Excited to share some new research hot off the press @FrontPsychiatry for my second #PhD paper. Here, we provide evidence that implicates Toxoplasma gondii and fox circovirus in the peculiar behaviour of wild UK red foxes with & #39;Dopey Fox Syndrome& #39;  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦊" title="Fuchsgesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Fuchsgesicht"> 1/n https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.513536/full?&utm_source=Email_to_authors_&utm_medium=Email&utm_content=T1_11.5e1_author&utm_campaign=Email_publication&field=&journalName=Frontiers_in_Psychiatry&id=513536">https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦊" title="Fuchsgesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Fuchsgesicht"> 1/n https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.513536/full?&utm_source=Email_to_authors_&utm_medium=Email&utm_content=T1_11.5e1_author&utm_campaign=Email_publication&field=&journalName=Frontiers_in_Psychiatry&id=513536">https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/...
Excellent work from @RoyalVetCollege vets & other collaborators ( @HarryJPeters, @CnpDr and co) and as always great supervision (& study design) @JoWebster_Group @DrMartinWalker. Huge thanks to National Fox Welfare Society and the Ginpat Trust for making this work possible. 2/n
What did we find? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑🔬" title="Scientist" aria-label="Emoji: Scientist">The prevalence of T. gondii, & of fox circovirus, was higher in neurologically-impaired & #39;Dopey& #39; foxes housed in UK sanctuaries than in culled wild foxes (presumably healthy). To see what DFS can look like, see this video
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧑🔬" title="Scientist" aria-label="Emoji: Scientist">The prevalence of T. gondii, & of fox circovirus, was higher in neurologically-impaired & #39;Dopey& #39; foxes housed in UK sanctuaries than in culled wild foxes (presumably healthy). To see what DFS can look like, see this video  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten"> 3/n https://www.facebook.com/kingfisherwildlifesanctuary/videos/2728067420551492">https://www.facebook.com/kingfishe...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten"> 3/n https://www.facebook.com/kingfisherwildlifesanctuary/videos/2728067420551492">https://www.facebook.com/kingfishe...
Although we had limited power due to small sample sizes, co-infections of T. gondi–fox circovirus were also more prevalent in sanctuary foxes. 4/n
Our paper hence provides preliminary support for a multi-infectious agent model of neurological disease causation. Similarly, in humans, mind-altering conditions like schizophrenia can be caused by a variety of different infectious agents  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> 5/n https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128009819000146">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Gehirn" aria-label="Emoji: Gehirn"> 5/n https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128009819000146">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
Microscopic examination of amygdala and nucleus accumbens brain regions more frequently revealed histological signs of inflammation in DFS foxes than wild culled foxes  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔬" title="Mikroskop" aria-label="Emoji: Mikroskop"> These regions have roles in fear responses, motivation & pleasure, & T. gondii-altered behaviour
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🔬" title="Mikroskop" aria-label="Emoji: Mikroskop"> These regions have roles in fear responses, motivation & pleasure, & T. gondii-altered behaviour  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😨" title="Angstvolles Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Angstvolles Gesicht">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😨" title="Angstvolles Gesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Angstvolles Gesicht"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🐈⬛" title="Black cat" aria-label="Emoji: Black cat">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🐈⬛" title="Black cat" aria-label="Emoji: Black cat"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🐀" title="Ratte" aria-label="Emoji: Ratte"> 6/n
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🐀" title="Ratte" aria-label="Emoji: Ratte"> 6/n
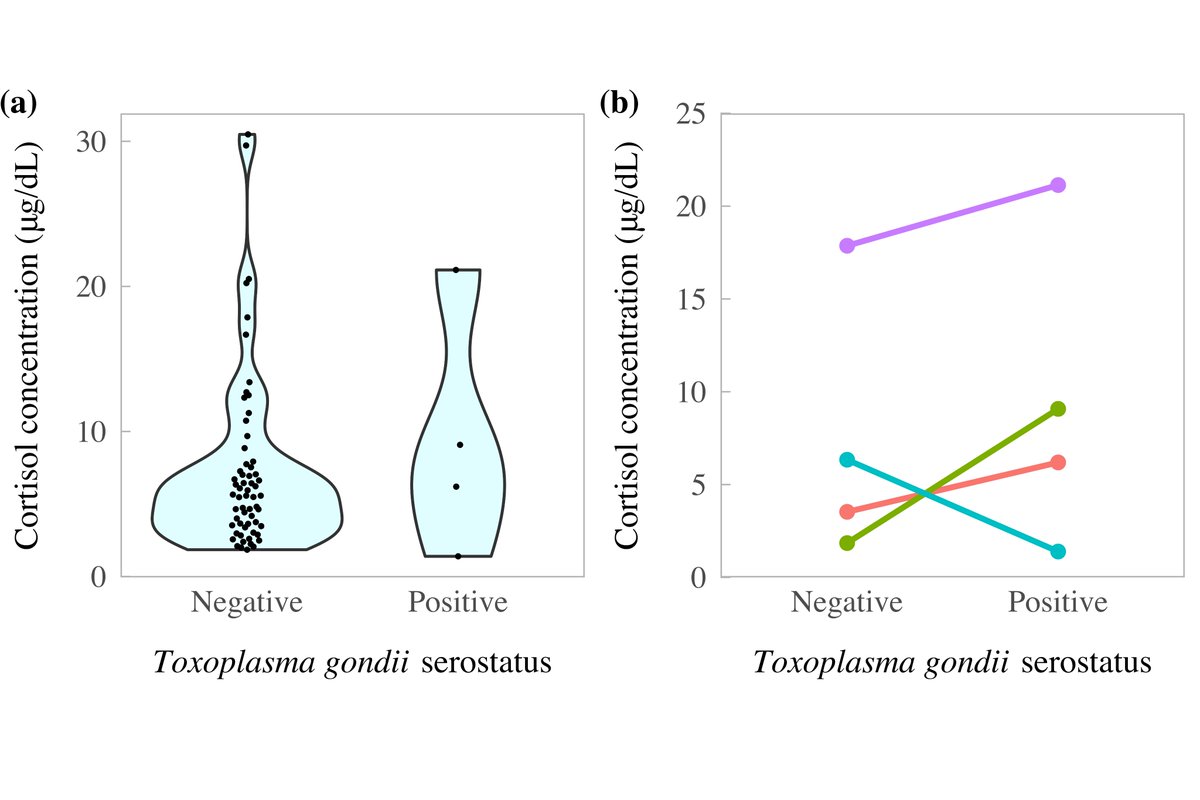
While we expected that infection might stress our furry fox friends, our #cortisol experiments (with excellent work from @HarryJPeters & @CnpDr) showed little difference between T. gondii infected and uninfected foxes. Plot a) shows all foxes, & b) pairs of matched foxes. 7/n
Now some behaviour results  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦊" title="Fuchsgesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Fuchsgesicht"> (but first some background for important context)....8/n
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦊" title="Fuchsgesicht" aria-label="Emoji: Fuchsgesicht"> (but first some background for important context)....8/n
T. gondii infection is known to make rats become attracted to cat urine (coined fatal feline attraction). This behaviour manipulation might increase the efficiency of parasite transmission from intermediate host (rat) -> definitive host (cat)  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😼" title="Katzengesicht mit ironischem Lächeln" aria-label="Emoji: Katzengesicht mit ironischem Lächeln"> 9/n
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😼" title="Katzengesicht mit ironischem Lächeln" aria-label="Emoji: Katzengesicht mit ironischem Lächeln"> 9/n
T. gondii infected men also rate the odour of cat urine as more pleasant than their uninfected counterparts (though gender-dependent effects exist; see the article below  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">). 10/n https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0001389">https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">). 10/n https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0001389">https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/...
Now back to our study...
We provide the first evidence that T. gondii infected foxes are similarly attracted to feline odour. In (previously validated) behaviour assays infected foxes (n=6) consistently visited cat urine odour "zones" more times than dog urine "zones". 11/n
We provide the first evidence that T. gondii infected foxes are similarly attracted to feline odour. In (previously validated) behaviour assays infected foxes (n=6) consistently visited cat urine odour "zones" more times than dog urine "zones". 11/n
As well as providing additional insight into T. gondii& #39;s broad host effects, our study brings forth new Qs regarding how neurological disease onset & maintenance is controlled – & more general Qs re infectious causation of a variety of mental disorders in vertebrate hosts. n/n

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter