THREAD: Does methane from cattle have the same warming impact as methane from fossil fuels? The answer is NO, but that’s the popular belief. Through science we will #rethinkmethane AND help curb the climate crisis. 1/
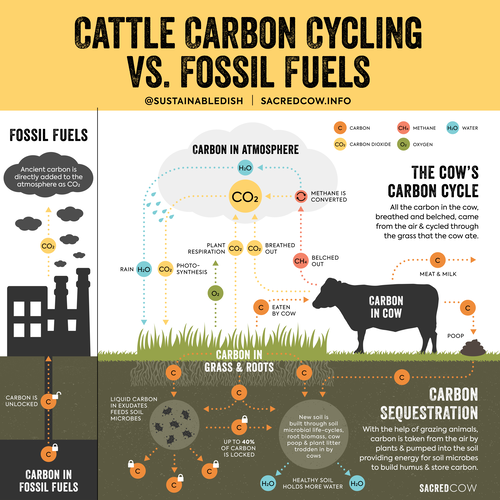
Biogenic & fossil methane originate from different sources. Biogenic methane starts as atmospheric CO2 before it’s been emitted by sources such as livestock. Fossil methane is geological carbon pulled from deep in the earth, where it’s been stored for millions of yrs. 2/
The @mfe_news provides a concise, accurate description of how biogenic methane & fossil methane behave differently. This distinction is key when discussing solutions to climate change. http://bit.ly/2DwFMvP ">https://bit.ly/2DwFMvP&q... 3/
If you take away one thing from the difference between the two types of methane, it should be: Biogenic methane is derived from carbon that’s ALREADY in the atmosphere in the form of CO2 and it is part of a short time cycle. 4/
At first glance, it may seem biogenic & fossil methane are the exact same. And chemically, they are the exact same. Methane is methane. But the two types of methane have different warming behaviors over their life-cycle b/c of where they originate from & what they become. 5/
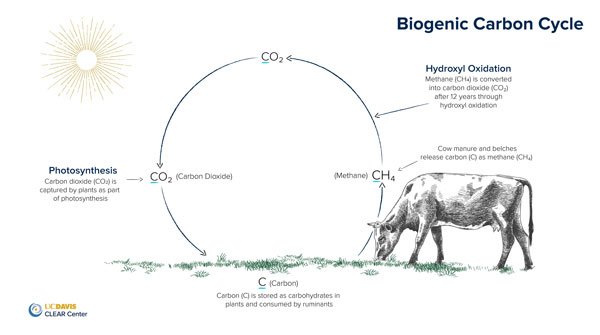
Methane is 28x more potent than CO2. But, over a short period of time – about 10 years – that methane decays into the atmospheric pool of CO2. Biogenic methane is different than fossil carbon in that it is part of the biogenic carbon cycle. 6/
During photosynthesis, plants draw CO2 from that atmospheric pool & convert carbon into carbohydrates, which cattle eat. They release some carbon as methane, which is then converted into CO2 and recycled back into the atmosphere. Again, it’s recycled. 7/
You can learn more about the biogenic carbon cycle in detail in this thread by the @UCDavisCLEAR: https://twitter.com/UCDavisCLEAR/status/1281021504524660739">https://twitter.com/UCDavisCL... 8/
Unlike biogenic methane, fossil methane is not recycled. Once released from under the earth, it produces new/additional carbon after oxidation & hence, new/additional warming to the atmosphere. 9/
Because fossil CO2 builds up the atmosphere at an alarmingly fast rate (remember, methane eventually converts into CO2), earth’s natural carbon sinks – the ocean, soils & plants – get overwhelmed. They can only sequester so much carbon.
https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainers/what-carbon-sequestration">https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainer... 10/
https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainers/what-carbon-sequestration">https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainer... 10/
Fossil CO2 stockpiles in the atmosphere, thus making it a stock gas. Biogenic methane flows through a cycle & is produced & destroyed at almost equal rates, making it a flow gas: https://clear.ucdavis.edu/news/greenhouse-gas-emissions-what-difference-between-stock-and-flow-gases">https://clear.ucdavis.edu/news/gree... 11/
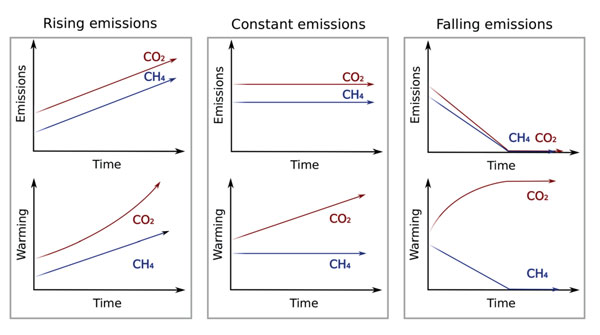
I want to make it clear: Regardless of the source, all methane causes warming. But if emissions of biogenic methane equal what’s being destroyed in the atmosphere, it doesn’t need to add MORE warming to the atmosphere, since there isn’t additional carbon being added. 12/
It’s best to keep fossil sourced methane underground where it& #39;s been for millions of years, to keep it from causing irreversible warming damage to the earth. And biogenic methane? It can actually help mitigate climate change. 13/
How? Well, if cattle herds stay constant, they don’t contribute additional methane & therefore, warming to the atmosphere, right? So, if livestock emissions are reduced, this can actually induce COOLING! Here’s more on this: https://twitter.com/GHGGuru/status/1269276499795783680?s=20">https://twitter.com/GHGGuru/s... 14/
This IS achievable. In California, dairy farmers have recently reduced methane by 25%: https://twitter.com/UCDavisCLEAR/status/1265329543444721664?s=20">https://twitter.com/UCDavisCL... 15/
I encourage you to be an ambassador for change. You can start by sharing this  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> using the hashtag: #rethinkmethane & rally others to do the same. Follow @UCDavisCLEAR (Facebook as well) for science-backed info. The CLEAR website is a great resource: http://clear.ucdavis.edu/ ">https://clear.ucdavis.edu/">... 16/
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> using the hashtag: #rethinkmethane & rally others to do the same. Follow @UCDavisCLEAR (Facebook as well) for science-backed info. The CLEAR website is a great resource: http://clear.ucdavis.edu/ ">https://clear.ucdavis.edu/">... 16/
Here’s a full explainer on the difference between methane from cattle & CO2 from fossil fuels: https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainers/why-methane-cattle-warms-climate-differently-co2-fossil-fuels">https://clear.ucdavis.edu/explainer... 17/
And here’s the CLEAR Center’s video, Rethinking Methane:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UOPrF8oyDYw">https://www.youtube.com/watch... 18/18
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UOPrF8oyDYw">https://www.youtube.com/watch... 18/18

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter