The country’s cities — historically the nation’s engines of opportunity — often exacerbate inequities today.
We& #39;ve got charts. (1/n) https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/05/13/opinion/inequality-cities-life-expectancy.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
We& #39;ve got charts. (1/n) https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/05/13/opinion/inequality-cities-life-expectancy.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
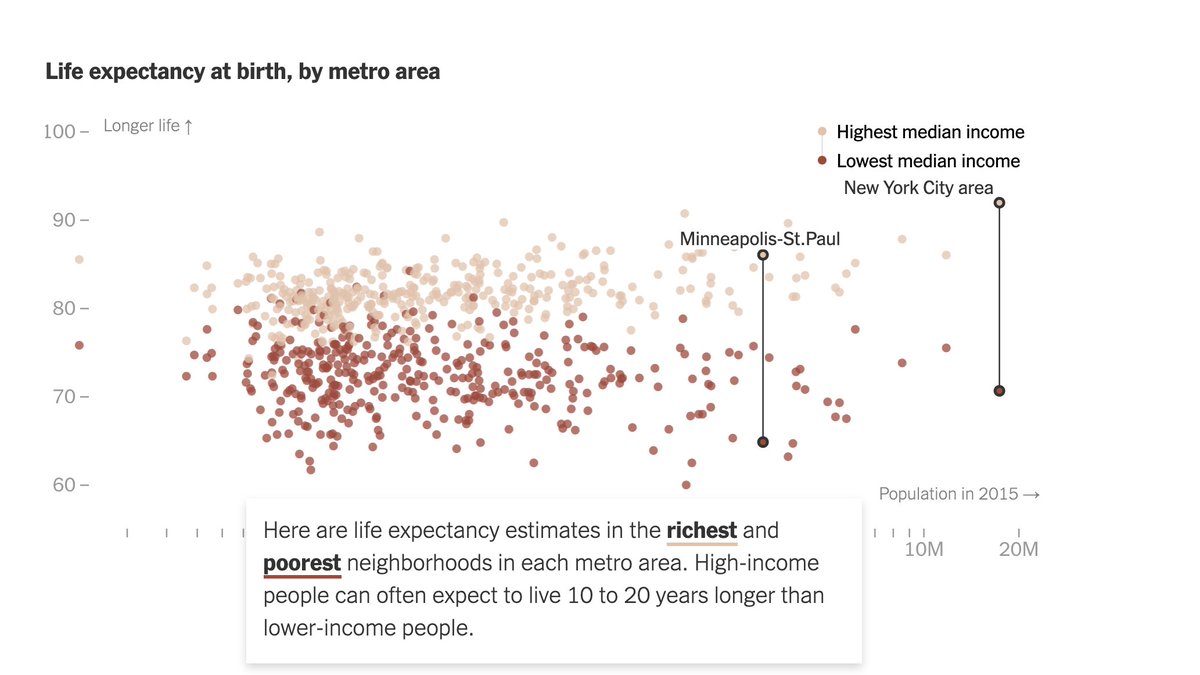
The average life expectancy in most American metro areas hovers around 80 years. But there are vast differences by neighborhood - sometimes more than 20 years between the richest and poorest.
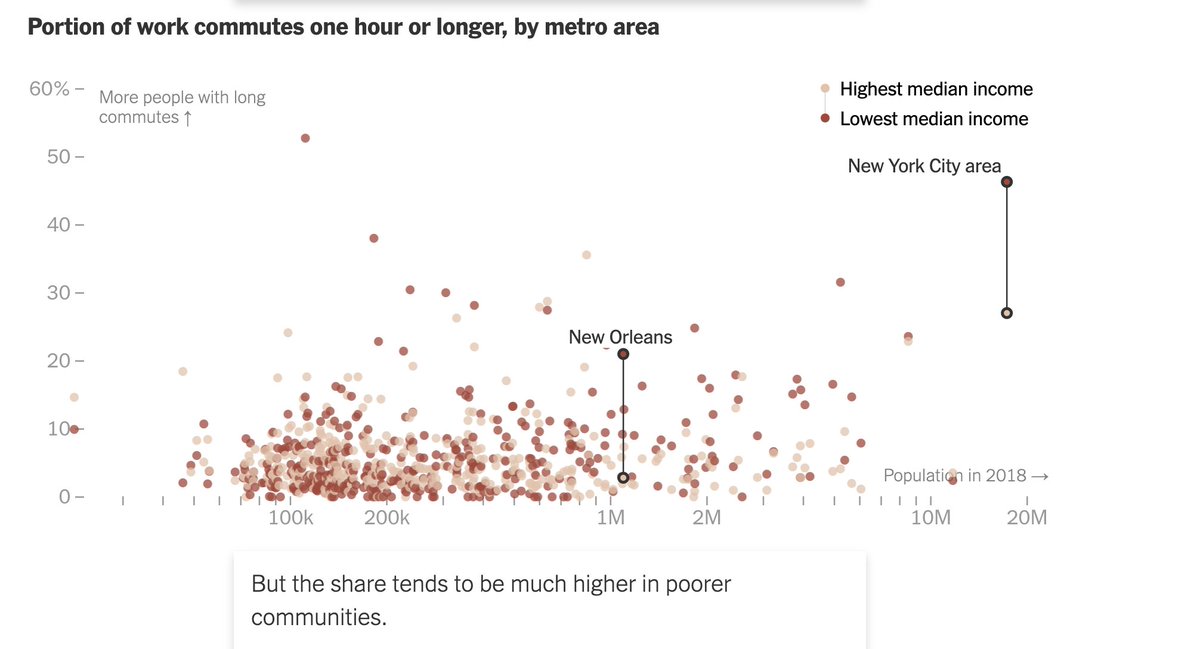
One of the forces holding down economic mobility is physical mobility. The poor face much longer commutes than the affluent:
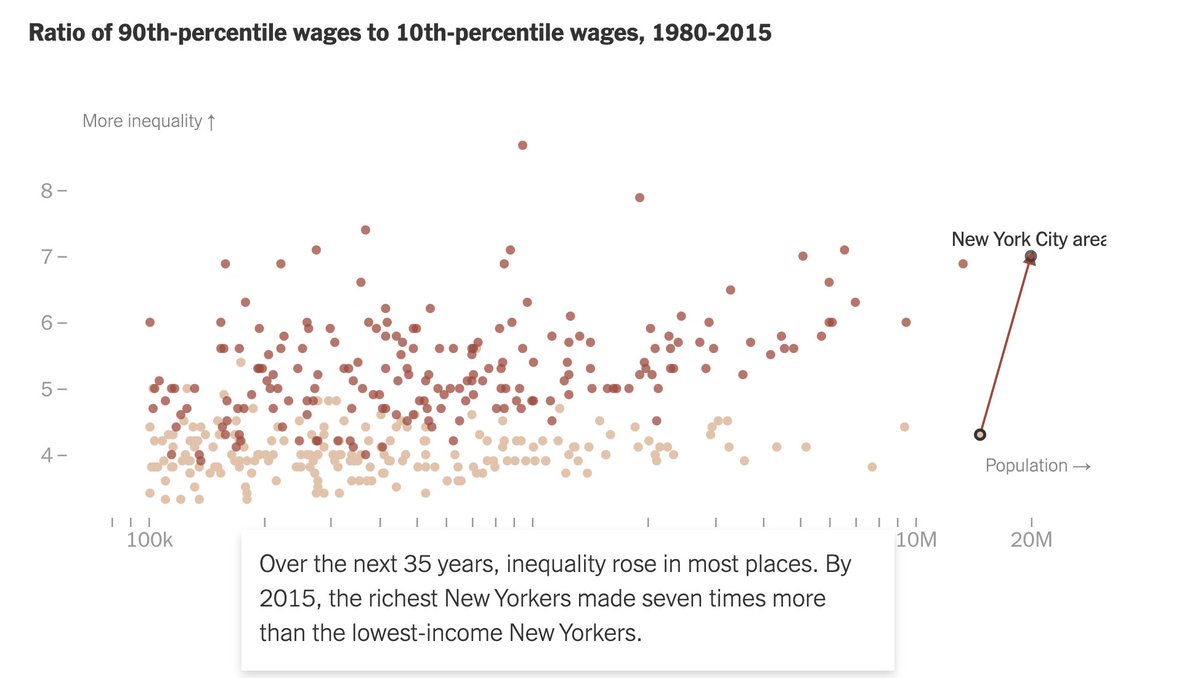
In addition to the growth in inequality within metro areas, inequality across metro areas has also surged. A small number of areas account for a large and growing share of jobs, income, wealth, venture-capital funding and more. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/05/13/opinion/inequality-cities-life-expectancy.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...
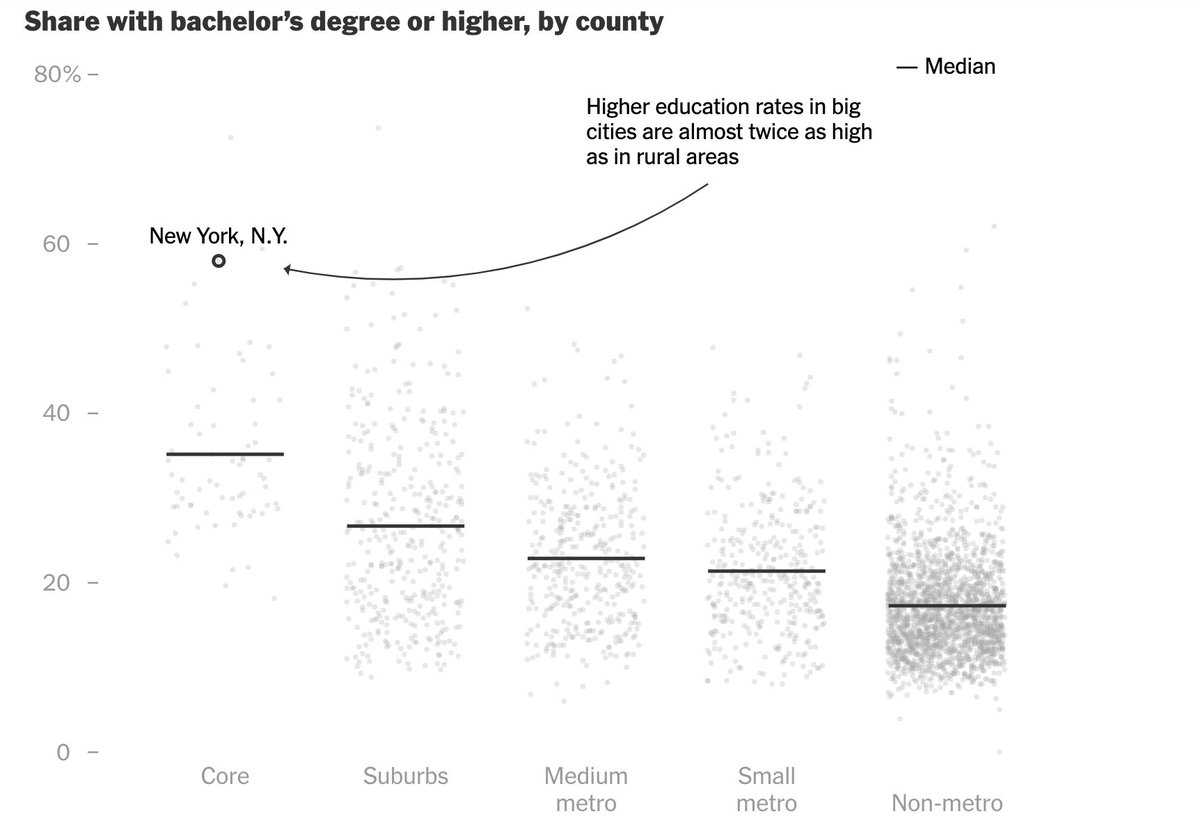
The largest and most prosperous metro areas now attract an even larger share of college graduates than in the past.
The largest metro areas also have a larger share of the country’s jobs than in the past. From 2010 to 2016, Manhattan accounted for almost 2% of the nation’s employment growth, despite having only about 0.5% of the population.
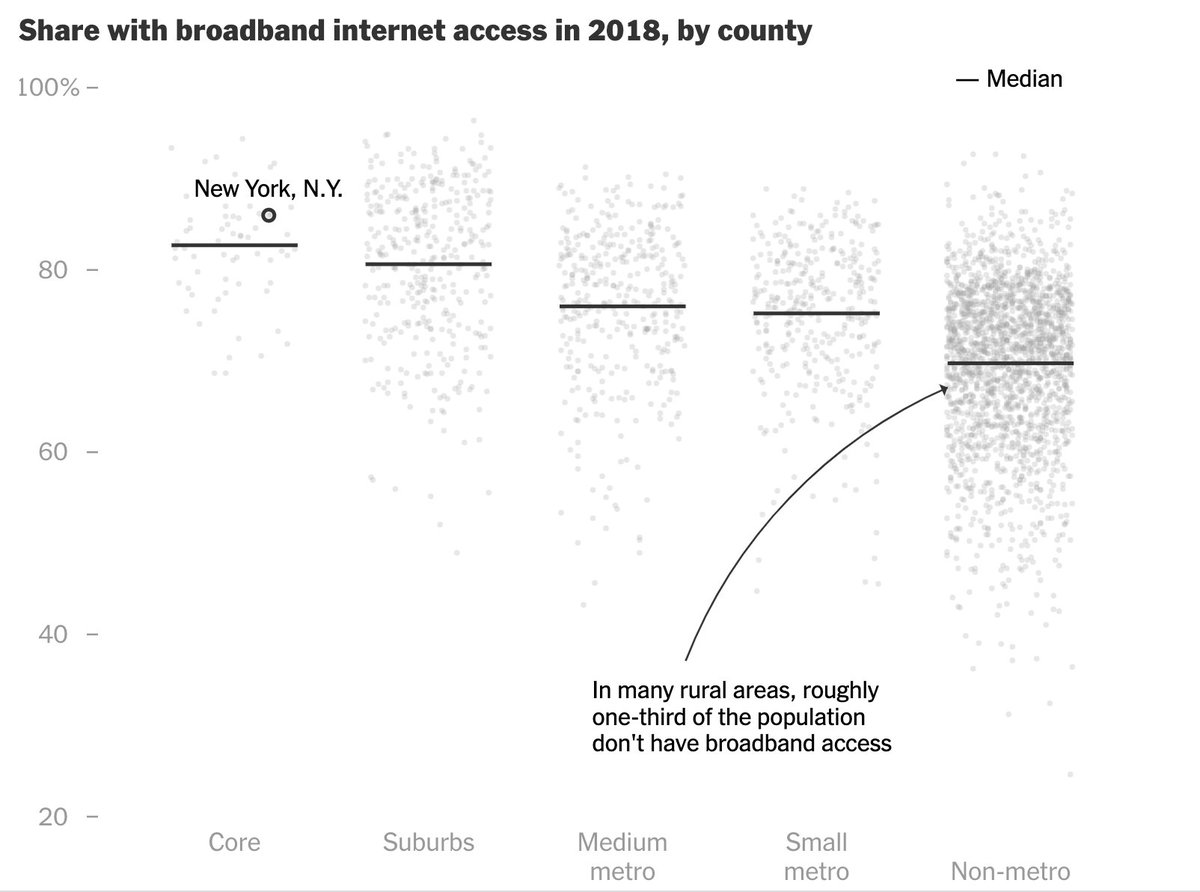
In smaller metro areas and rural regions, a sizable share of the population often broadband internet access.
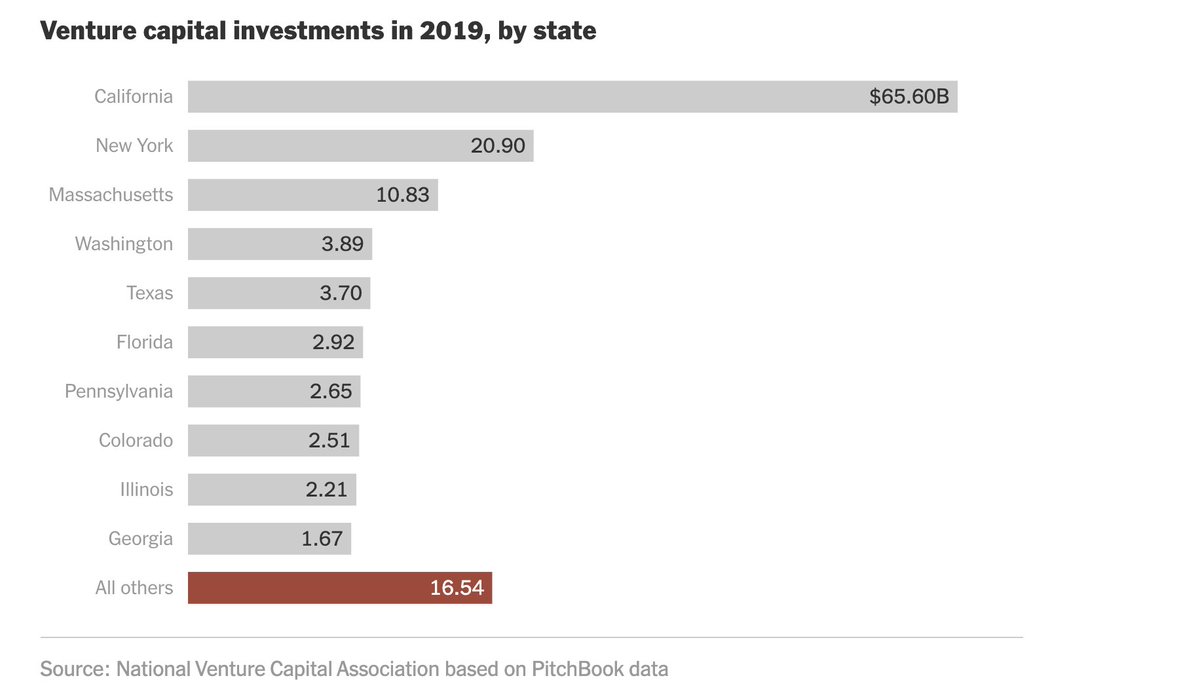
The same patterns show up with venture capital investment. More than 70 percent of it has recently flowed to only three states: California, New York and Massachusetts:
Cities are still the country’s most economically dynamic places. But they are also a microcosm of the extreme inequality that shapes so much of American life in the early 21st century. (end) https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/05/13/opinion/inequality-cities-life-expectancy.html">https://www.nytimes.com/interacti...

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter