This is a result that many hoped. Today the @NEJM published a small cohort study on the compassionate use of Remdesivir for severe #COVID19 patients in ICU under mechanical ventilation showing 18% mortality (6/34). Let& #39;s have a look at the details
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2007016?query=featured_coronavirus">https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/...
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2007016?query=featured_coronavirus">https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/...
First the basics. What is Remdesivir? In short it is an antiviral drug, nucleic analog incorporating into the viral RNA, which leads to termination of transcription, which blocks virus replication
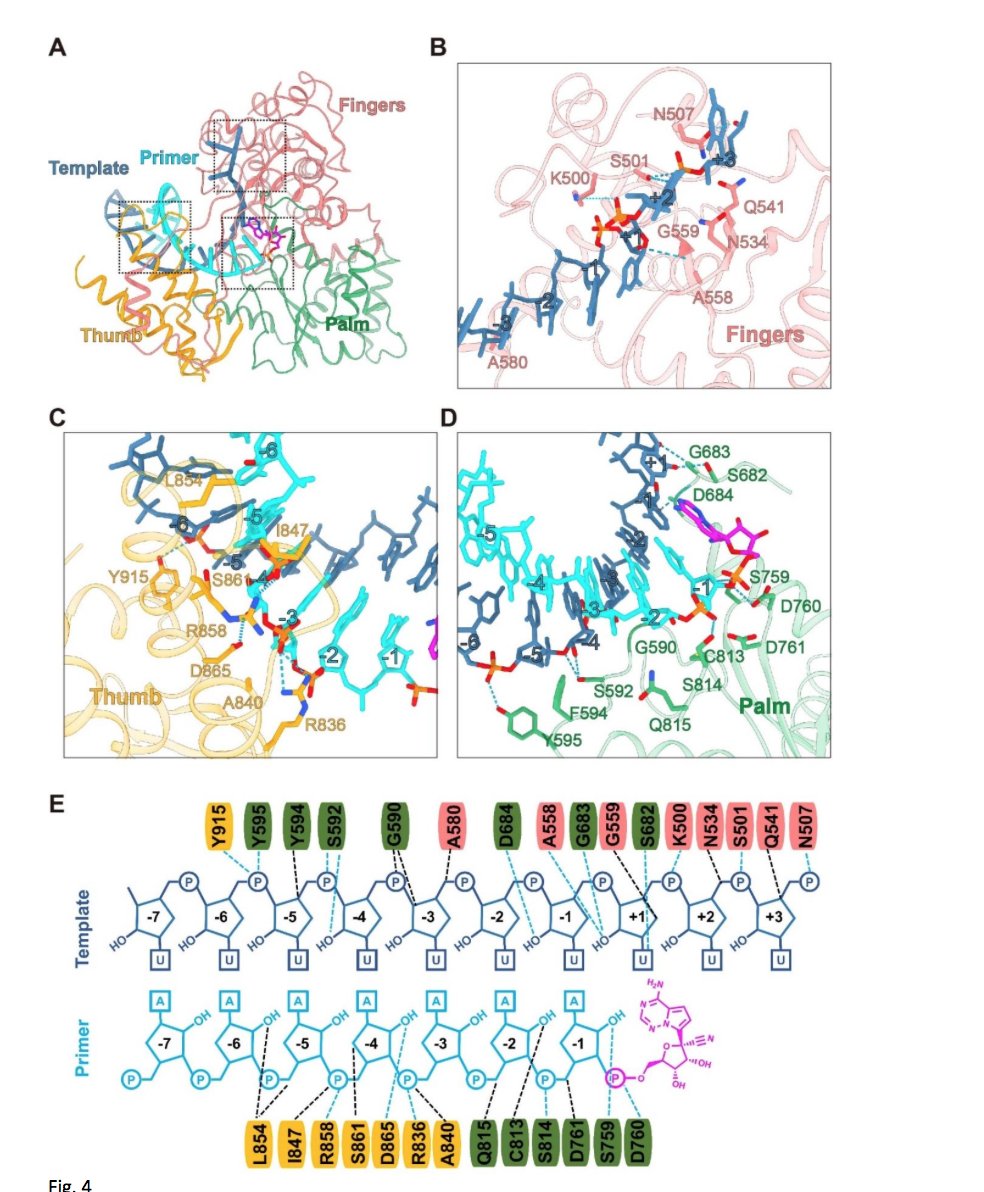
We have now a very good idea how does Remedesivir blocks #SARSCoV2 virus replication from a beautiful paper that came out yesterday detailing the mechanisms -> directly targeting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), critical for many virus to replicate
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.08.032763v2">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.08.032763v2">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
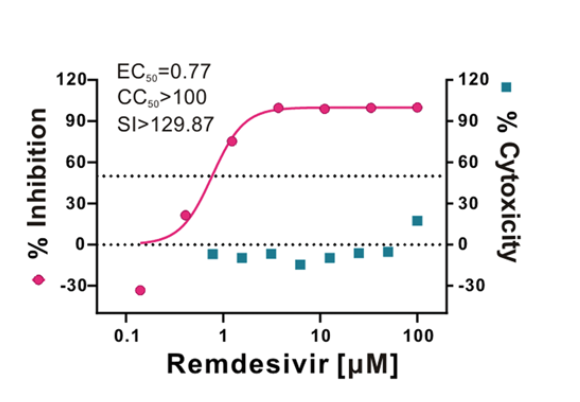
As Remdesivir blocks viral RNA polymerase, an hypothesis is it might be blocking viral replication for many viruses. Remedisivir was tried for few viruses such as Ebola, MERS or SARS. Remdesivir was assayed In-vitro for #SARSCoV2 & the EC50 was 0.77 µM https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-020-0282-0">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
So next what about Remdesivir clinical efficacy against #COVID19? Wile while randomized clinical trials are still underway, this cohort study came out today in @NEJM. This is a small cohort study of 61 patients. Let& #39;s now go into the details of this study.
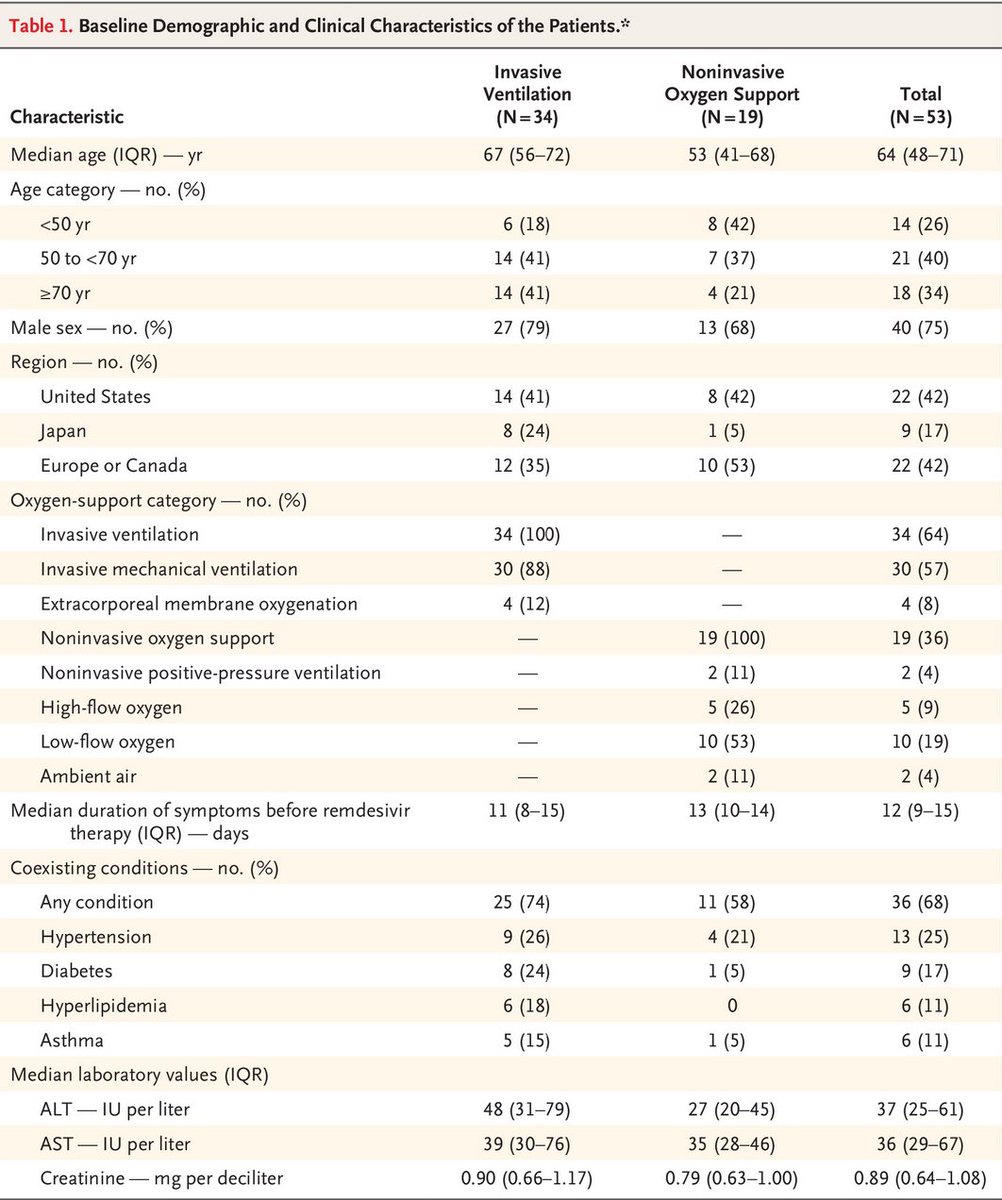
This study is based on the compassionate use of remdesivir on #COVID19 patients in ICU. Incl criteria -> hospitalized patients, Sao2 <94%, RT-PCR for SARSCov2 pos, creatininemia >30 ml/min, ALT & AST enzymes < 5x normal and agreed to do not use others investigative drugs
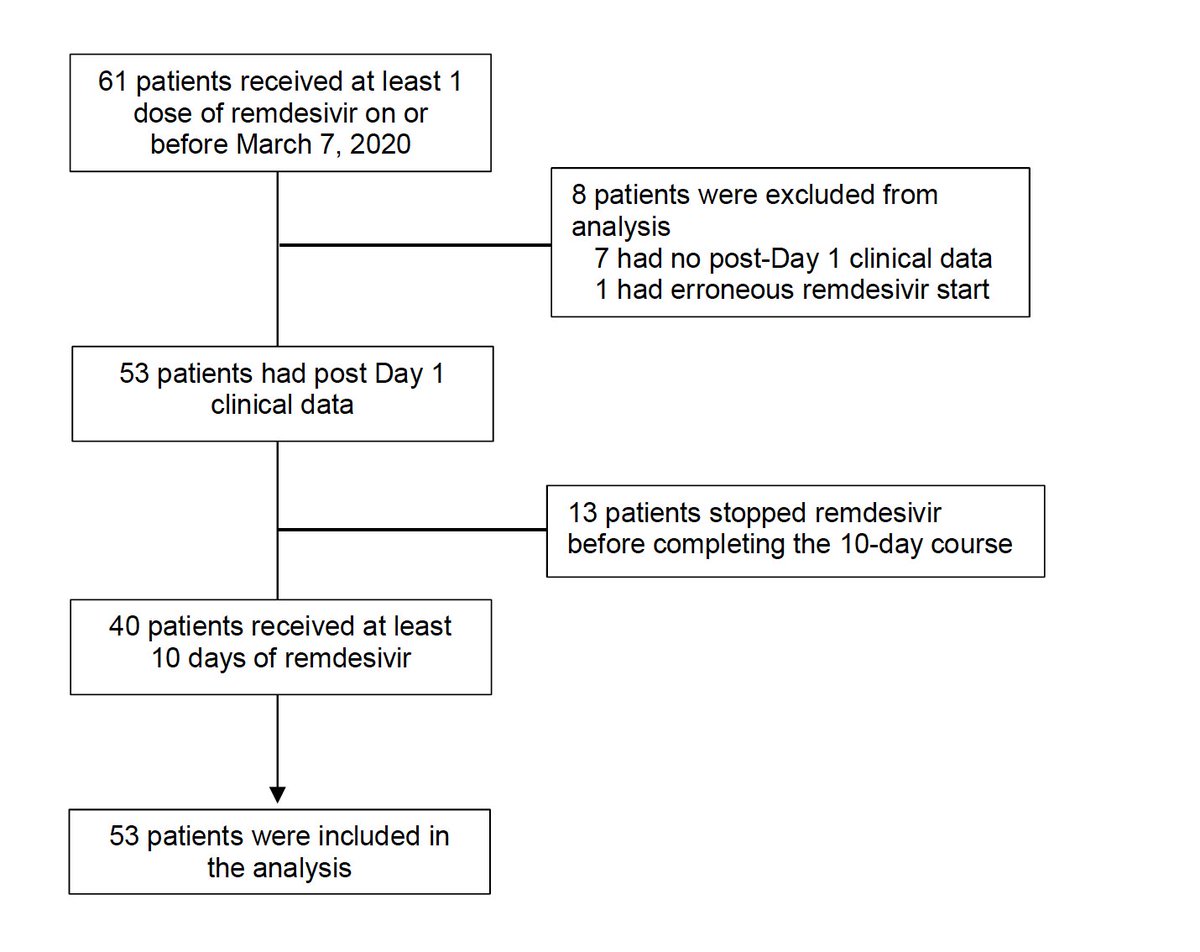
Treatment: 200 mg day1 IV followed by 100 mg/day for 9 days.Follow up for 28 days. Caveat: IV administration -> No remdesivir outside hospital 2/ Open labeled, 3/ no control included. So 61 patients enrolled, 8 excluded and 13 stopped for side effects. 40 received full treatment.
Outcomes based on clinical assessment (improvement such as oxygen requirement or extubation), laboratory analysis (creat, ALT, AST level) but not viral load ! In short we don& #39;t know if the treatment regimen has reduced viral load. No power calculation done for patient inclusion
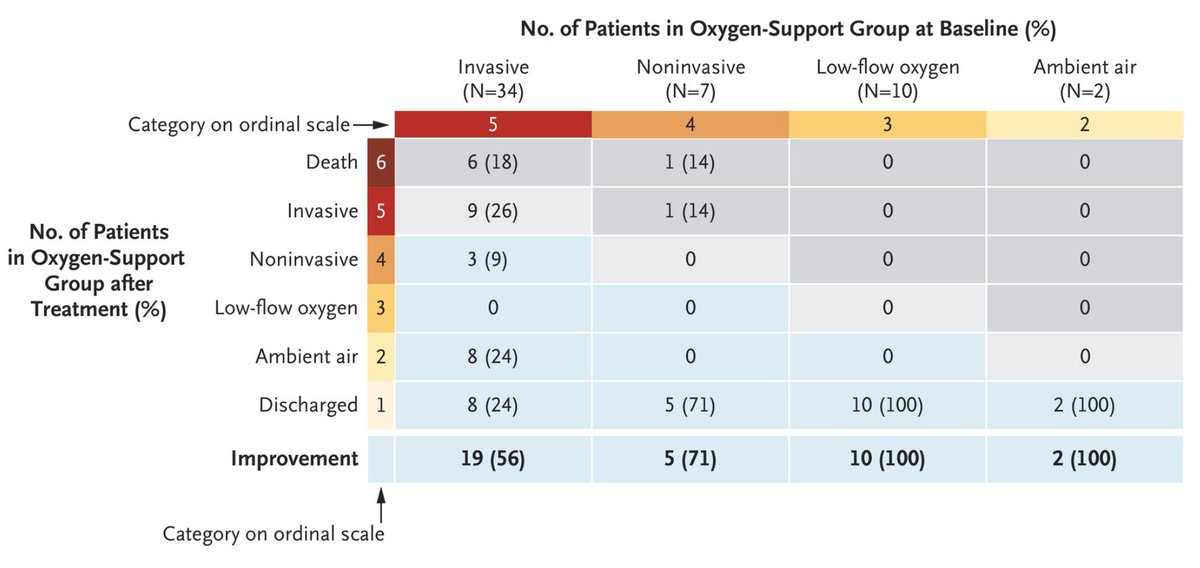
Results. 34/41 on invasive ventilation, 8/42 on non invasive oxygen support. Cohort age > mechanical ventilation than non invasive one. Important point fatality rate for #COVID19 ventilated patients is high (>50%) from various reports https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(20)30079-5/fulltext">https://www.thelancet.com/journals/...
Outcome mortality 6/34 = 18%, which seems low as 50% mortality is expected for these patients but 8/53 patients worsened. According to the Kaplan-Meier younger patients improves better, which is not a surprise. Is this due to the remdesivir treatment? I have no idea
Side effects: There are quite a few reported on 60% of this cohort, mainly on those that underwent mechanical ventilation. Side effect, Diarrhea, hypotension, increase ALT, AST... but again caveat, we don& #39;t know if this is due to the treatment of the patient condition.
In conclusion, it seems Remdesivir might improve clinical outcomes in these #COVID19 severe patient from this small cohort. However there are so many caveats in this study that is almost impossible to conclude anything about it. Of course a randomized trial is needed.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter