Vitamin K & #COVID19:
Thrombosis is a major manifestation of COVID-19 that contributes to poor outcomes. Vitamin K plays a crucial role in the activation of both pro & anti-clotting factors in the liver, prevent elastic fiber degradation, possibly prevent comorbidities. THREAD
Thrombosis is a major manifestation of COVID-19 that contributes to poor outcomes. Vitamin K plays a crucial role in the activation of both pro & anti-clotting factors in the liver, prevent elastic fiber degradation, possibly prevent comorbidities. THREAD
1. Matrix Gla protein (MGP) is a vitamin K-dependent inhibitor of soft tissue calcification & elastic fiber degradation. Severe extrahepatic vitamin K insufficiency is recently demonstrated in COVID-19 pts, w/high inactive MGP levels correlating w/elastic fiber degradation rates.
MGP Protects against elastic fiber degradation that provides deformability to the lungs & arteries, which facilitates respiration & circulation. The balance between elastic fiber degradation & repair is of vital importance in cardiac & pulmonary health. https://www.nature.com/articles/386078a0">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
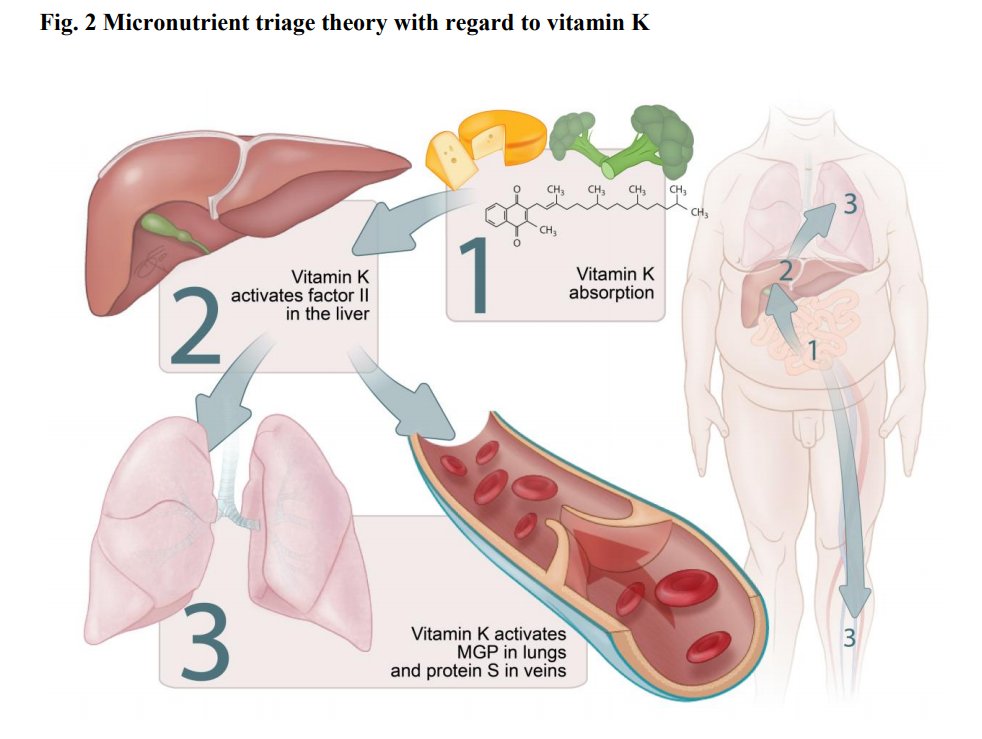
2. Endothelial protein S and Thrombosis: About 50% of anticoagulant protein S is produced outside the liver, in the endothelial cells. This protein has the ability to associate with the cell surface and promote procoagulant factor V. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2939094/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2939094/&...
3. Comorbidities and Desphospho-uncarboxylated MGP (dp-ucMGP): Extrahepatic vitamin K status is severely reduced in Covid-19 patients, reflected by elevated
dp-ucMGP levels. This elevation could be due to pre-infection Vitamin D deficiency or..(contd.)
https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202004.0457/v1">https://www.preprints.org/manuscrip...
dp-ucMGP levels. This elevation could be due to pre-infection Vitamin D deficiency or..(contd.)
https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202004.0457/v1">https://www.preprints.org/manuscrip...
dp-ucMGP levels are elevated in diseases that are associated with elastic fiber calcification & degradation such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, etc. It is possible that reduced vitamin K intake increases the risk of developing these conditions. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-54762-2">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
4. Interaction between vitamin D and K:
a. High-dose vitamin D administration in rats depletes extrahepatic vitamin K stores by strongly upregulating MGP synthesis leading to the acceleration of elastic fiber calcification and degradation. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11694617/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11694617/...
a. High-dose vitamin D administration in rats depletes extrahepatic vitamin K stores by strongly upregulating MGP synthesis leading to the acceleration of elastic fiber calcification and degradation. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11694617/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11694617/...
b. Vitamin D administration in a state of vitamin K deficiency may thereby endanger pulmonary and vascular health. Vitamin D supplementation was associated with premature mortality in vitamin K insufficient stable kidney transplant recipients. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30753729/ ">https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30753729/...
c. It& #39;s important to first supplement vitamin K in invariably vitamin K-insufficient COVID-19 hospitalized patients and to start vitamin D supplementation in those who are vitamin D-deficient only when extrahepatic vitamin K status has been restored.
5. Immunity & Inflammation: Vitamin K can act as an anti-inflammatory agent by suppressing nuclear factor κB (NFκB) signal transduction. It may also exert a protective effect against oxidative stress by blocking the generation of reactive oxygen species.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6747195/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6747195/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
6. Vitamin K1 and K2:
Half-life times of most K2 vitamins are longer than K1, and vitamin K2 may have more extrahepatic potential than K1.
Vitamin K1 - Green vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and kale.
Vitamin K2 - Cheese, curd, sauerkraut.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7353270/pdf/nutrients-12-01852.pdf">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
Half-life times of most K2 vitamins are longer than K1, and vitamin K2 may have more extrahepatic potential than K1.
Vitamin K1 - Green vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, and kale.
Vitamin K2 - Cheese, curd, sauerkraut.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7353270/pdf/nutrients-12-01852.pdf">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
7. Further reading: Vitamin D3 and K2 and their potential contribution to reducing the COVID-19 mortality rate by Dr. Simon Goddek. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7406600/">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/artic...
8. April 2020 study revealed Better vitamin K status in patients with COVID-19 has been linked to improved health outcomes, compared to patients with poor vitamin K status. https://www.nutritioninsight.com/news/study-links-better-vitamin-k-status-with-improved-covid-19-outcomes.html">https://www.nutritioninsight.com/news/stud...

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter