My very first #ExerciseIsMedicine #Tweetorial is here: Breaking “it makes me feel good” into pieces https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Brain" aria-label="Emoji: Brain">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Brain" aria-label="Emoji: Brain"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😀" title="Grinning face" aria-label="Emoji: Grinning face">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😀" title="Grinning face" aria-label="Emoji: Grinning face"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏊♂️" title="Man swimming" aria-label="Emoji: Man swimming">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏊♂️" title="Man swimming" aria-label="Emoji: Man swimming"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> #Thread
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> #Thread  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">
#TwitterPoll at the END
#TwitterPoll at the END
1/ Are you exercising https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">to boost your mental well-being during the pandemic
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">to boost your mental well-being during the pandemic https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦠" title="Microbe" aria-label="Emoji: Microbe">? People exercise because it makes them feel good
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🦠" title="Microbe" aria-label="Emoji: Microbe">? People exercise because it makes them feel good https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙃" title="Upside-down face" aria-label="Emoji: Upside-down face">, but what exactly happens in our body? Keep reading to satisfy your curiosity & learn about the #mechanisms behind aerobic exercise & #mentalhealth
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙃" title="Upside-down face" aria-label="Emoji: Upside-down face">, but what exactly happens in our body? Keep reading to satisfy your curiosity & learn about the #mechanisms behind aerobic exercise & #mentalhealth  https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt="">
https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt="">
2/ Anxiety and depression are common mental health conditions. The prevalence in cardiac patients is ~20-30% & 2x higher in  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♀️" title="Female sign" aria-label="Emoji: Female sign"> vs
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♀️" title="Female sign" aria-label="Emoji: Female sign"> vs  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♂️" title="Male sign" aria-label="Emoji: Male sign">. Social roles (e.g. caregiver role), cultural norms (e.g. societal sexism) and more pronounced hormonal shifts in
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♂️" title="Male sign" aria-label="Emoji: Male sign">. Social roles (e.g. caregiver role), cultural norms (e.g. societal sexism) and more pronounced hormonal shifts in  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♀️" title="Female sign" aria-label="Emoji: Female sign"> influence this sex-difference
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♀️" title="Female sign" aria-label="Emoji: Female sign"> influence this sex-difference
3/ Pharmacotherapy https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💊" title="Pill" aria-label="Emoji: Pill"> and psychotherapy (e.g. CBT)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💊" title="Pill" aria-label="Emoji: Pill"> and psychotherapy (e.g. CBT)  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">levels of anxiety and depression, yet many patients discontinue (e.g. side effects) or do not respond to treatment
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">levels of anxiety and depression, yet many patients discontinue (e.g. side effects) or do not respond to treatment https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😟" title="Worried face" aria-label="Emoji: Worried face">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😟" title="Worried face" aria-label="Emoji: Worried face"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> Exercise
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> Exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤸♀️" title="Woman cartwheeling" aria-label="Emoji: Woman cartwheeling">comes to the rescue as a low-risk, cost-effective, and easily accessible therapeutic option
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤸♀️" title="Woman cartwheeling" aria-label="Emoji: Woman cartwheeling">comes to the rescue as a low-risk, cost-effective, and easily accessible therapeutic option
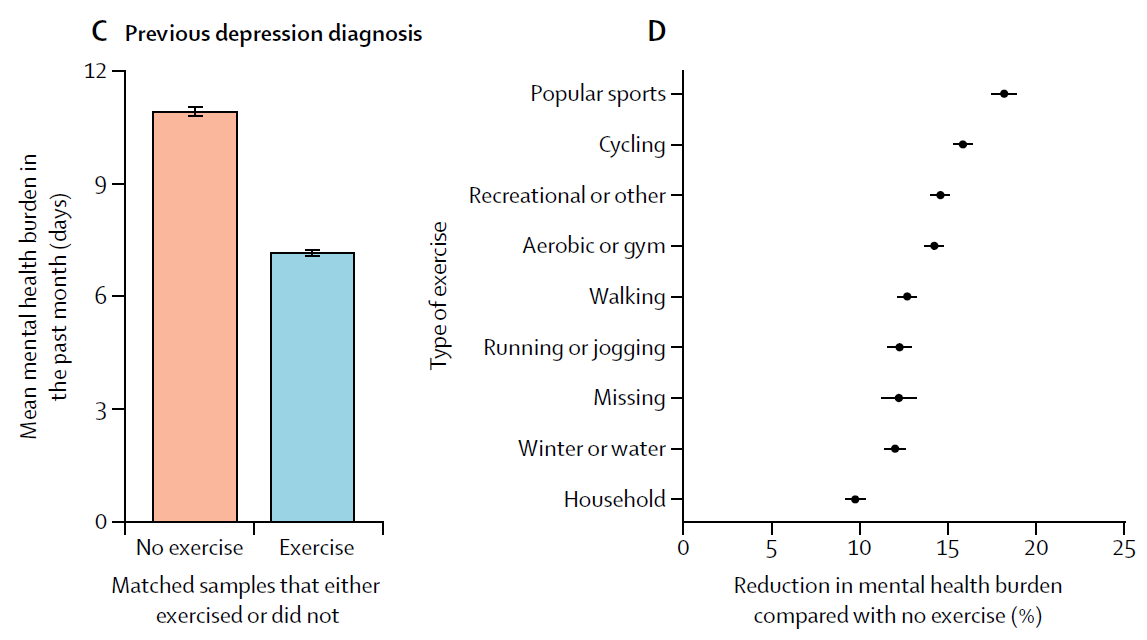
4/  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">PA is associated with improved #anxiety #depression & #mood in population studies
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">PA is associated with improved #anxiety #depression & #mood in population studies
MA show https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression with
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression with https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">in healthy (-0.38 & -0.50) & cardiac populations (-2.59 & -0.61) Figure: http://b.link/Chekroud2018 ;">https://b.link/Chekroud2... http://b.link/Rebar2015 ;">https://b.link/Rebar2015... http://b.link/Zheng2019 ">https://b.link/Zheng2019...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">in healthy (-0.38 & -0.50) & cardiac populations (-2.59 & -0.61) Figure: http://b.link/Chekroud2018 ;">https://b.link/Chekroud2... http://b.link/Rebar2015 ;">https://b.link/Rebar2015... http://b.link/Zheng2019 ">https://b.link/Zheng2019...
MA show
5/ Anxiety and depression modify the body’s healthy neurobiological state through continued https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">levels of catecholamines, cortisol, inflammatory markers &
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">levels of catecholamines, cortisol, inflammatory markers &  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">serotonin; leading to overactivity of the SNS & the HPA axis. It is hard to establish the true direction of this relationship
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">serotonin; leading to overactivity of the SNS & the HPA axis. It is hard to establish the true direction of this relationship
6/ A key difference between “good” (e.g. aerobic exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚶♀️" title="Woman walking" aria-label="Emoji: Woman walking">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚶♀️" title="Woman walking" aria-label="Emoji: Woman walking"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💃" title="Woman dancing" aria-label="Emoji: Woman dancing">) and “bad” stressors (e.g. persistent anxiety
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💃" title="Woman dancing" aria-label="Emoji: Woman dancing">) and “bad” stressors (e.g. persistent anxiety https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😟" title="Worried face" aria-label="Emoji: Worried face">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😟" title="Worried face" aria-label="Emoji: Worried face"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😨" title="Fearful face" aria-label="Emoji: Fearful face">) is the prolonged state of hypercortisolemia in the latter, which is associated with inflammation, hypertension, hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😨" title="Fearful face" aria-label="Emoji: Fearful face">) is the prolonged state of hypercortisolemia in the latter, which is associated with inflammation, hypertension, hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia
7/  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">may reverse the altered neurobiological state & thus
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">may reverse the altered neurobiological state & thus https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety & depression
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety & depression
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty: #physiological & #psychological mechanisms responsible for the #mentalhealth https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> benefits of
https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> benefits of https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">
(1) Aerobic exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release & function of neurotransmitters/neurotrophins:
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release & function of neurotransmitters/neurotrophins:
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty: #physiological & #psychological mechanisms responsible for the #mentalhealth
(1) Aerobic exercise
8/ β-endorphins regulate emotions.  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in the levels of β-endorphins during & following exercise are linked with
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in the levels of β-endorphins during & following exercise are linked with  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety and better mood (ever felt the runner’s high?
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety and better mood (ever felt the runner’s high? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤩" title="Star-struck" aria-label="Emoji: Star-struck">). Aerobic exercise
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤩" title="Star-struck" aria-label="Emoji: Star-struck">). Aerobic exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running"> can
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running"> can  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">the levels of β-endorphins up to 7-fold
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">the levels of β-endorphins up to 7-fold
9/ Adults with poor mental health have https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">BDNF. Acute exercise
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">BDNF. Acute exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">BDNF (SMD 0.46) and this acute effect is
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">BDNF (SMD 0.46) and this acute effect is https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">after an exercise program (ES 0.59). Chronic
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">after an exercise program (ES 0.59). Chronic https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in BDNF with exercise have also been reported (ES 0.27). Studies with more
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in BDNF with exercise have also been reported (ES 0.27). Studies with more  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♀️" title="Female sign" aria-label="Emoji: Female sign"> show smaller effect sizes
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="♀️" title="Female sign" aria-label="Emoji: Female sign"> show smaller effect sizes  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☹" title="Frowning face" aria-label="Emoji: Frowning face"> http://b.link/Szuhany2015 ">https://b.link/Szuhany20...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☹" title="Frowning face" aria-label="Emoji: Frowning face"> http://b.link/Szuhany2015 ">https://b.link/Szuhany20...
10/ The https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in BDNF with exercise
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in BDNF with exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤼♀️" title="Women wrestling" aria-label="Emoji: Women wrestling">has been linked with
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤼♀️" title="Women wrestling" aria-label="Emoji: Women wrestling">has been linked with https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">levels of depression. Higher-intensity exercise may lead to greater
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">levels of depression. Higher-intensity exercise may lead to greater https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in BDNF than lower-intensity exercise
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in BDNF than lower-intensity exercise
http://b.link/Gourgouvelis2018;https://b.link/Gourgouve... href=" http://b.link/Hotting2016 ">https://b.link/Hotting20...
http://b.link/Gourgouvelis2018;
11/ Persistent anxiety blocks the cortisol feedback loop responsible for down-regulating the HPA axis. Atrial natriuretic peptides (ANP) facilitates the inhibition of the HPA axis to limit overactivity. During exercise, the https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in atrial stretch
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">in atrial stretch https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🫀" title="Anatomical heart" aria-label="Emoji: Anatomical heart"> from
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🫀" title="Anatomical heart" aria-label="Emoji: Anatomical heart"> from https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">venous return:
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">venous return: https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">ANP levels
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">ANP levels
12/ In healthy adults, 30 min of aerobic exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running"> significantly
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running"> significantly  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">ANP levels &
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">ANP levels &  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety in response to a stressor. Enhanced ANP contributes to the anxiolytic effects of #exercise (r=0.69, p=0.03) http://b.link/Strohle2006 ">https://b.link/Strohle20...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety in response to a stressor. Enhanced ANP contributes to the anxiolytic effects of #exercise (r=0.69, p=0.03) http://b.link/Strohle2006 ">https://b.link/Strohle20...
13/ Monoamines dysfunction is involved in the pathogenesis of #anxiety and #depression. Exercise  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">serotonin synthesis (by
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">serotonin synthesis (by https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">free form of tryptophan) and downregulates serotonin receptors
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">free form of tryptophan) and downregulates serotonin receptors  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">
 https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">serotonin availability &
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">serotonin availability & https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release of norepinephrine & dopamine
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release of norepinephrine & dopamine
14/ (2) Cross-stressor adaptation: during https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">our bodily systems transiently adapt to meet the
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">our bodily systems transiently adapt to meet the https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">metabolic demand. Repeated physiological challenges with chronic exercise lead to
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">metabolic demand. Repeated physiological challenges with chronic exercise lead to https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">improved physiological control in future exercise bouts which can translate to other daily stressors
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">improved physiological control in future exercise bouts which can translate to other daily stressors
15/ As a result, https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">cardiovascular reactivity. E.g. Acute:
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">cardiovascular reactivity. E.g. Acute:
#bloodpressure response to a stressor is https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">if preceded by an exercise bout (ES -0.40). State anxiety
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">if preceded by an exercise bout (ES -0.40). State anxiety https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">for 2-24h after exercising
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">for 2-24h after exercising https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧘♀️" title="Woman in lotus position" aria-label="Emoji: Woman in lotus position">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧘♀️" title="Woman in lotus position" aria-label="Emoji: Woman in lotus position">
This is why you should https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">before your exam!
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">before your exam!
http://b.link/RaglinMorgan1987;">https://b.link/RaglinMor... http://b.link/Hamer2006 ">https://b.link/Hamer2006...
#bloodpressure response to a stressor is
This is why you should
http://b.link/RaglinMorgan1987;">https://b.link/RaglinMor... http://b.link/Hamer2006 ">https://b.link/Hamer2006...
16/ Chronic: Trained adults show a lower HR and cortisol response to a stress task vs untrained. How? https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">Tranquilizing;
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">Tranquilizing; https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">vasodilation,
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">vasodilation, https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">catecholamine levels &
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">catecholamine levels &  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">TPR due to SNS inhibition & improved β-receptors responsiveness
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">TPR due to SNS inhibition & improved β-receptors responsiveness
http://b.link/Rimmele2009 ;https://b.link/Rimmele20... href=" http://b.link/DeVries1981 ">https://b.link/DeVries19...
http://b.link/Rimmele2009 ;
17/ (3) Anxiety sensitivity: tendency to misinterpret anxiety sensations (e.g. rising HR https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">“I’m going to have a
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">“I’m going to have a https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="❤️" title="Red heart" aria-label="Emoji: Red heart">attack”
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="❤️" title="Red heart" aria-label="Emoji: Red heart">attack” https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙀" title="Weary cat face" aria-label="Emoji: Weary cat face">)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙀" title="Weary cat face" aria-label="Emoji: Weary cat face">)
The repeated exposure to a new environment (sweat, heavy breathing https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking">) not leading to bad outcomes:
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking">) not leading to bad outcomes: https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety when encountering other unfamiliar situations
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety when encountering other unfamiliar situations
The repeated exposure to a new environment (sweat, heavy breathing
18/ (4) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙂" title="Slightly smiling face" aria-label="Emoji: Slightly smiling face">mood
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙂" title="Slightly smiling face" aria-label="Emoji: Slightly smiling face">mood https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">HPA axis reactivity while
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">HPA axis reactivity while  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☹" title="Frowning face" aria-label="Emoji: Frowning face">mood
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="☹" title="Frowning face" aria-label="Emoji: Frowning face">mood https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow"> reactivity. Mood is improved for>30 min post
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow"> reactivity. Mood is improved for>30 min post https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">(ES 0.47). Enjoyment may be key.
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">(ES 0.47). Enjoyment may be key.
High-intensity https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">negative affect more than low-intensity during but NOT after
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">negative affect more than low-intensity during but NOT after https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">. This change may coincide with
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">. This change may coincide with https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">self-efficacy http://b.link/Reed2006 ">https://b.link/Reed2006&...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">self-efficacy http://b.link/Reed2006 ">https://b.link/Reed2006&...
High-intensity
19/ (5) https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">self-efficacy (ES 0.21) & self-esteem (ES 0.23) are viable mediators of improved #mentalhealth
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">self-efficacy (ES 0.21) & self-esteem (ES 0.23) are viable mediators of improved #mentalhealth  https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> with
https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> with https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">E.g. running 5K regularly
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">E.g. running 5K regularly https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">body satisfaction &
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">body satisfaction &  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">sense of mastery that can be transferred to other situations:
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">sense of mastery that can be transferred to other situations: https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">confidence to cope with stressors http://b.link/White2009 ">https://b.link/White2009...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">confidence to cope with stressors http://b.link/White2009 ">https://b.link/White2009...
20/ (6) Social #isolation worsens mental health. Anxiety & depression have a greater inverse association with team sports & recreational activities(often group-based https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤼♀️" title="Women wrestling" aria-label="Emoji: Women wrestling">) than with domestic chores/work-related PA (often individual)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤼♀️" title="Women wrestling" aria-label="Emoji: Women wrestling">) than with domestic chores/work-related PA (often individual)
http://b.link/Harvey2018 ;https://b.link/Harvey201... href=" http://b.link/stephens1988 ">https://b.link/stephens1...
http://b.link/Harvey2018 ;
21/ In https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚺" title="Women’s symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Women’s symbol">in particular, group-based
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚺" title="Women’s symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Women’s symbol">in particular, group-based https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💃" title="Woman dancing" aria-label="Emoji: Woman dancing">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💃" title="Woman dancing" aria-label="Emoji: Woman dancing"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴♀️" title="Woman biking" aria-label="Emoji: Woman biking">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴♀️" title="Woman biking" aria-label="Emoji: Woman biking"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">with an emphasis on social interactions
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">with an emphasis on social interactions https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤼♀️" title="Women wrestling" aria-label="Emoji: Women wrestling"> may maximize
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤼♀️" title="Women wrestling" aria-label="Emoji: Women wrestling"> may maximize https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression. Upon an adverse situation,
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression. Upon an adverse situation, https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚺" title="Women’s symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Women’s symbol">tend to seek support from others, while
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚺" title="Women’s symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Women’s symbol">tend to seek support from others, while https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚹" title="Men’s symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Men’s symbol">are more likely to escape or cope by taking action
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚹" title="Men’s symbol" aria-label="Emoji: Men’s symbol">are more likely to escape or cope by taking action
Check: http://b.link/Vidal2020 ">https://b.link/Vidal2020...
Check: http://b.link/Vidal2020 ">https://b.link/Vidal2020...
22/ That was a “brief” summary of major #mechanisms behind the #exercise & #mentalhealth  https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> relationship
https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> relationship https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📚" title="Books" aria-label="Emoji: Books"> One thing is clear: if you don’t routinely exercise, the time to start is now! Please feel free to share your thoughts and papers to generate discussion
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📚" title="Books" aria-label="Emoji: Books"> One thing is clear: if you don’t routinely exercise, the time to start is now! Please feel free to share your thoughts and papers to generate discussion
23/ Last but not least  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> #Poll time
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> #Poll time https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="❣️" title="Heart exclamation" aria-label="Emoji: Heart exclamation">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="❣️" title="Heart exclamation" aria-label="Emoji: Heart exclamation">
If you provide care to patients, do you routinely recommend exercise https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴♀️" title="Woman biking" aria-label="Emoji: Woman biking">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴♀️" title="Woman biking" aria-label="Emoji: Woman biking"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running"> https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚶♂️" title="Man walking" aria-label="Emoji: Man walking">as a primary treatment for your patients with high levels of anxiety or depression? Why? (Please
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚶♂️" title="Man walking" aria-label="Emoji: Man walking">as a primary treatment for your patients with high levels of anxiety or depression? Why? (Please https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙏" title="Folded hands" aria-label="Emoji: Folded hands">share comments/successful stories/concerns)
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🙏" title="Folded hands" aria-label="Emoji: Folded hands">share comments/successful stories/concerns)
If you provide care to patients, do you routinely recommend exercise
24/ Despite https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">being easily accessible, low-risk and cost-effective with remarkable health benefits, only 5% of physicians surveyed
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">being easily accessible, low-risk and cost-effective with remarkable health benefits, only 5% of physicians surveyed https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤪" title="Zany face" aria-label="Emoji: Zany face">chose exercise as 1 of their 3 most used treatments for depression, while 92% chose medications
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🤪" title="Zany face" aria-label="Emoji: Zany face">chose exercise as 1 of their 3 most used treatments for depression, while 92% chose medications https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💊" title="Pill" aria-label="Emoji: Pill"> with multiple side effects http://b.link/reportuk ">https://b.link/reportuk&...
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="💊" title="Pill" aria-label="Emoji: Pill"> with multiple side effects http://b.link/reportuk ">https://b.link/reportuk&...
25/ Let’s advocate for exercise! Please help get the message across with a #RT, lack of education is often a barrier to exercise referral and participation.
If you liked the #tweetorial https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">follow https://twitter.com/sol_vidalalmela ">https://twitter.com/sol_vidal... for more!
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow">follow https://twitter.com/sol_vidalalmela ">https://twitter.com/sol_vidal... for more!
Please unroll @threadreaderapp
If you liked the #tweetorial
Please unroll @threadreaderapp
#EPCHL #ExerciseIsMedicine #ExercisePhysiology #MedEd #Tweetorials #KnowledgeTranslation #SciComm #AcademicTwitter #MedTwitter #CardioTwitter #MentalHealthMonth  https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt="">
https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt="">
@EIM_Canada @exerciseworks @PA_Researcher @activeforlife @EuSport @UOHIResearch @uOttawaHK @uOHealthRes @uOttawaMed
@EIM_Canada @exerciseworks @PA_Researcher @activeforlife @EuSport @UOHIResearch @uOttawaHK @uOHealthRes @uOttawaMed

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😀" title="Grinning face" aria-label="Emoji: Grinning face">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏊♂️" title="Man swimming" aria-label="Emoji: Man swimming">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> #Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow"> #TwitterPoll at the END" title="My very first #ExerciseIsMedicine #Tweetorial is here: Breaking “it makes me feel good” into pieceshttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Brain" aria-label="Emoji: Brain">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😀" title="Grinning face" aria-label="Emoji: Grinning face">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏊♂️" title="Man swimming" aria-label="Emoji: Man swimming">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> #Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow"> #TwitterPoll at the END" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😀" title="Grinning face" aria-label="Emoji: Grinning face">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏊♂️" title="Man swimming" aria-label="Emoji: Man swimming">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> #Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow"> #TwitterPoll at the END" title="My very first #ExerciseIsMedicine #Tweetorial is here: Breaking “it makes me feel good” into pieceshttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧠" title="Brain" aria-label="Emoji: Brain">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😀" title="Grinning face" aria-label="Emoji: Grinning face">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏊♂️" title="Man swimming" aria-label="Emoji: Man swimming">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚴" title="Person biking" aria-label="Emoji: Person biking"> #Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow"> #TwitterPoll at the END" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 PA is associated with improved #anxiety #depression & #mood in population studiesMA showhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression withhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">in healthy (-0.38 & -0.50) & cardiac populations (-2.59 & -0.61) Figure: https://b.link/Chekroud2... https://b.link/Rebar2015... https://b.link/Zheng2019..." title="4/ https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">PA is associated with improved #anxiety #depression & #mood in population studiesMA showhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression withhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">in healthy (-0.38 & -0.50) & cardiac populations (-2.59 & -0.61) Figure: https://b.link/Chekroud2... https://b.link/Rebar2015... https://b.link/Zheng2019..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
PA is associated with improved #anxiety #depression & #mood in population studiesMA showhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression withhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">in healthy (-0.38 & -0.50) & cardiac populations (-2.59 & -0.61) Figure: https://b.link/Chekroud2... https://b.link/Rebar2015... https://b.link/Zheng2019..." title="4/ https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">PA is associated with improved #anxiety #depression & #mood in population studiesMA showhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">in anxiety & depression withhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃" title="Person running" aria-label="Emoji: Person running">in healthy (-0.38 & -0.50) & cardiac populations (-2.59 & -0.61) Figure: https://b.link/Chekroud2... https://b.link/Rebar2015... https://b.link/Zheng2019..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
 may reverse the altered neurobiological state & thushttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety & depressionLet’s get into the nitty-gritty: #physiological & #psychological mechanisms responsible for the #mentalhealth https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> benefits ofhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">(1) Aerobic exercisehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release & function of neurotransmitters/neurotrophins:" title="7/ https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">may reverse the altered neurobiological state & thushttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety & depressionLet’s get into the nitty-gritty: #physiological & #psychological mechanisms responsible for the #mentalhealth https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> benefits ofhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">(1) Aerobic exercisehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release & function of neurotransmitters/neurotrophins:" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
may reverse the altered neurobiological state & thushttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety & depressionLet’s get into the nitty-gritty: #physiological & #psychological mechanisms responsible for the #mentalhealth https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> benefits ofhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">(1) Aerobic exercisehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release & function of neurotransmitters/neurotrophins:" title="7/ https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">may reverse the altered neurobiological state & thushttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬇️" title="Downwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Downwards arrow">anxiety & depressionLet’s get into the nitty-gritty: #physiological & #psychological mechanisms responsible for the #mentalhealth https://abs.twimg.com/hashflags... draggable="false" alt=""> benefits ofhttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🏃♀️" title="Woman running" aria-label="Emoji: Woman running">(1) Aerobic exercisehttps://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="⬆️" title="Upwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Upwards arrow">release & function of neurotransmitters/neurotrophins:" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>


