Breaking: HUGE MUTATION STUDY—Scientists in Houston just released a study of >5,000 genetic sequences of #SARSCoV2: continual accumulation of mutations, one of which maybe made more contagious—mutation is associated with a higher viral load among patients upon diagnosis. #COVID19
2) new report, however, did not find that these mutations have made the virus deadlier. All viruses accumulate genetic mutations, and most are insignificant, scientists say. Coronaviruses are relatively stable as viruses go, because they have a proofreading mechanism.
3) But every mutation is a roll of the dice. u2029“We have given this virus a lot of chances. There is a huge population size out there right now.”
4) “David Morens, a virologist at the NIAID, reviewed the new study and said the findings point to the strong possibility that the virus, as it has moved through the population, has become more transmissible, and that this “may have implications for our ability to control it.”
5) Morens noted that this is a single paper, and “you don’t want to over-interpret what this means.” But the virus, he said, could potentially be responding — through random mutations — to such interventions as mask-wearing and social distancing, Morens said Wednesday.
6) “Wearing masks, washing our hands, all those things are barriers to transmissibility, or contagion, but as the virus becomes more contagious it statistically is better at getting around those barriers,” said Morens, senior adviser to Anthony S. Fauci, the director of NIAID.
7) “Although we don’t know yet, it is well within the realm of possibility that this coronavirus, when our population-level immunity gets high enough, this coronavirus will find a way to get around our immunity. If that happened, we’d be in the same situation as with flu...
8) We’ll have to chase the virus and, as it mutates, we’ll have to tinker with our vaccine.”u2029At Houston Methodist, whose main hospital is part of the Texas Medical Center in central Houston. scientists have been sequencing the 30,000-character genome  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> since early March
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧬" title="DNA" aria-label="Emoji: DNA"> since early March
9) The research shows that the virus disseminated across Houston neighborhoods in two waves, first striking wealthier and older individuals but then spreading, in the second wave, to younger people and lower income neighborhoods — affecting many Latinos.
10) “genetic data show the virus arrived in Houston many times, presumably at first by air travel. Notably, 71% of the viruses that arrived initially were characterized by a now famous mutation that scientists increasingly suspect may give virus biological advantage in spreading.
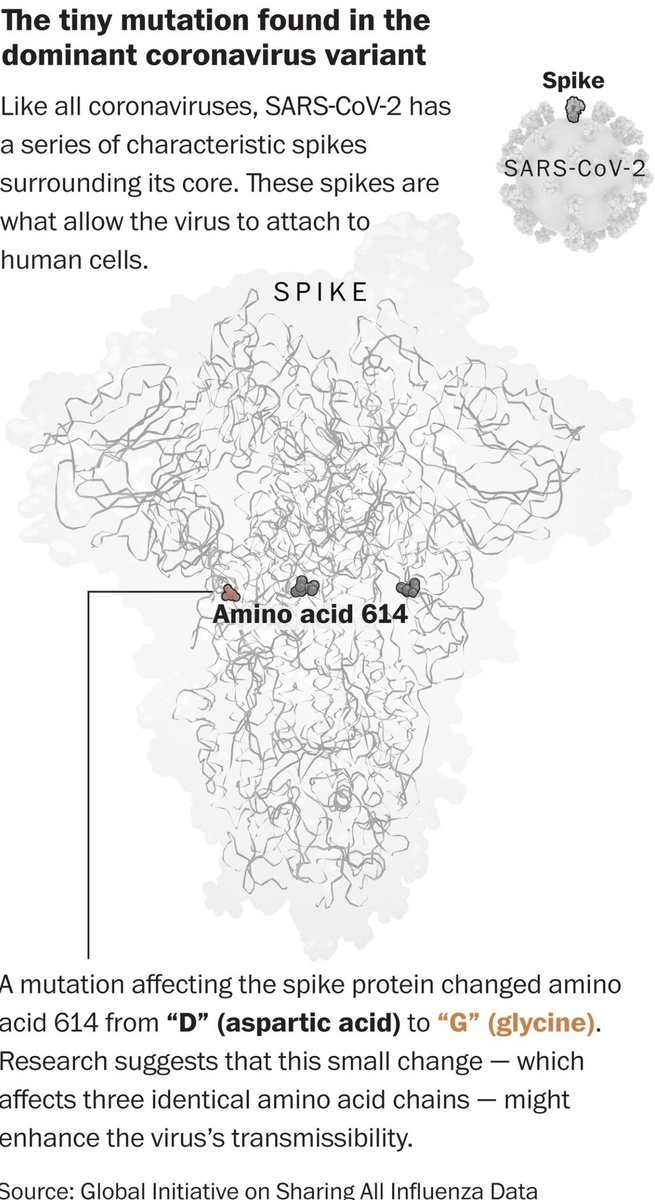
11) It is called D614G, referring to the substitution of an amino acid called aspartic acid (D) for one called glycine (G) in a region of the genome that encodes for the spike protein.u2029By 2nd wave of the outbreak, this variant had leaped to 99.9% prevalence —complete domination.
12) The researchers found that people infected with the strain had higher loads of virus in their upper respiratory tracts, a potential factor in making the strain spread more effectively.
13) Earlier report finds the D614G is more efficient. But not necessarily affects vaccine. Unclear https://twitter.com/DrEricDing/status/1301386722383663114">https://twitter.com/DrEricDin...
14) But there are many ways the now dominant strain could be better survivor overall which we have suspected since June. https://twitter.com/drericding/status/1277645902329634824">https://twitter.com/drericdin...
15) And here is the study showing the D614G yields a higher viral load (lower Ct value) https://twitter.com/drericding/status/1278727698521763840">https://twitter.com/drericdin...
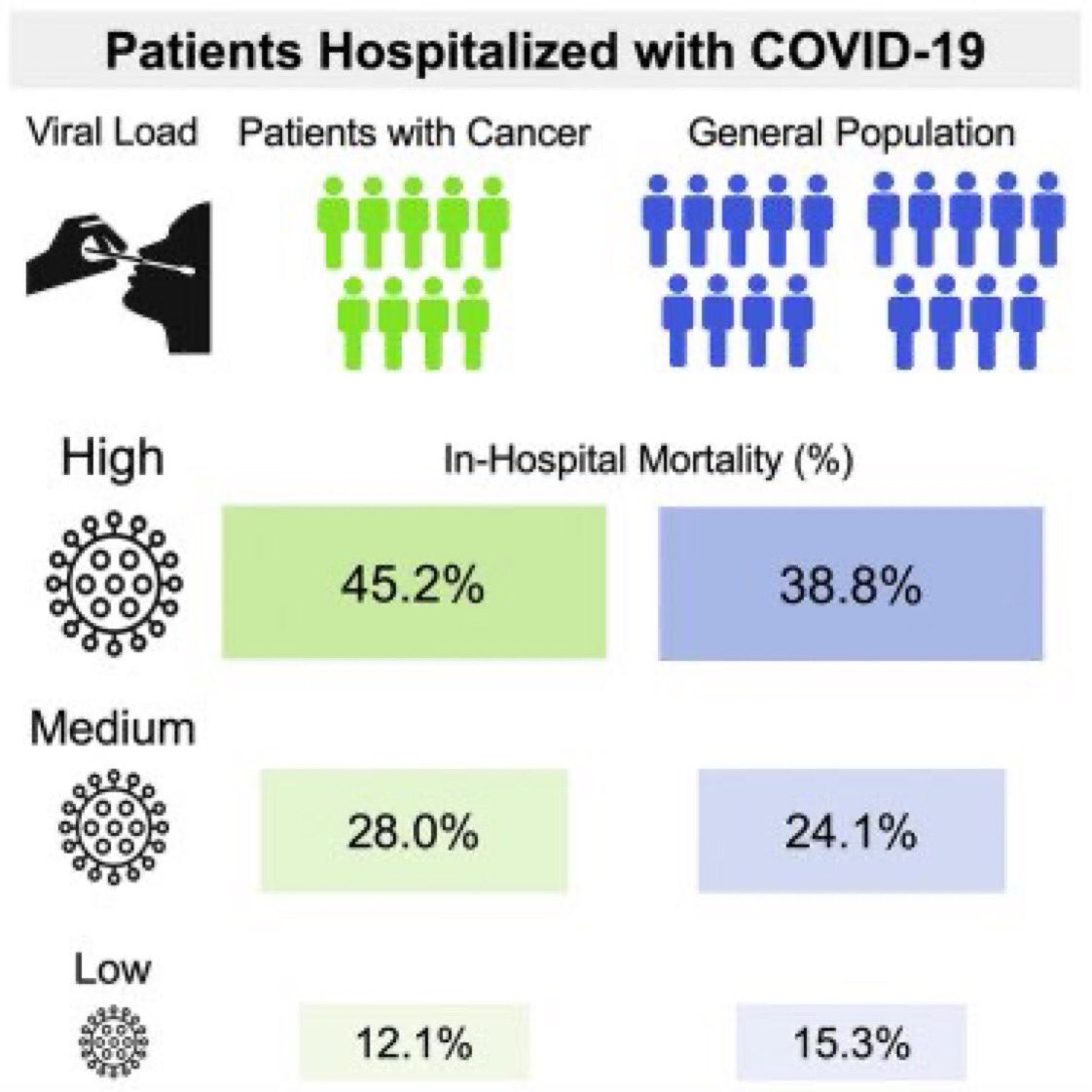
16) And viral load of #SARSCoV2 does affect mortality from #COVID19
What is high/medium/low? And higher load yields 2.5-3x higher mortality vs low.
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">High viral load = CT value <25
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">High viral load = CT value <25
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">medium viral load = CT value 25-30
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">medium viral load = CT value 25-30
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">low viral load = CT value>30
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">low viral load = CT value>30
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1535610820304815">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
What is high/medium/low? And higher load yields 2.5-3x higher mortality vs low.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1535610820304815">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
17) Caveat that the above study is not specifically comparing the new strain vs old. Just comparing high vs low viral loans and death from Covid. The D614G is not proven yet if it’s deadlier. It’s not so far; yet.
18) Bottomline though is D614G strain is now fully dominant in Houston area with 99.9% prevalence and it is likely more infectious (another study) may yield slightly high viral load (another study). And viral load in general maybe related to #COVID19 death risk (another study).

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter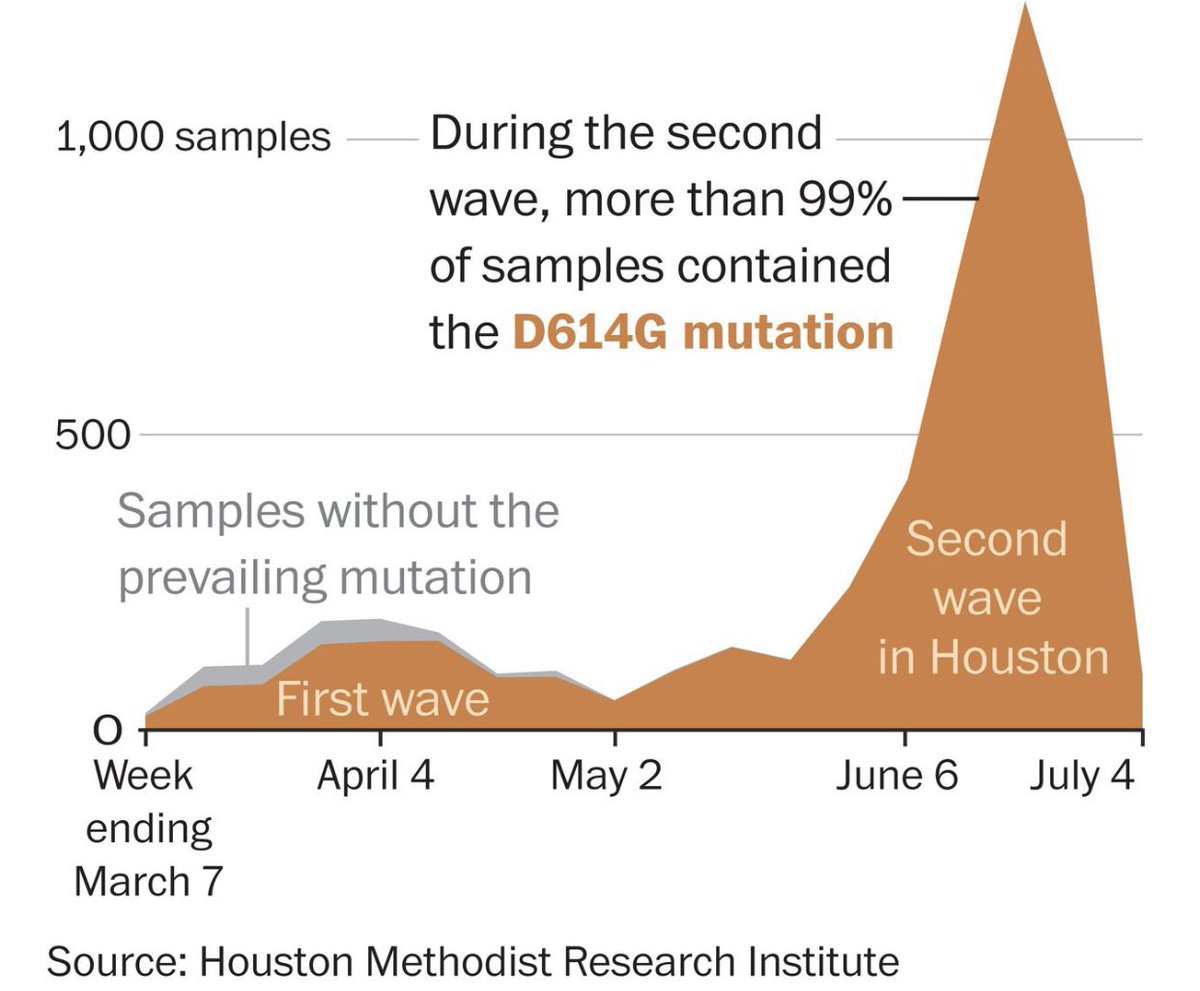
 High viral load = CT value <25https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">medium viral load = CT value 25-30https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">low viral load = CT value>30 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." title="16) And viral load of #SARSCoV2 does affect mortality from #COVID19 What is high/medium/low? And higher load yields 2.5-3x higher mortality vs low.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">High viral load = CT value <25https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">medium viral load = CT value 25-30https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">low viral load = CT value>30 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
High viral load = CT value <25https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">medium viral load = CT value 25-30https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">low viral load = CT value>30 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." title="16) And viral load of #SARSCoV2 does affect mortality from #COVID19 What is high/medium/low? And higher load yields 2.5-3x higher mortality vs low.https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">High viral load = CT value <25https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">medium viral load = CT value 25-30https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Reißzwecke" aria-label="Emoji: Reißzwecke">low viral load = CT value>30 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>


