Brief anatomic-functional review of main white-matter tracts! Open Thread.
Covering corticospinal, ventral and dorsal associative streams, frontal aslant, and cingulum.
#neurorad #FOAMrad #neurosurg
Covering corticospinal, ventral and dorsal associative streams, frontal aslant, and cingulum.
#neurorad #FOAMrad #neurosurg
Dorsal associative stream. WHERE pathway. Language role: Speech articulation and phonological processing.
Arcuate /superior longitudinal fasciculus composed of 3 segments.
- Long (fronto-temp) - classical arcuate
- Short horizontal (fronto-pariet)
- Short vertical (pariet-temp)
Arcuate /superior longitudinal fasciculus composed of 3 segments.
- Long (fronto-temp) - classical arcuate
- Short horizontal (fronto-pariet)
- Short vertical (pariet-temp)
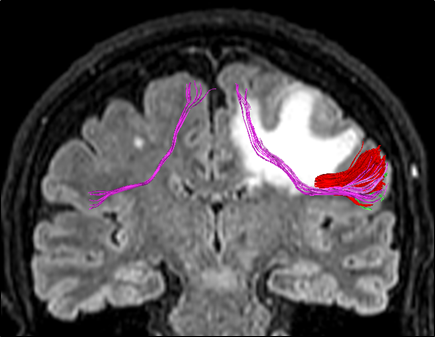
RED: Long segment of arcuate: Inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) to posterior lateral temporal region
GREEN: Horizontal Short segment of arcuate: IFG to inferior parietal lobe.
YELLOW: Short vertical segment of arcuate: Inferior parietal lobe to posterior lateral temporal region.
GREEN: Horizontal Short segment of arcuate: IFG to inferior parietal lobe.
YELLOW: Short vertical segment of arcuate: Inferior parietal lobe to posterior lateral temporal region.
Ventral associative stream. WHAT pathway. Language role. Words -> meaning.
- Direct pathway: Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF)
- Indirect pathway:
- Uncinate (fronto-temporal)
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) (temporo-occipital)
- Direct pathway: Inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus (IFOF)
- Indirect pathway:
- Uncinate (fronto-temporal)
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF) (temporo-occipital)
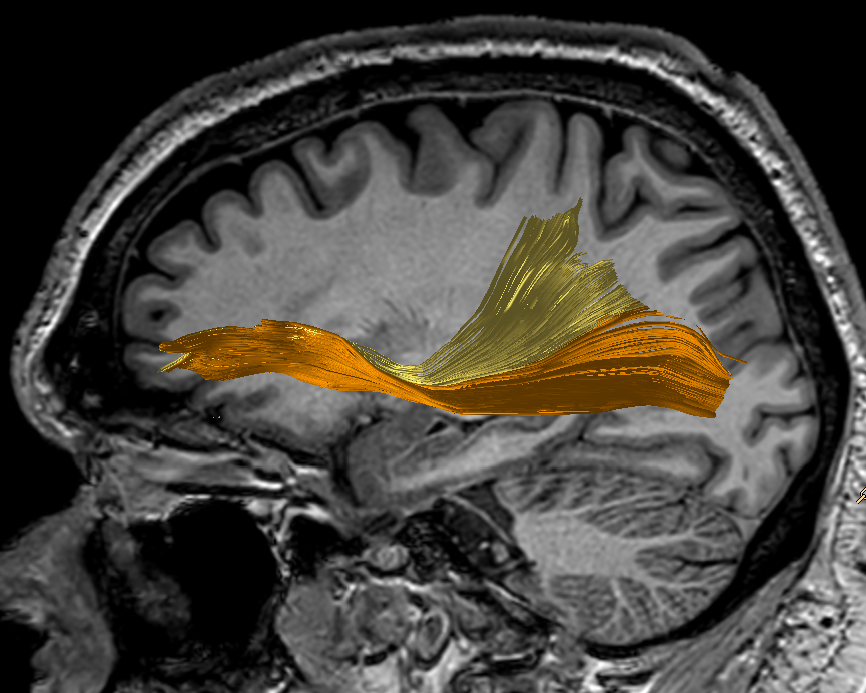
IFOF superficial (yellow) and deep (orange segments). Longest associative tract connects prefrontal areas to parietal (superficial segment) and occipital (deep segment) lobes via the infeiror external capsule and posterior temporal white-matter.
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus. Along with Uncinate fasciculus, it is part of the indirect ventral associative stream. Connects anterior temporal pole to occipital pole. Courses immediately infero-lateral to IFOF.
Uncinate fasciculus. Part of the indirect ventral stream and also part of the limbic system. Connects prefrontal regions to temporal pole via the temporal stem.
Cingulum. Part of the limbic system, surrounds the corpus callosum medial to other associative and projection fibers. At the level of the splenium an narrow extension of white-matter tract through the parahippocampal gyrus extends to the amygdala.
Corticospinal tract. Most important projection fiber tract. Contains motor and sensory fibers from pre-motor, precentral (primary motor) and post-central cortices via the posterior limb of the internal capsule all the way to the spinal cord. Most fibers decussate in the medulla.
Damage to the corticospinal tract can cause permanent motor damage! Especially damage to pre-central fibers.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter