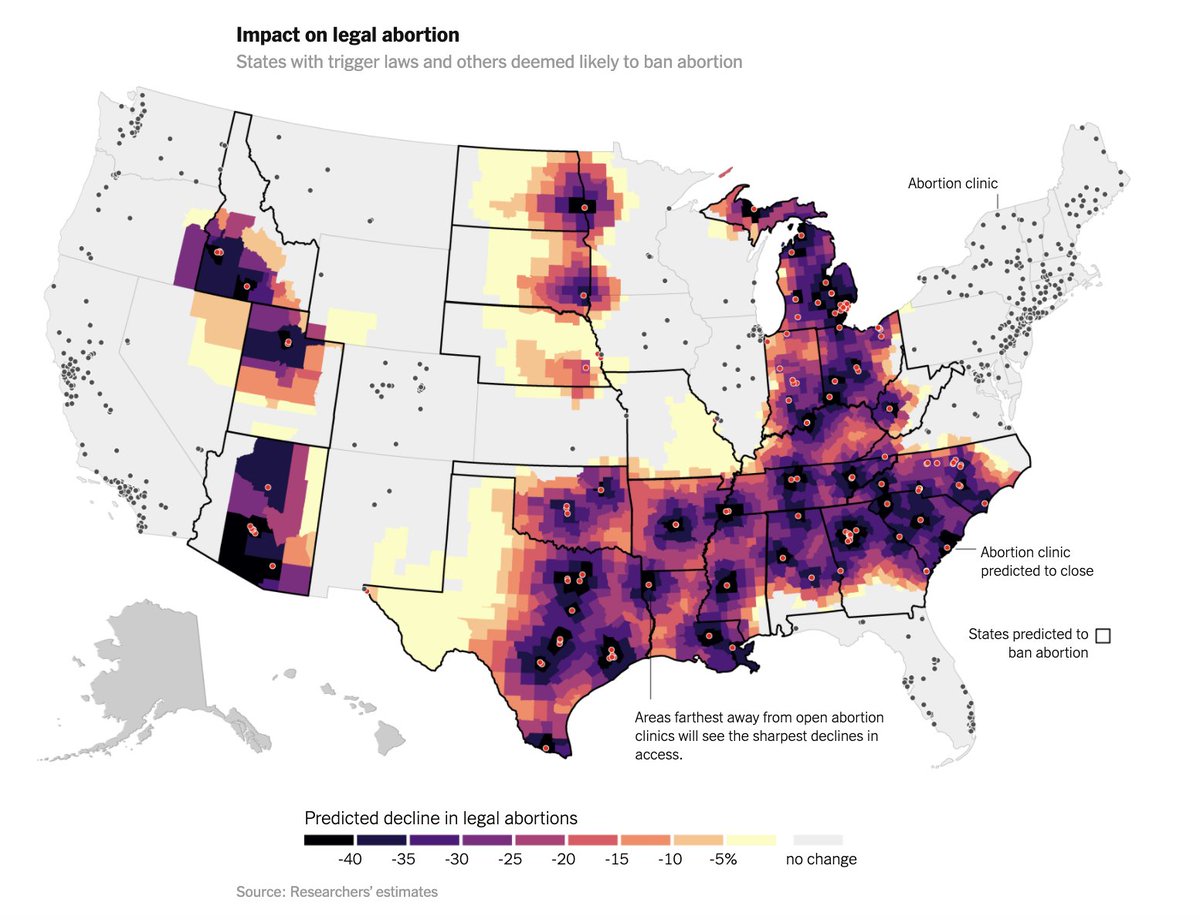
If states ban legal abortion, clinics will close. When clinics close, women have to travel further to out-of-state clinics. When women have to travel further, fewer of them end up having abortions. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/10/15/upshot/what-happens-if-roe-is-overturned.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
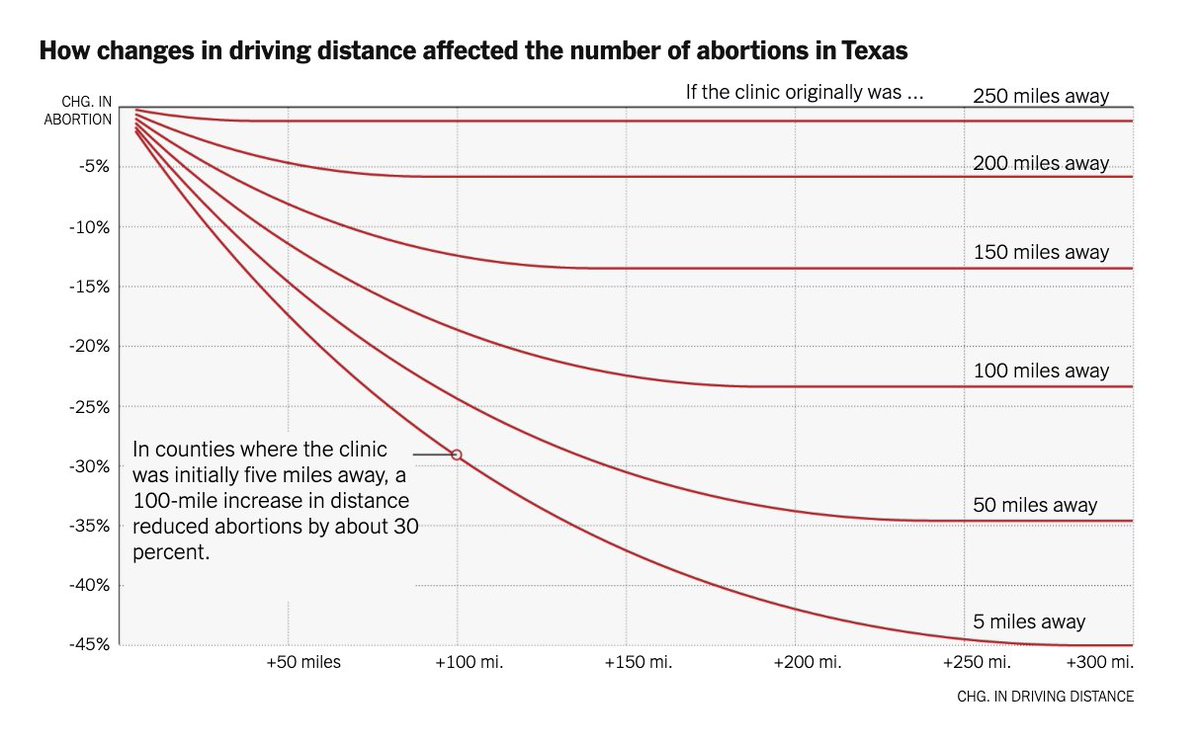
The calculations in our article are based on what happened when a Texas abortion law caused clinics there to close—and on an analysis of which states are most likely to restrict access to abortions if Roe is overturned. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/10/15/upshot/what-happens-if-roe-is-overturned.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
This article is an update of a previous story we wrote on this research. But has updated to take note of changes to clinic locations and state laws. Here’s the earlier piece: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2019/07/18/upshot/roe-v-wade-abortion-maps-planned-parenthood.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
Our story doesn& #39;t measure any abortions that may occur outside of legal clinics. But @clairecm took a look at the evidence that women are illicitly ordering pills to manage their own abortions now. This practice could expand in a post-Roe world. https://www.nytimes.com/2019/09/20/upshot/abortion-pills-rising-use.html">https://www.nytimes.com/2019/09/2...
Even without Roe, abortion access would be unchanged in many parts of the country. In some places, the distances to clinics are already hundreds of miles. In others, state legislatures are unlikely to pass new laws restricting abortion. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/10/15/upshot/what-happens-if-roe-is-overturned.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
Many thanks to @Caitlin_K_Myers and her colleagues for sharing this data with us.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter