Good evening! Excited to discuss an article by @drkeithsiau published in @AmCollegeGastro focusing on colonoscopy training, with expert commentary by @Samir_Grover from @UofT. Lets begin
https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Abstract/2020/02000/Colonoscopy_Direct_Observation_of_Procedural.17.aspx">https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Abstr...
https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Abstract/2020/02000/Colonoscopy_Direct_Observation_of_Procedural.17.aspx">https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Abstr...
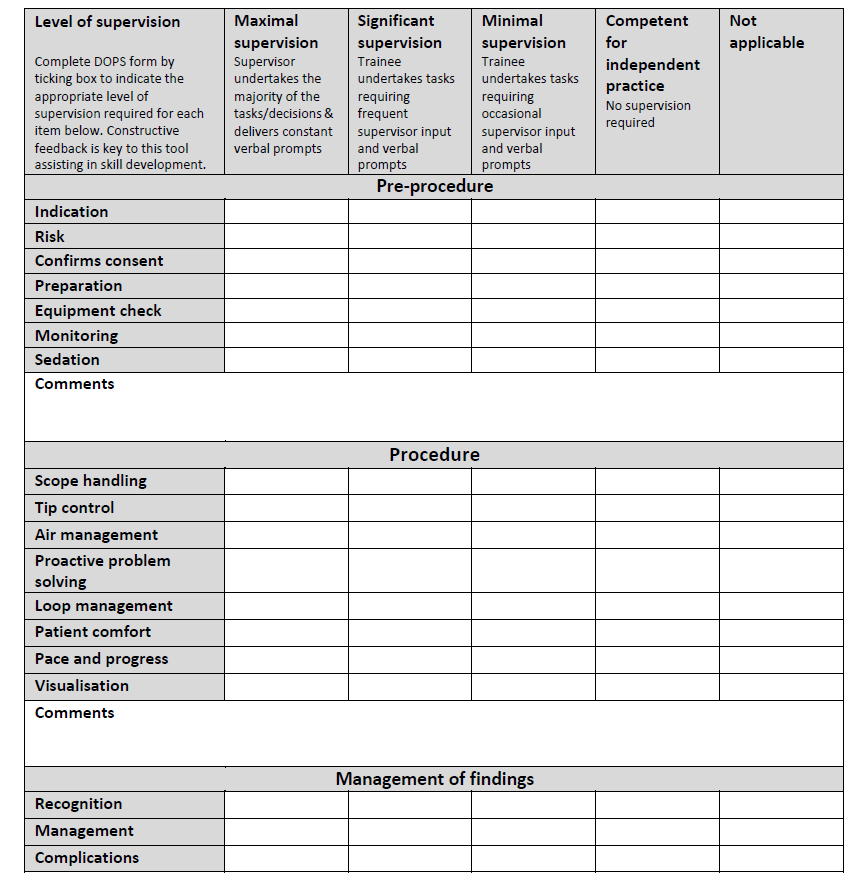
Background: Joint Advisory Group on GI Endoscopy (JAG) supported development of direct observation of procedural skills (DOPS) as assessment tool.Filled by trainers immediately after observing trainee+entered into web system. Each DOPS assesses 24 individual competencies.1/2
JAG criteria for provisional cscope certification: lifetime colonoscopy count>200, unassisted cecal intubation rate (CIR)>90% over prev 3m, attendance @ JAG basic skills colonoscopy course, and competency in the preceding 5 formative DOPS 2/2
Aim of study:
(i) assess the validity and reliability
of formative DOPS
(ii) analyze DOPS data to benchmark competence
and evaluate competence development during training
(iii) identify independent predictors of DOPS competence
(i) assess the validity and reliability
of formative DOPS
(ii) analyze DOPS data to benchmark competence
and evaluate competence development during training
(iii) identify independent predictors of DOPS competence
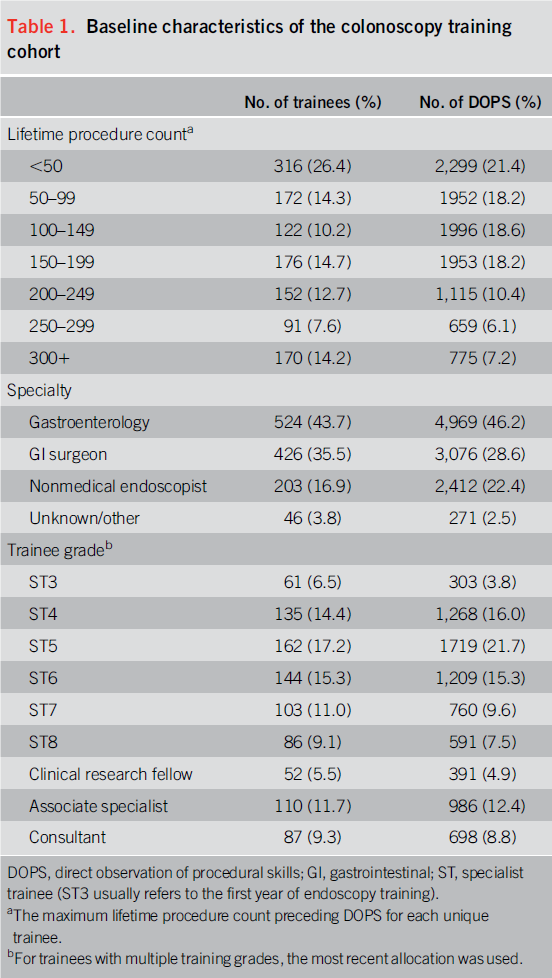
Methods: prospective, UK wide observational study. Summative colonoscopy DOPS from 2016-2018 appraised. Factors studied: individual item scores, case difficulty, and overall DOPS rating awarded by the assessor/trainer,
trainee grade( ST3-5: junior, ST6+ : senior), lifetime count
trainee grade( ST3-5: junior, ST6+ : senior), lifetime count
cont& #39;d...EGD certification, unassisted CIR calculated over the preceding 30 procedures etc.
1⁰ outcome: overall DOPS rating (score 1: requiring maximal supervision; 2: significant supervision;
3: minimal supervision; 4: competent without
supervision).
1⁰ outcome: overall DOPS rating (score 1: requiring maximal supervision; 2: significant supervision;
3: minimal supervision; 4: competent without
supervision).
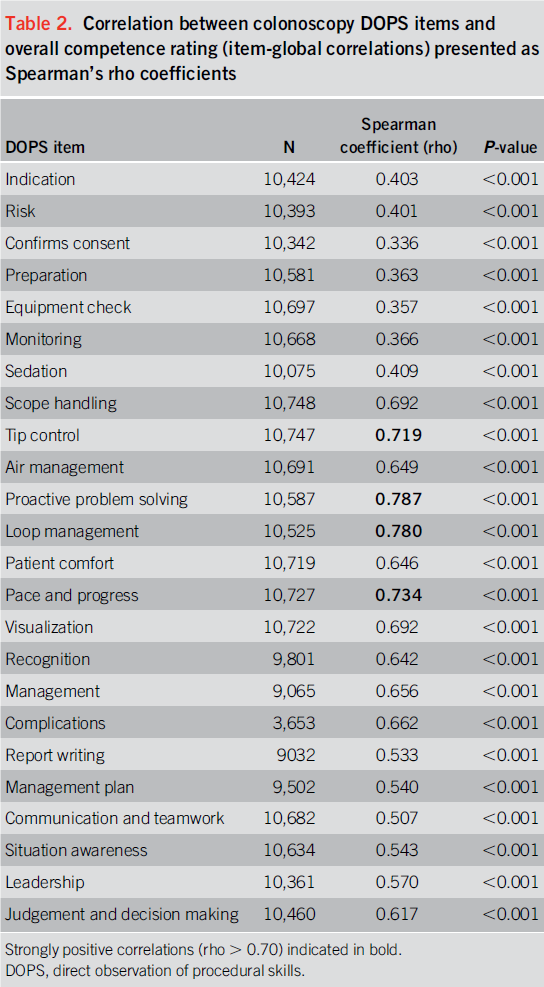
Analysis: item-total correlations to evaluate diff b/w each DOPS item and overall DOPS score. Reliability of DOPS evaluated using generalizability theory. Learning curves for competency and predictors of competence derived.
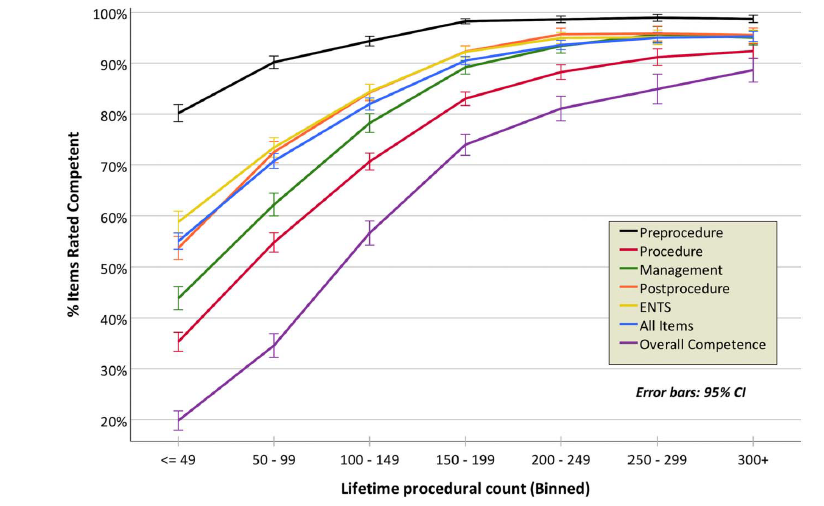
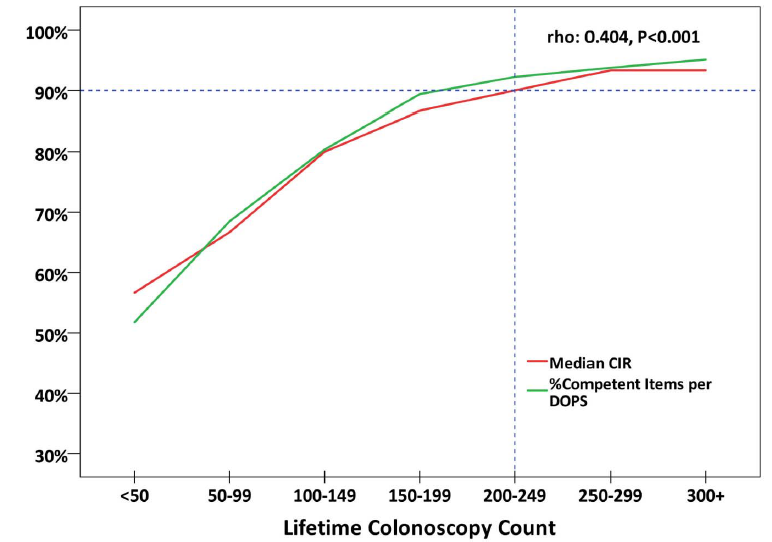
Results: >10,000 DOPS for 1200~ trainees. Acceptable reliability threshold (G > 0.70) was achieved with 3 assessors performing 2 DOPS each. DOPS competency rates correlated with the unassisted CIR. 1/3
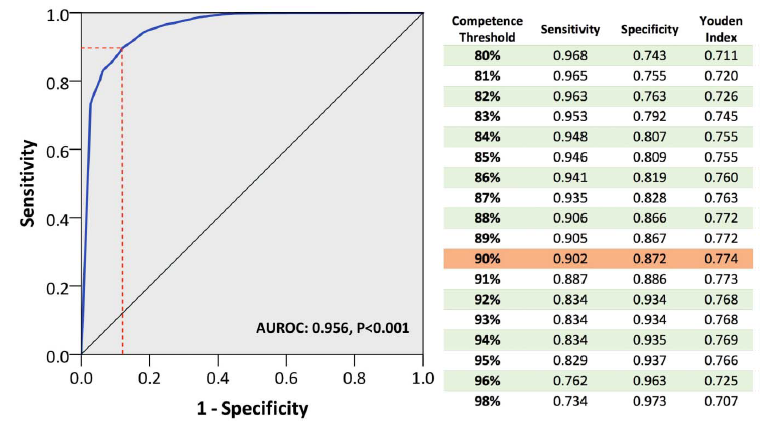
Demonstrating competency in 90% of assessed items provided optimal sensitivity (90.2%) and specificity (87.2%) for benchmarking overall DOPS competence. competency in “proactive problem solving” and “loop management” correlated strongest with the overall DOPS+last to develop. 2/3
Multivariable predictors of competence:
-Lifetime procedure count
-DOPS count
-trainer specialty
-easier case difficulty
-higher CIR
3/3
-Lifetime procedure count
-DOPS count
-trainer specialty
-easier case difficulty
-higher CIR
3/3

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter