#JoburgIDP20 comments, BE HEARD. This is a platform for you to raise concerns and propose solutions that could benefit you and your community at large. Share your ideas, use feedback link https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉🏿" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉🏿" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉🏿" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)"> https://share.hsforms.com/1puiRfx1FSO606r27262qHA469tl">https://share.hsforms.com/1puiRfx1F... ^PS
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👉🏿" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach rechts (dunkler Hautton)"> https://share.hsforms.com/1puiRfx1FSO606r27262qHA469tl">https://share.hsforms.com/1puiRfx1F... ^PS
Fighting poverty, unemployment and inequality is a complex matter and important for the City to adopt a developmental paradigm, which is articulated in the GDS 2040. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Johannesburg, like its counterparts elsewhere in the country, also has to overcome significant developmental challenges, with emphasis needing to be placed on improving sustainability without necessary increasing resource consumption. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City’s IDP is translated into desired outcomes through development of medium-term programmes for implementation. On an annual basis,IDP is reviewed and business plans are developed by the Departments & Municipal Entities, detailing short term operational plans. #JoburgIDP20^PS
These are linked to annual budgets and the City’s annual Service Delivery and Budget Implementation Plan (SDBIP). The City’s long and medium term strategies (GDS and IDP) recognizes the importance of conserving natural resources. #JoburgIDP20^PS
Natural resources are materials found in nature which can be used or processed by man for sustaining human life.These resources cannot be created; however they can be modified and used accordingly (consumption of natural resources). #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
There are two types of natural resources:  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
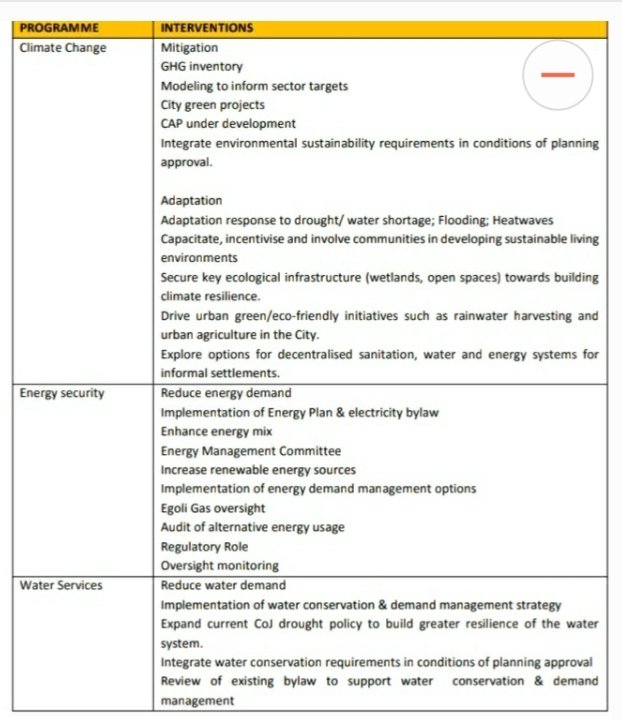
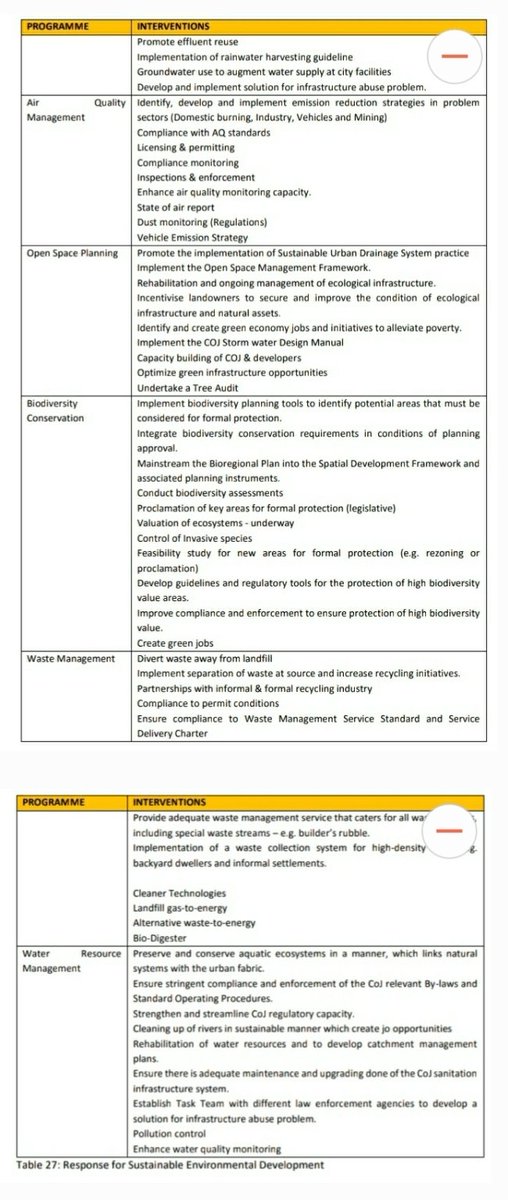
The figure below provides an overview of the various programmes relating to the Government of Local Unity Priority on Sustainable Environmental Development. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The context for Sustainable Environmental Development takes into cognisance that economic growth is strongly interrelated with the demand for these resources be it as - water, energy & ecological goods & services -with consequent generation of waste(solid,gas, liquid-pollution).
Globally, human activities are depleting our natural “capital” and the long-term capacity of our ecosystems to sustain future generations. As non-renewable resources become scarcer, their supply will become less reliable and the associated price will increase. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
If the City is able to do more with fewer non-renewable resources, it will be better prepared for the future decline in resources – in contrast with cities that are resource-driven. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Johannesburg therefore like its counterparts elsewhere in the country, still has to overcome significant developmental challenges, with emphasis needing to be placed on improving equity and sustainability without necessary increasing resource consumption. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Strategic response for sustainable environmental development, several interventions are listed below, which highlights the overall programmes & related interventions to respond to the challenges mentioned above. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Globally, a ‘Smart City’ approach is most commonly defined as a city that uses Information and Communication Technology (ICT) as an enabler. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
This type of Smart City focuses on the use of Internet of Things, robotics,block chain,artificial intelligence, machine learning, serious gamification,& automated data collection to play a significant role in delivering efficient & effective services to the citizens. #JoburgIDP20
This Smart City is a municipality where smart meters & energy saving systems manage buildings,cognitive analytics & machine learning algorithms manage multiple modes of transportation,robots & drones provide security, build data & manage infrastructure assets. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The alternative globally accepted approach to a Smart City is one that creates an innovation ecosystem where technology is leveraged to improve the relationship between citizens and their government. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It enables social innovation, not merely technological innovation, to improve the quality of life in a City. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
This Smart City is a municipality where citizens collaborate with local government to improve service delivery, design their community, and co-create solutions to improve their quality of life through an innovation ecosystem where technology is leveraged. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City merges these two globally accepted approaches of becoming a Smart City to address this city’s unique challenges. A Joburg Smart City takes into account our Apartheid past and the inequalities created by its spatial design. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
With the continuing inequities that exist in this City, we can ill afford taking a purely technological approach to becoming Smarter when so many residents on the periphery are excluded from accessing broadband and technology. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
We apply a Smart City approach that jointly pursues the use of ICT as an enabler, prioritises access to broadband connectivity and actively engages citizens to co-create solutions that will accelerate the speed,quality & reliability of municipal service delivery. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Hence, Joburg as a Smart City is not just about the administration of municipal programs and services. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It is a Joburg that creates thriving communities in which an Innovation ecosystem isdeveloped between government, academia, residents and industry to share information, ideas, and resources for the betterment of the whole City. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Over the last decade, the Smart City concept has grown in popularity and has become an integral part of global cities’ policy.With the advent of the 4IR, we witness technology transforming society and infiltrating every aspect of human engagement. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It is logical that technology be used as an enabler to tackle some of our most urgent urban challenges. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It is also a logical progression of the idea that cities are complex systems and can be optimised and designed to work better using technology to respond to the changing (and growing) needs of those who live and work within its boundaries. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
These challenges include rapid urbanisation, large informal economies and shifting forms of governance, which requires more than just a technological fix to service delivery, but a systemic change in urban governance. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Our transition to a Smart City is about doing business Unusual;disrupting the old forms of service delivery&governance;making way for a better future of municipal services & a renewed commitment to tackle the 3 critical threats of unemployment,inequality& inequity. #JoburgIDP20
A Joburg Smart City improves the lives of its residents daily; especially the poor, marginalised Majority. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Joburg’s transformation into a Smart City is about the City becoming adaptive to a constantly changing environment, becoming agile in the presence of unpredictability, emergencies and the unforeseen. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It actively supports the development of the talent necessary to carry the City forward into a future that is liveable, safe, sustainable, accessible, supportive and simply better for everyone. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A Smart Joburg is a 2040 City that is a desired place to call home and raise generations to come. The Joburg Smart City Strategy, entitled “Leap into our Future”, provides strategic guidance to design a Smart Joburg City. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Building upon its 8 strategic pillars, the municipality will - in partnership with its residents and relevant stakeholders - construct a tomorrow that our youth will want to inherit. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The outputs driving Leap into our Future are: To enhance the quality of life for all its residents, especially the poor; and to rectify the longstanding spatial and economic barriers inherited from our apartheid past. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Leap Into our Future offers a way to think differently about how services can be delivered. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It guides the creation of a Smart City by identifying the elements necessary to innovate across departments and achieve better integration, cost efficiencies, data sharing and broader delivery of services that positions Joburg as a “future-proof,” Smart City. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Technology creates new opportunities to monitor infrastructure networks, decongest highways,improve health care systems,create safer neighbourhoods, minimise energy consumption,& leverage data to improve decision making and governance for better service delivery. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The pursuit of a Smart City plays a critical role in the process of a city to Leap into the Future. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City has already made considerable progress implementing Smart City measures (including the expansion of the Johannesburg broadband network, the rollout of free Wi-Fi, e-Health and e-Learning projects). #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City has also localised and revised the 2014 Smart City Strategy to the recent 2020 strategy to be more responsive, inclusive and holistic whilst incorporating human needs sustainability and liveability. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The primary tenet of the revised City Smart City strategy is to “Leap into the Future” and to “do more with less” by leveraging technology and innovation to enhance institutional efficiency, service delivery and citizen engagement. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The previous Smart City Strategy had four programmes to realise a Smart City; namely; Smart Citizen, Universal Access, Smart Governance and Institution and Smart and Green Technology. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
As the City’s needs grew more intensely, and a greater awareness developed regarding the benefits of evolving into a Smart City, there arose the need to consider other factors that had to be addressed to realize the 2040 vision of a Smart Joburg. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The Smart City Strategy now presents 8 Pillars:
Smart Citizen, Smart Services, Safe City, Liveable, Sustainable and Resilient City, Connected, Intelligent City, Smart Governance, Smart Institution, Smart Digital Economy #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Smart Citizen, Smart Services, Safe City, Liveable, Sustainable and Resilient City, Connected, Intelligent City, Smart Governance, Smart Institution, Smart Digital Economy #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The Smart Citizen Pillar encourages an approach to service delivery that places citizens at the centre of all initiatives; as well as the selection of digital platforms from which they are intended to engage. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Improved resident interaction will be achieved with online platforms that empower communities to engage with the City on a regular basis, to share their experiences, report problems and comment on City delivery. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Digital platforms empower residents to closely participate in the City’s planning efforts and for residents’ voices to be heard through online chats, social media, and surveys. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City will build systems that allow smart citizens to be the eyes and ears of the city, to report problems and get a team to respond within scheduled times of reporting. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
These systems will provide real-time alerts to citizens of pending problems such as load-shedding, water closures, road closures, slow traffic and other issues that will allow them to better plan their lives and experience less frustration. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
This pillar encourages empowering residents, businesses, and visitors with knowledge and tools required to access, exchange and share information and ideas with the municipality. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
To adequately engage residents, they must firstly be connected, have access to sufficient levels of data, be skilled to engage with technology and innovation as well as provided with the means to readily be participative in local governance. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A Joburg of the near future is a city that offers citizens access to services through smart technologies, including smart cards and providing services to citizens in a more efficient, effective and expeditious manner; #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Empowering citizens to solve their issues when convenient and in their own homes (even after hours). #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Ensuring residents access to efficient, innovative, & affordable services through the use of technology and digital platforms (e-Government services); including kiosks powered by Free Wi-Fi in public places to enable the vision of a live, work & play environment. #JoburgIDP20^PS
At the centre of every smart city globally are the services that are delivered to residents via a smart platform. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The ‘Smart City’ concept brings together characteristics associated with organisational change, technological advancement, economic and social development and other dynamics of a modern city. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Using traditional approaches to service delivery and governance has already shown signs of being antiquated and lacking the adaptability needed within Joburg to meet the growing demands of the current population. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Governments world wide recognise that they can no longer rely on traditional approaches to meet their responsibilities for the built-environment,energy,telecommunications,transportation, water,waste management,health, human services,public safety,& municipal finances. #JoburgIDP20
These services become automated in order to make them more accessible to a broader population, deliver them faster and resolve queries and issues more efficiently. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City desires to evolve into a 24 / 7 and Queue-less City where services are available anytime, anywhere via mobile and web-based citizen portals. Where services are provided via innovative means within walking distances or at the homes of residents. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Full Wifi roll-out, Joburg App for service delivery, push alerts to citizens will become a common service to warn residents of load-shedding, traffic hot spots, , and any other dangers or interruption of services. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Public safety is one of the key areas critical to the success of the Johannesburg’s 2040 GDS strategy.
A safe and liveable city is desired by all citizens, businesses and visitors.
#JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A safe and liveable city is desired by all citizens, businesses and visitors.
#JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It is largely the responsibility of government to create a secure environment for everyone to enjoy. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The Safe City Pillar focuses on the integration of technology to increase the effectiveness of for safety and security toward the reduction of crime, emergencies and accidents. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Based on the digital infrastructure and e-services elements proposed by the Smart City Strategy, the hearth of the Safe City pillar be IIOC that provides, (remote/digital) surveillance, automated data analysis (patterns, suspects); #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
with real time alerts and service delivery coordination (dashboards, incident management). #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
First responders support to react quicker, better informed & well-coordinated to safety incidents, disasters and emergencies events, but also to act pro-actively prevent incidents from happening by predictive analytics & pre-allocated dispatching of ground staff. #JoburgIDP20^PS
The Safe City Pillar will coordinate departments to produce a City – from end-to-end - that is safe from crime, grime, dilapidation and bylaw infringements. It will produce residents that understand their role in making environments unsafe. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A smarter, safer city will make people feel safer not because of the number of police officers and cameras on the streets but because it creates an atmosphere/spirit of trust and law abidance within our communities. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Globally, cities are becoming flocked with vast amount of residents and vehicles. Infrastructure tends to deteriorate and climate change becomes evident as larger populations demand services and the use of city infrastructure. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Infrastructure tends to deteriorate and climate change becomes evident as larger populations demand services and the use of city infrastructure. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City envisions itself as a resilient city that can be able to adapt to climate change, counteract urbanization while enhancing smart and innovative planning solutions. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A liveable Joburg will be one that supports development of a green economy that dually creates jobs whilst minimising climatic change. It is a sustainable environment that makes use of alternative power generate to ensure energy, water, and waste sustainability. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A future Joburg will ensure enhance water catchment systems that retrieve and store larger quantities of rain water, to ensure that water does not become a scarce resource in the near or distant future. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Equally it will better protect and warn against flooding and the damage it causes to lives and homes. A sustainable Joburg creates value out of waste to incentivise residents against dumping and soiling the environment. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It reduces energy costs and climatic impact of all its buildings, infrastructure, equipment and fleet. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A liveable Joburg facilitates the planning process to expedite development permits, deed transfers and other services that makes the built environment transform at an accelerated pace. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The City implements targeted spatial development plans that reconfigure and redesign the City to, once and for all, address the spatial inequalities of this city. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A Connected, Intelligent City is a Joburg that features Wall-to-Wall Connectivity, Universal access to broadband and higher levels of data to create a holistically connected environment for residents. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It is a City that eliminates the digital divide through the availability of Free Wi-Fi in public places and extends internet availability to the home so that citizen can easily engage with each other, business and with government. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Access to broadband networks is a driver of growth and development across the globe,by improving community development,ensuring access to economic opportunities & knowledge & allowing for greater access of services,high speed broadband access remains an imperative. #JoburgIDP20
In the 2014 Smart City Strategy, one of the principal obstacles to the transition to a Smart City and Smart Services was the unequal access of information technologies and broadband across the city. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
This disparity was referred to as the ‘digital divide’. However, According to the City’s 2017/2018 Quality of Life Surveys, 35% of the population in Johannesburg currently live without access to the internet. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Therefore, 65% of our residents now have access to technology and the internet principally via mobile devices. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The 2020 Strategy therefore expands the City’s strategic focus to solving the “Data Divide” disparities alongside rectifying the “digital divide” for the remaining 35% of residents without access. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The renewed focus is to increase the quantity of data accessible to each resident of the City through the proliferation of free and/or subsidised Wi-fi alongside the expansion of the fibre network to augment speed and reliability. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
In Johannesburg, a significant minority enjoy high-speed access via corporate networks, domestic connections and wireless 3G networks. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Broadband networks are clustered in the main urban economic nodes, effectively excluding township areas, informal settlements and non-urban/agricultural areas.
The areas targeted for digital divide intervention are: https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
The areas targeted for digital divide intervention are:
-Diepsloot West
- Slovo
- Ebony Park
- Kaaifontein (Ext. 6,7 & 8)
- Orange Farm & Poortije
- Alexandre (Ext. 23,35,57)
- Chris Hani and
- Vrededorp
The Goal of this pillar is to ensure that City leadership fosters collaboration and expedient service delivery. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
- Slovo
- Ebony Park
- Kaaifontein (Ext. 6,7 & 8)
- Orange Farm & Poortije
- Alexandre (Ext. 23,35,57)
- Chris Hani and
- Vrededorp
The Goal of this pillar is to ensure that City leadership fosters collaboration and expedient service delivery. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Strategic coordination & cooperation at the highest levels of government is required to facilitate the City’s transition to being more transparent, financially sustainable and accountable to adhering to service excellence as a means to guard the City’s reputation. #JoburgIDP20^PS
The achievement of this pillar will produce a 2040 city that sees growth in revenue principally by a reduction in losses, lack of productivity, wastage and corruption. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
It is a Joburg that has a single view of its information, makes data based political and administrative decisions, develops productive interdependencies that minimise silos, duplication and wasteful expenditure. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
A city that is experienced by its residents as being well-planned, interoperable and coordinated and responsive. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
An institution that is digitally transformed to create an innovative and efficient administration that is data and evidence driven toward “One Version of the Truth”. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS
Having a strategic nerve centre, or “brain” that collects data from all departments and entities, collates the data, interprets and then reports on it for accurate and productive decision-making, improved service delivery. #JoburgIDP20 ^PS

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS" title="There are two types of natural resources: https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS" title="There are two types of natural resources: https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="👇" title="Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten" aria-label="Emoji: Rückhand Zeigefinger nach unten"> #JoburgIDP20 ^PS" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>