(1/13) Please RT: our first #tweetorial!
Here& #39;s a https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread">on our new paper which is also my 1st time being (joint) last author
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread">on our new paper which is also my 1st time being (joint) last author https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✍️" title="Schreibende Hand" aria-label="Emoji: Schreibende Hand">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="✍️" title="Schreibende Hand" aria-label="Emoji: Schreibende Hand">
Congrats to all, especially superstar med student @LuszczakSabina!
#AcademicTwitter @AcademicChatter @OpenAcademics #womeninSTEM https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
Here& #39;s a
Congrats to all, especially superstar med student @LuszczakSabina!
#AcademicTwitter @AcademicChatter @OpenAcademics #womeninSTEM https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
(2/13) In #prostatecancer cell lines & human tissue, co-targeting #PIM & #PI3K #kinases seems promising!
We reckon ~20% of prostate cancer patients could benefit from this approach in future & these tend to be the sicker patients.
Scroll for #science! https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
We reckon ~20% of prostate cancer patients could benefit from this approach in future & these tend to be the sicker patients.
Scroll for #science! https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
(3/13) Fig1a:
From publicly available data we see that some patients overexpress either the #PIM pathway, the #PI3K pathway, or both. Each of these targets have inhibitors in development, that could theoretically be of benefit to any of these patient groups when combined https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤞" title="Crossed fingers" aria-label="Emoji: Crossed fingers">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤞" title="Crossed fingers" aria-label="Emoji: Crossed fingers">
From publicly available data we see that some patients overexpress either the #PIM pathway, the #PI3K pathway, or both. Each of these targets have inhibitors in development, that could theoretically be of benefit to any of these patient groups when combined
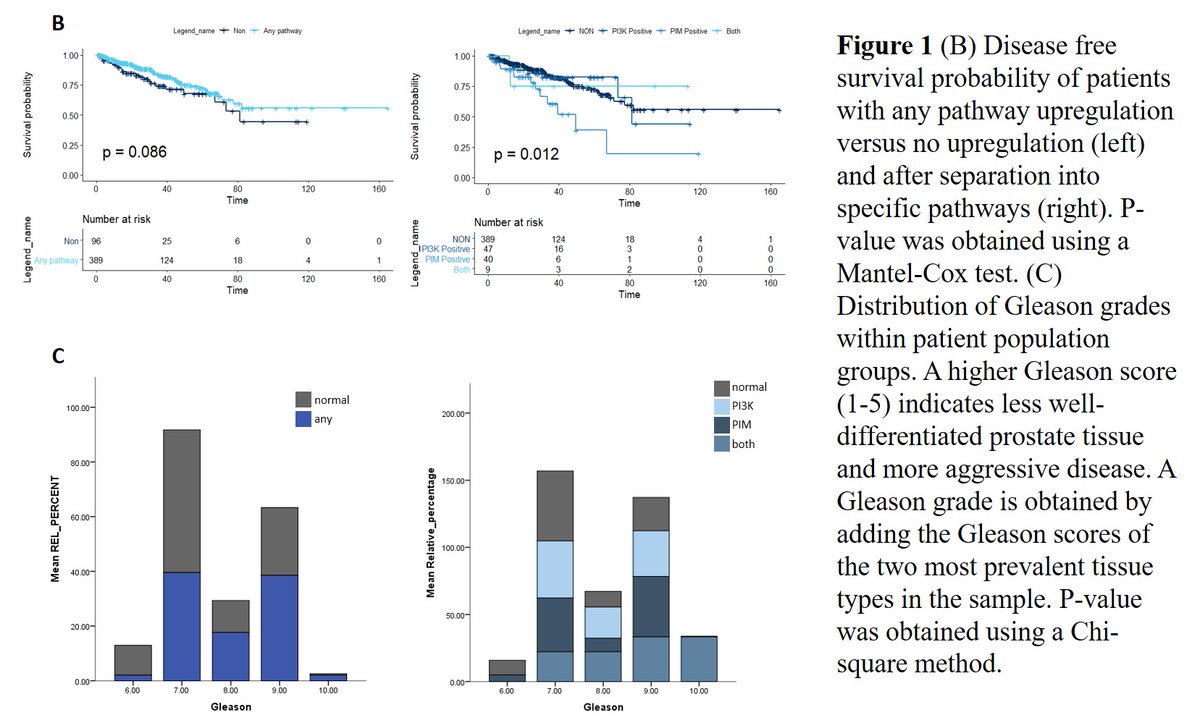
(4/13) Fig1b+c:
These patients who could hopefully benefit from this co-targeted approach also happen to tend to be sicker (higher Gleason, lower survival) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏥" title="Krankenhaus" aria-label="Emoji: Krankenhaus">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏥" title="Krankenhaus" aria-label="Emoji: Krankenhaus">
These patients who could hopefully benefit from this co-targeted approach also happen to tend to be sicker (higher Gleason, lower survival)
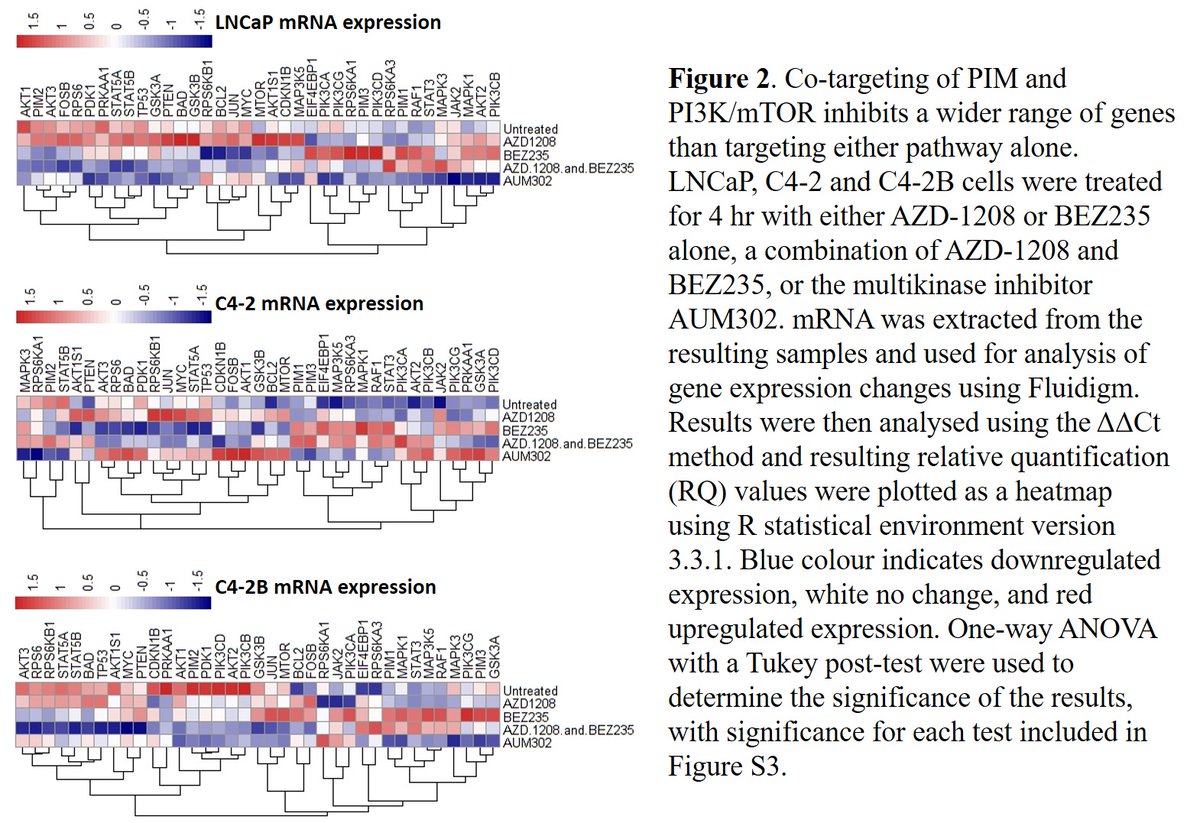
(5/13) Fig2:
At the RNA level in 3 #prostatecancer cell lines, inhibition of #PIM/ #PI3K lead to decreased expression of a range of downstream genes, & co-targeted inhibition of both pathways lead to decreased expression of a wider range of #genes, as you might expect!
At the RNA level in 3 #prostatecancer cell lines, inhibition of #PIM/ #PI3K lead to decreased expression of a range of downstream genes, & co-targeted inhibition of both pathways lead to decreased expression of a wider range of #genes, as you might expect!
(6/13) Fig3: At the phospho-protein level, we see similar trends, with the co-targeted approach yielding the most striking inhibition, particularly in the most aggressive cell line (C4-2B) - this was encouraging https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👍" title="Thumbs up" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs up">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👍" title="Thumbs up" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs up">
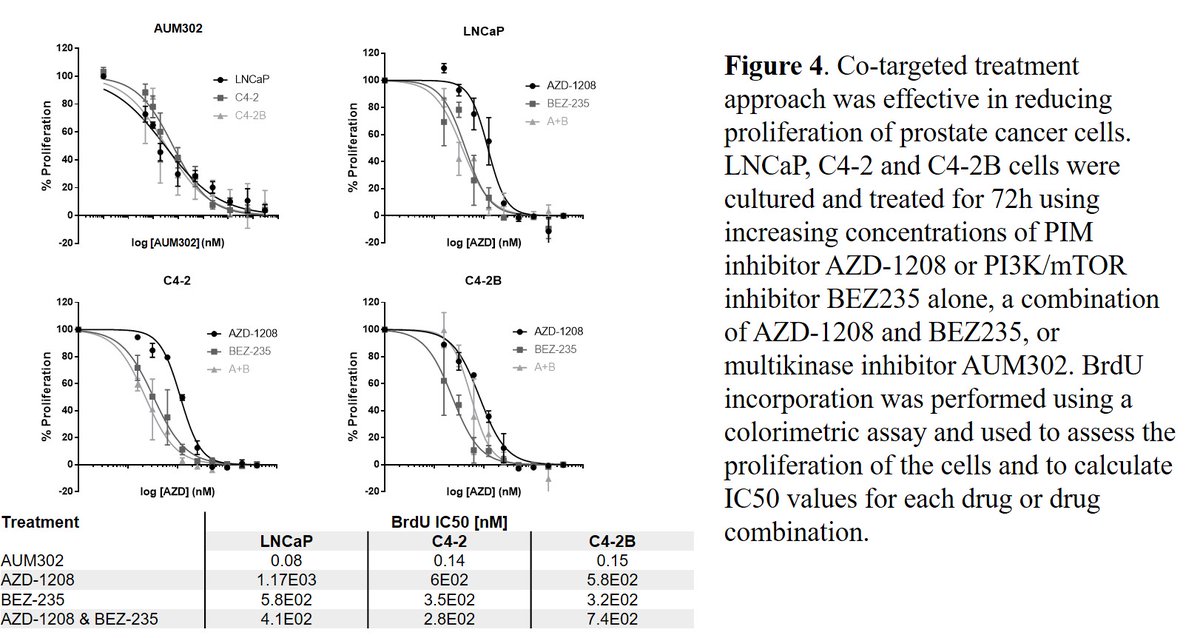
(7/13) Fig4: All the inhibitors lead to dose-dependent reductions in proliferation in all cell lines, with the lowest IC50s coming from the triple kinase inhibitor #AUM302, in the nM range.
Nice drug! Thanks: @AumBiosciences @InflectionBio @CNIOStopCancer #drugdevelopment
Nice drug! Thanks: @AumBiosciences @InflectionBio @CNIOStopCancer #drugdevelopment
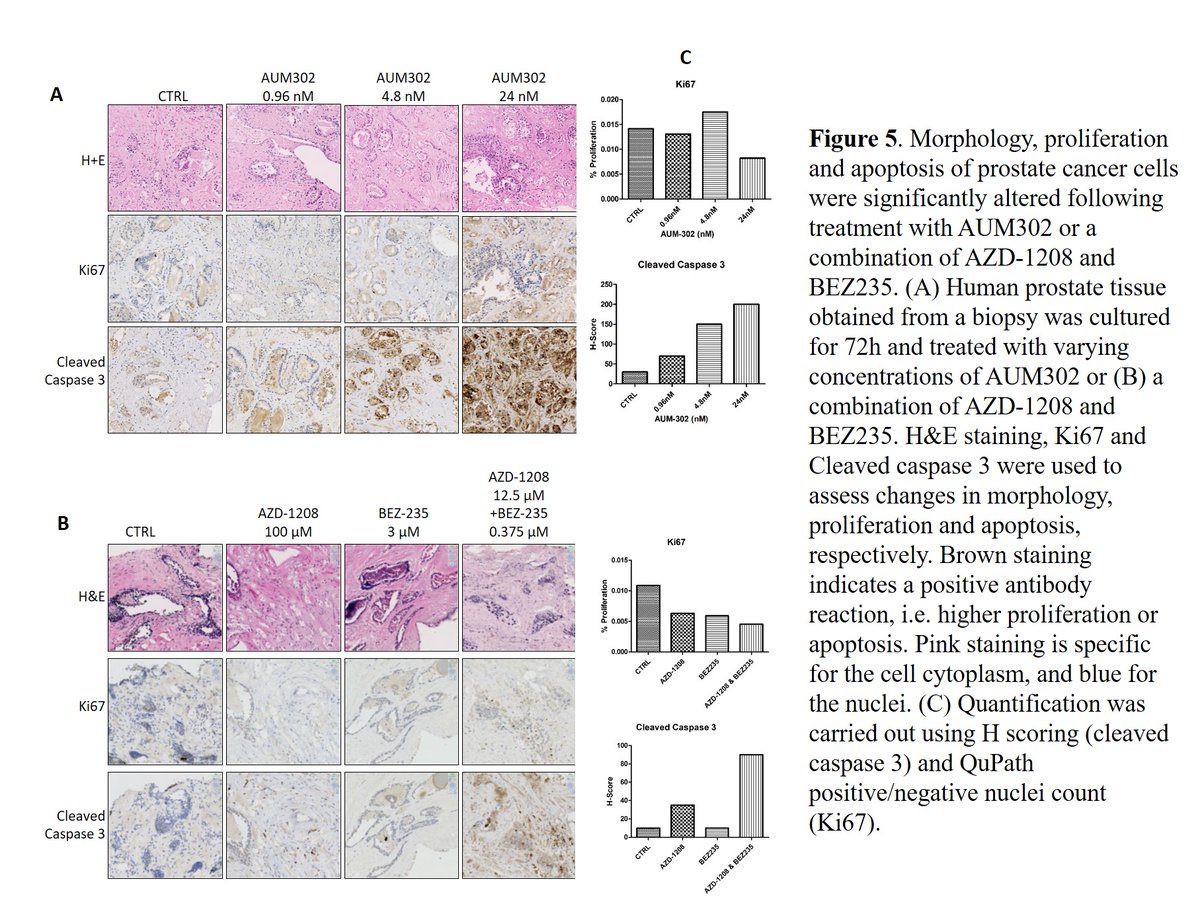
(8/13) Fig5: In human #exvivo cultures, we see the same story, with improved inhibition of proliferation & induction of apoptosis when we co-target both pathways. Note the conc differences!
This fig is a taster of the work to be expanded on in my new lab #comingsoon #heaveylab
This fig is a taster of the work to be expanded on in my new lab #comingsoon #heaveylab
(9/13) limitations: the ex vivo work is only in a few patients, we may have been lucky & we can’t assume this would work so well for everyone – probably only around a fifth will respond like this. Or maybe more… only one way to find out!
(10/13) Next steps: @ProstateUK @MovemberUK have funded us to expand this cohort substantially & carry out detailed molecular work. Much of the collection & culture has already happened, with thanks to @UCLpathology @uclhrobotics
https://prostatecanceruk.org/research/research-we-fund/tld-pf16-004">https://prostatecanceruk.org/research/... #fellowship #womeninSTEM
https://prostatecanceruk.org/research/research-we-fund/tld-pf16-004">https://prostatecanceruk.org/research/... #fellowship #womeninSTEM
(11/13) Acknowledgements [part 1] for the work above!
Big thanks to the authors including these tweeters -follow them! @LuszczakSabina @HayleyWhitaker @kathygately1 @b3nsimp @hayleyjeanpye @linamacarmona @aimhaider @acesridhar @greglshaw @TheWhitakerlab https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
Big thanks to the authors including these tweeters -follow them! @LuszczakSabina @HayleyWhitaker @kathygately1 @b3nsimp @hayleyjeanpye @linamacarmona @aimhaider @acesridhar @greglshaw @TheWhitakerlab https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
(12/13) Acknowledgements [part 2] for the work above!
Many thanks for supporting this work:
Collab: @InflectionBio @AumBiosciences
Journal: @SciReports @SpringerNature
Funders: @ProstateUK @MovemberUK
Hosts: @UCLDivofSurgery @UCL @UCLpathology @uclhrobotics https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
Many thanks for supporting this work:
Collab: @InflectionBio @AumBiosciences
Journal: @SciReports @SpringerNature
Funders: @ProstateUK @MovemberUK
Hosts: @UCLDivofSurgery @UCL @UCLpathology @uclhrobotics https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
(13/13) Now we party?  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥳" title="Partying face" aria-label="Emoji: Partying face">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🥳" title="Partying face" aria-label="Emoji: Partying face"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙌" title="Raising hands" aria-label="Emoji: Raising hands">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙌" title="Raising hands" aria-label="Emoji: Raising hands"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎊" title="Konfettiball" aria-label="Emoji: Konfettiball">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎊" title="Konfettiball" aria-label="Emoji: Konfettiball"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎏" title="Karpfen" aria-label="Emoji: Karpfen">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🎏" title="Karpfen" aria-label="Emoji: Karpfen">
( https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">please imagine them 2m apart
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Pfeil nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Pfeil nach unten">please imagine them 2m apart  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😷" title="Gesicht mit Mundschutz" aria-label="Emoji: Gesicht mit Mundschutz">)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😷" title="Gesicht mit Mundschutz" aria-label="Emoji: Gesicht mit Mundschutz">)
#publication #AcademicChatter #AcademicTwitter #WomeninSTEM #scicomm
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
(
#publication #AcademicChatter #AcademicTwitter #WomeninSTEM #scicomm
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-71263-9">https://www.nature.com/articles/...

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter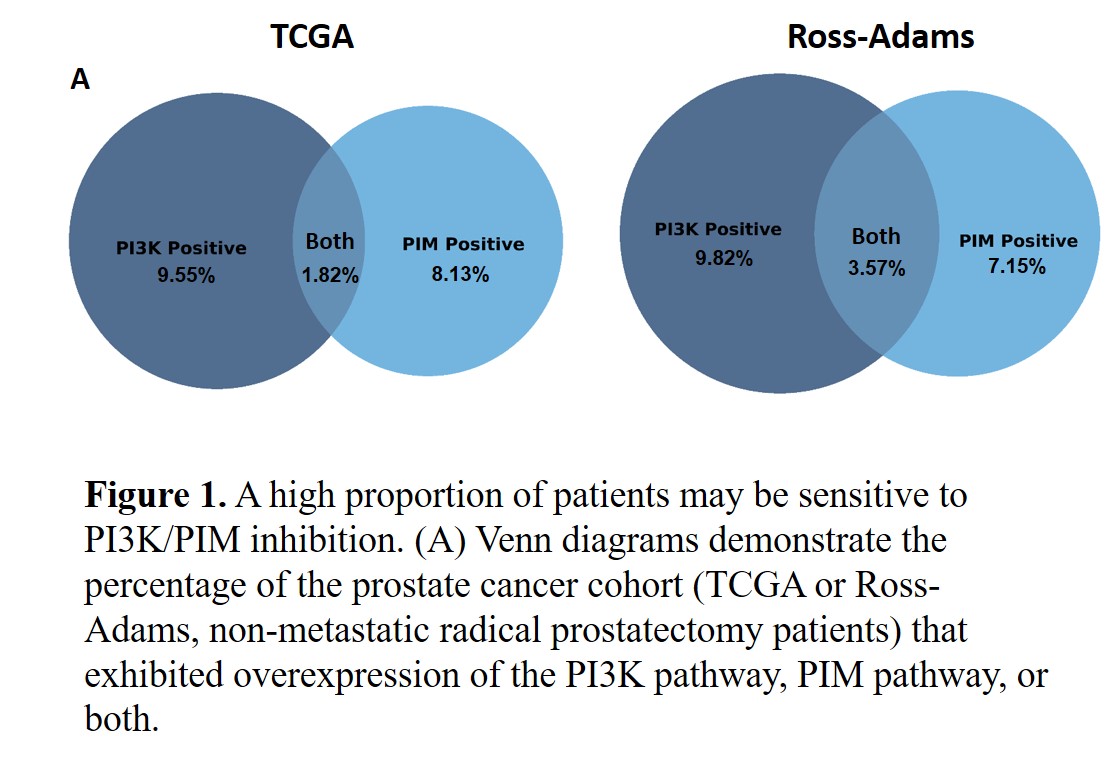 " title="(3/13) Fig1a: From publicly available data we see that some patients overexpress either the #PIM pathway, the #PI3K pathway, or both. Each of these targets have inhibitors in development, that could theoretically be of benefit to any of these patient groups when combined https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤞" title="Crossed fingers" aria-label="Emoji: Crossed fingers">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
" title="(3/13) Fig1a: From publicly available data we see that some patients overexpress either the #PIM pathway, the #PI3K pathway, or both. Each of these targets have inhibitors in development, that could theoretically be of benefit to any of these patient groups when combined https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤞" title="Crossed fingers" aria-label="Emoji: Crossed fingers">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 " title="(4/13) Fig1b+c:These patients who could hopefully benefit from this co-targeted approach also happen to tend to be sicker (higher Gleason, lower survival) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏥" title="Krankenhaus" aria-label="Emoji: Krankenhaus">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
" title="(4/13) Fig1b+c:These patients who could hopefully benefit from this co-targeted approach also happen to tend to be sicker (higher Gleason, lower survival) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏥" title="Krankenhaus" aria-label="Emoji: Krankenhaus">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
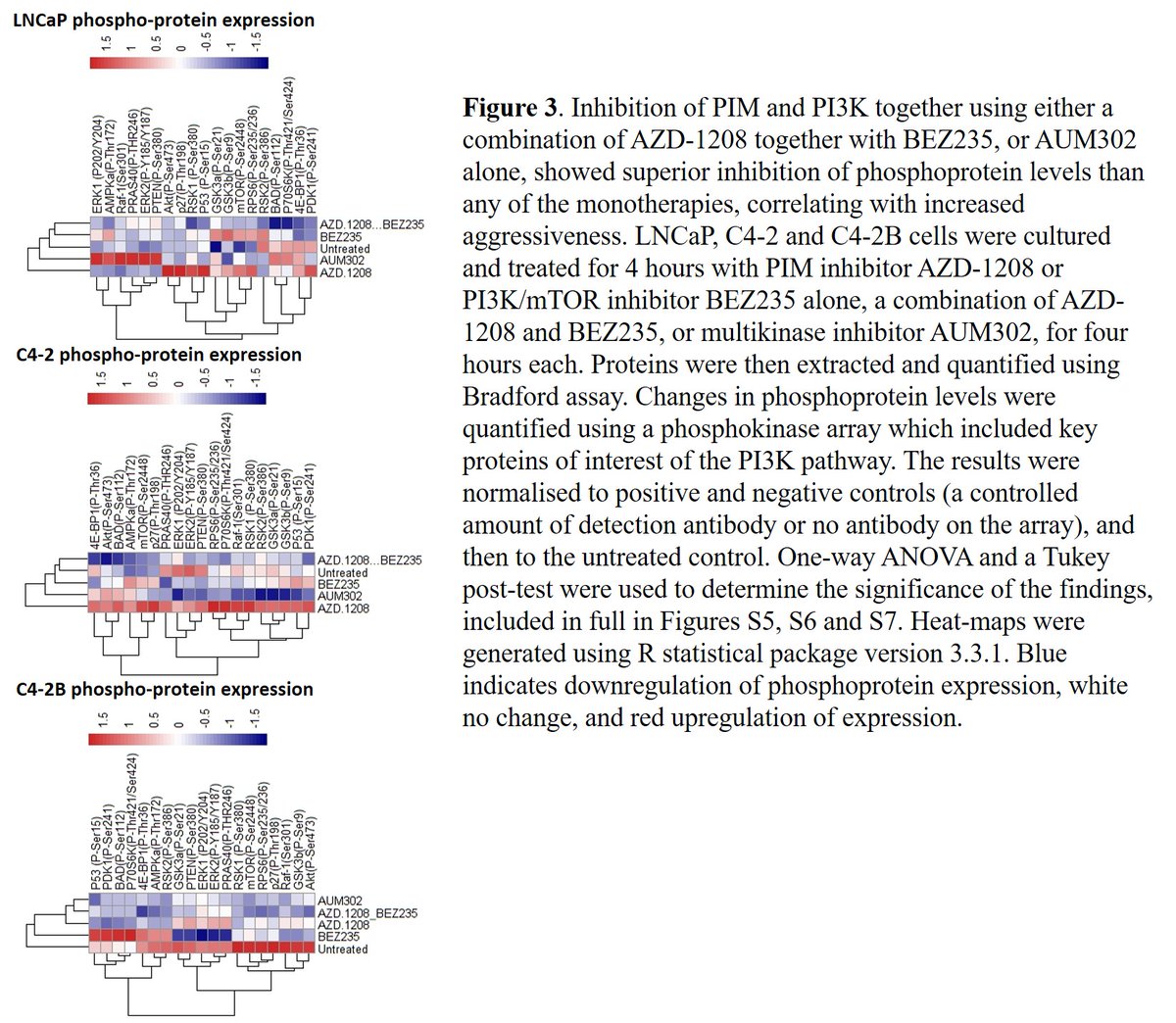 " title="(6/13) Fig3: At the phospho-protein level, we see similar trends, with the co-targeted approach yielding the most striking inhibition, particularly in the most aggressive cell line (C4-2B) - this was encouraginghttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👍" title="Thumbs up" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs up">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
" title="(6/13) Fig3: At the phospho-protein level, we see similar trends, with the co-targeted approach yielding the most striking inhibition, particularly in the most aggressive cell line (C4-2B) - this was encouraginghttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👍" title="Thumbs up" aria-label="Emoji: Thumbs up">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>