Here is @EricMeyerowitz and my #COVID-19 literature UPDATE 3/25-4/8
Slides: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/13nbSCnJDQKtidyZR663GkmE5cX9wCwa7U5hwHWDgRnY/edit?usp=sharing
Recording:
https://docs.google.com/presentat... href="
Key">https://www.youtube.com/watch... messages with study links below:
Slides: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/13nbSCnJDQKtidyZR663GkmE5cX9wCwa7U5hwHWDgRnY/edit?usp=sharing
Recording:
Key">https://www.youtube.com/watch... messages with study links below:
63% of in-room air samples in mild cases were positive for viral RNA, but importance of airborne transmission remains uncertain. Our health system has started using N95s for all suspected/confirmed COVID-19
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.23.20039446v2">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.23.20039446v2">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
SARS-CoV-2 viable after 2 weeks at 4C, but rapidly degrades at 56C or higher
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.15.20036673v2">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.15.20036673v2">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
In influenza and non-COVID coronaviruses, masks reduce recovery of droplets and aerosols => suggested importance of masks in reducing transmission for SARS-CoV-2 presymptomatic phase?
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-020-0843-2">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-020-0843-2">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
Case report of pre-symptomatic infant with positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR, viral RNA isolated multiple places within the room. Are children, even non-mobile infants, an important source of asymptomatic viral transmission?
https://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2764249/environment-personal-protective-equipment-tests-sars-cov-2-isolation-room">https://annals.org/aim/fulla...
https://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2764249/environment-personal-protective-equipment-tests-sars-cov-2-isolation-room">https://annals.org/aim/fulla...
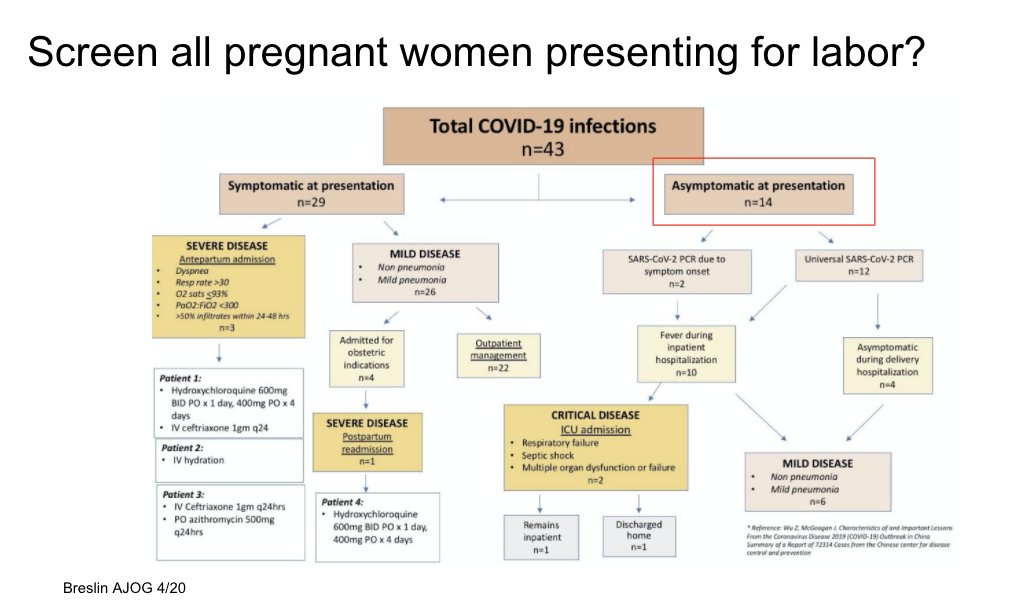
Early data from Columbia experience with pregnant women with COVID-19. Importantly, they initiated universal screening and identified a significant number of women who were presymptomatic at presentation. Important infection control implications.
…https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets/raw/Health%20Advance/journals/ymob/43_COVID_040320-1586192348270.pdf">https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets...
…https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets/raw/Health%20Advance/journals/ymob/43_COVID_040320-1586192348270.pdf">https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets...
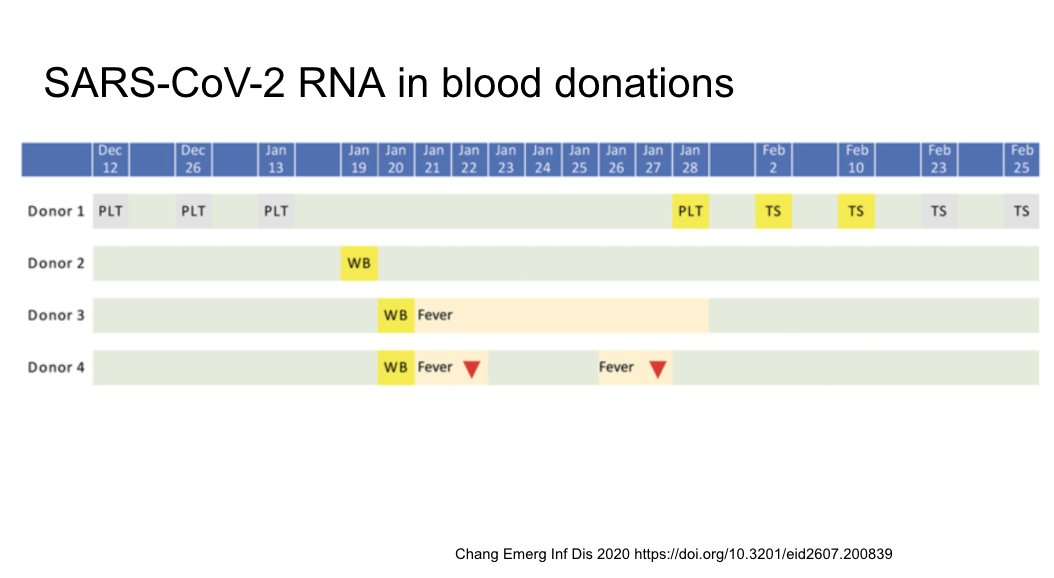
Screening of the Wuhan blood supply identified four cases of +RNA in the blood. Importance of viremia and bloodborne transmission is still unknown.
https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/26/7/20-0839_article">https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/artic...
https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/26/7/20-0839_article">https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/artic...
Cohort study of 33 neonates in which 1 was infected after strict quarantine after delivery. Authors hypothesize vertical transmission but nosocomial transmission still probably more likely?
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2763787">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2763787">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
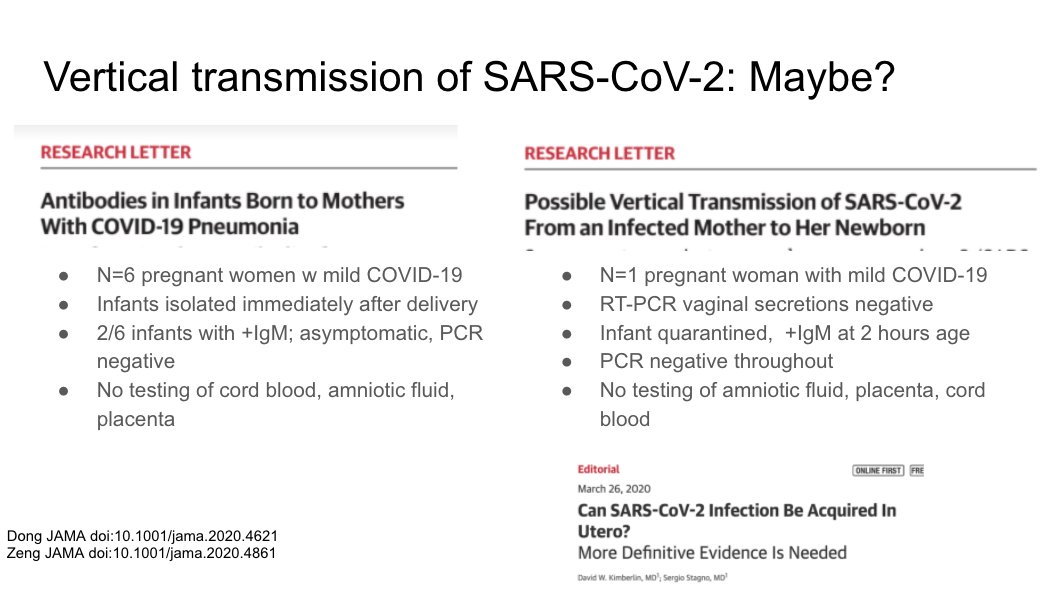
Two studies finding positive IgM in neonates, they hypothesize vertical transmission / in utero infection. However, many caveats to this as beautifully described in the accompanying editorial.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763854
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/... href=" https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763853
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/... href=" https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763851">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763854
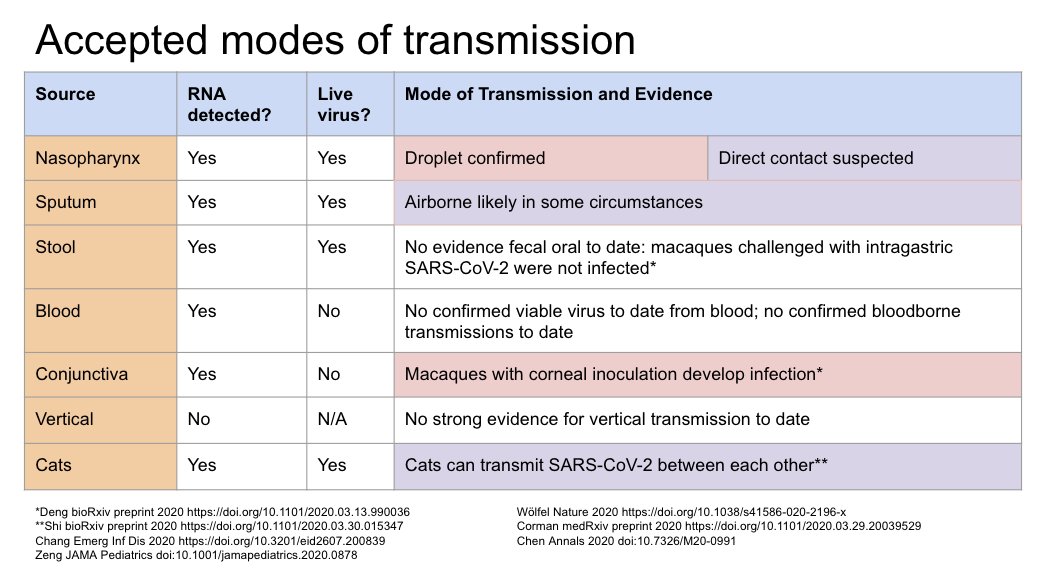
New table by @EricMeyerowitz outlining accepted modes of transmission and summarizing the evidence. References below.
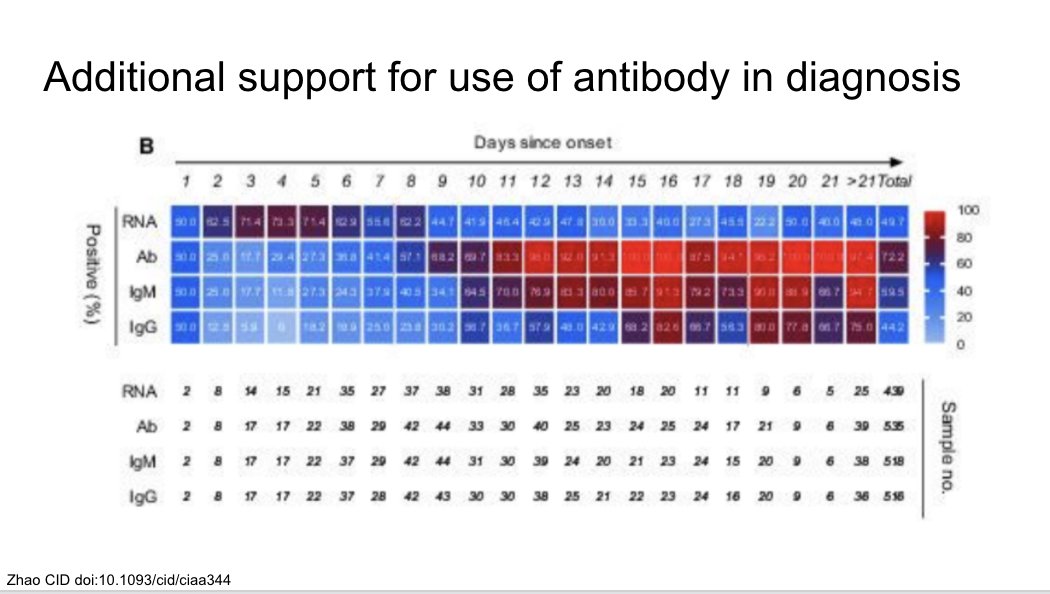
Another study in CID supporting the use of IgM in diagnosis in certain situations: 7+ days of illness, consistent syndrome, and negative PCR testing. Redder boxes in the figure are higher rates of positivity.
https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa344/5812996">https://academic.oup.com/cid/advan...
https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa344/5812996">https://academic.oup.com/cid/advan...
In line with anecdotal reports, obesity seems to be an independent risk factor for severe disease.
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3556658">https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/pape...
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3556658">https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/pape...
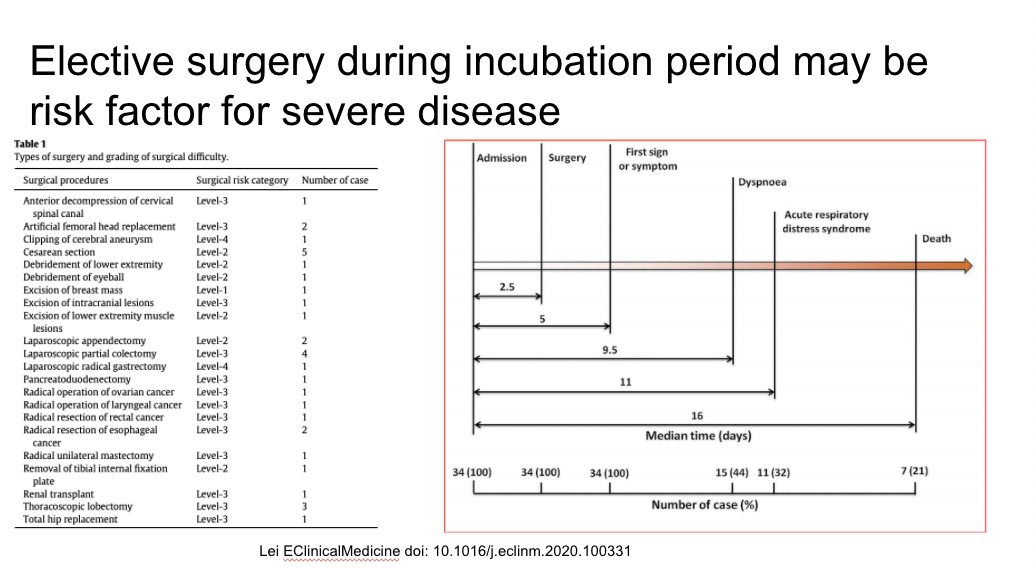
Very poor outcomes in this group that had elective surgery during the incubation period. Should all elective surgeries be pre-screened if prevalence is high enough?
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(20)30075-4/fulltext">https://www.thelancet.com/journals/...
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370(20)30075-4/fulltext">https://www.thelancet.com/journals/...
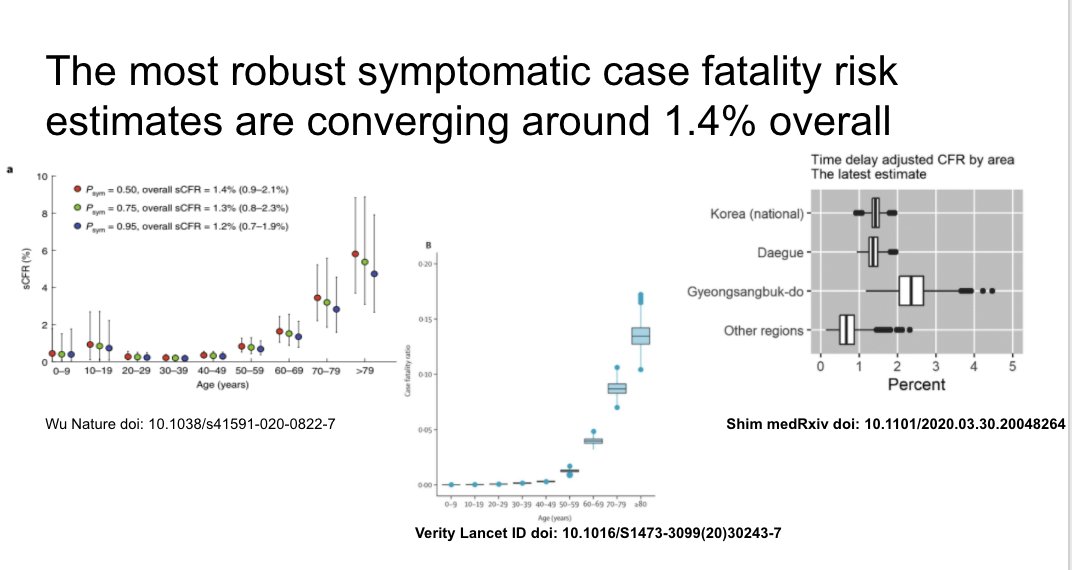
Most robust symptomatic CFR estimates converging around 1.4% overall. Will vary by age distribution in a given place, how deaths defined, testing strategy.
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(20)30243-7/fulltext
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/... href=" https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.30.20048264v1
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1... href=" https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-020-0822-7">https://www.nature.com/articles/...
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(20)30243-7/fulltext
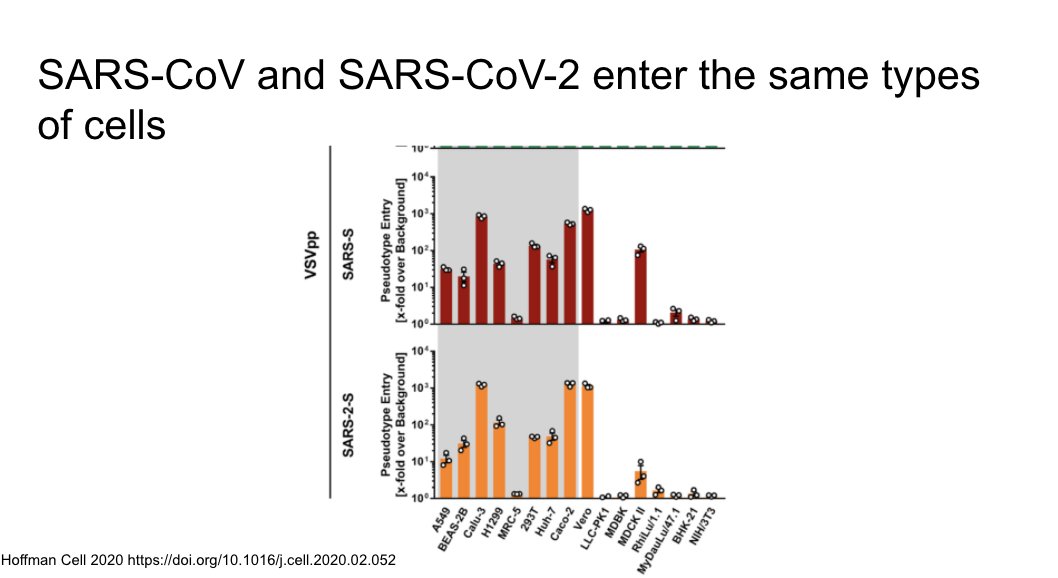
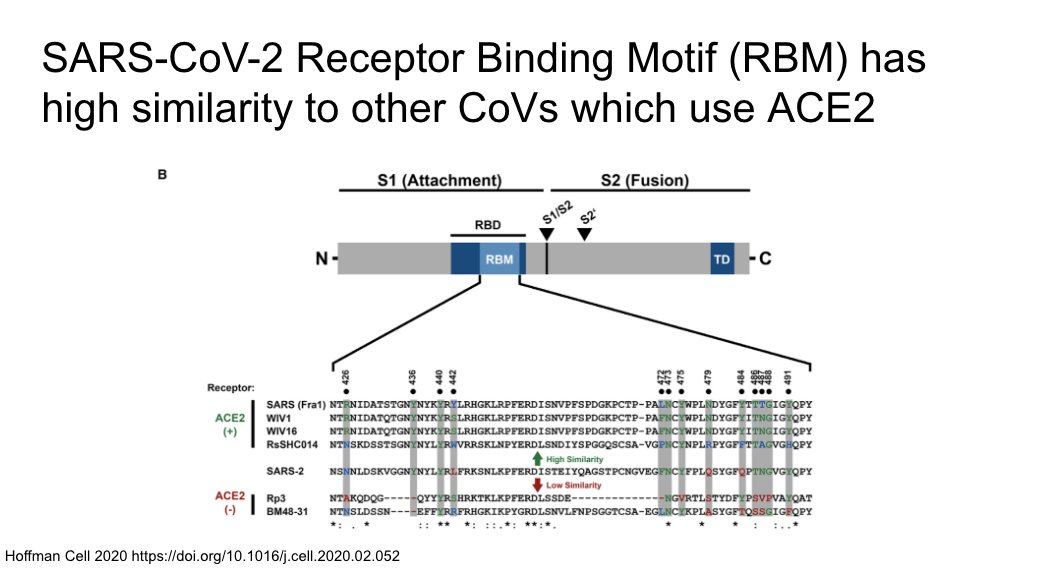
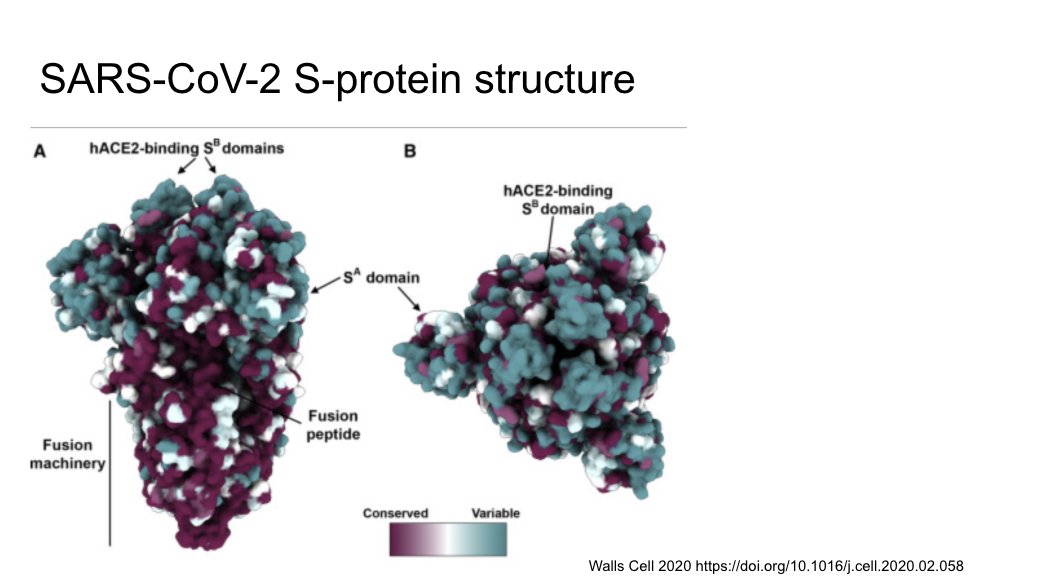
SARS 1 and 2 both enter the same types of cells
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302294">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302294">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
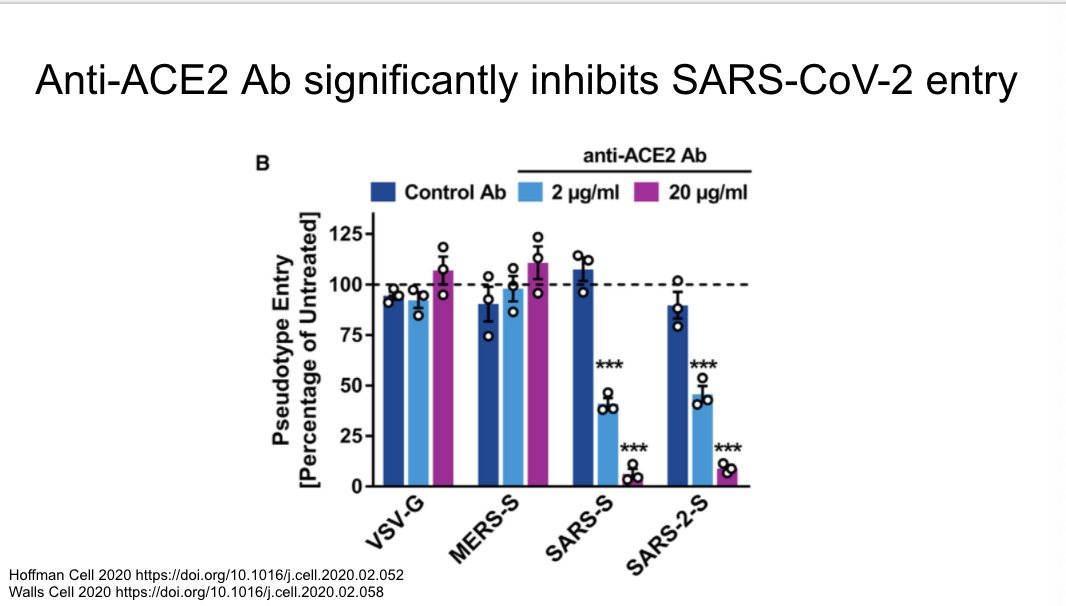
Anti-ACE2 ab significantly inhibits SARS-CoV-2
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302622">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302622">https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a...
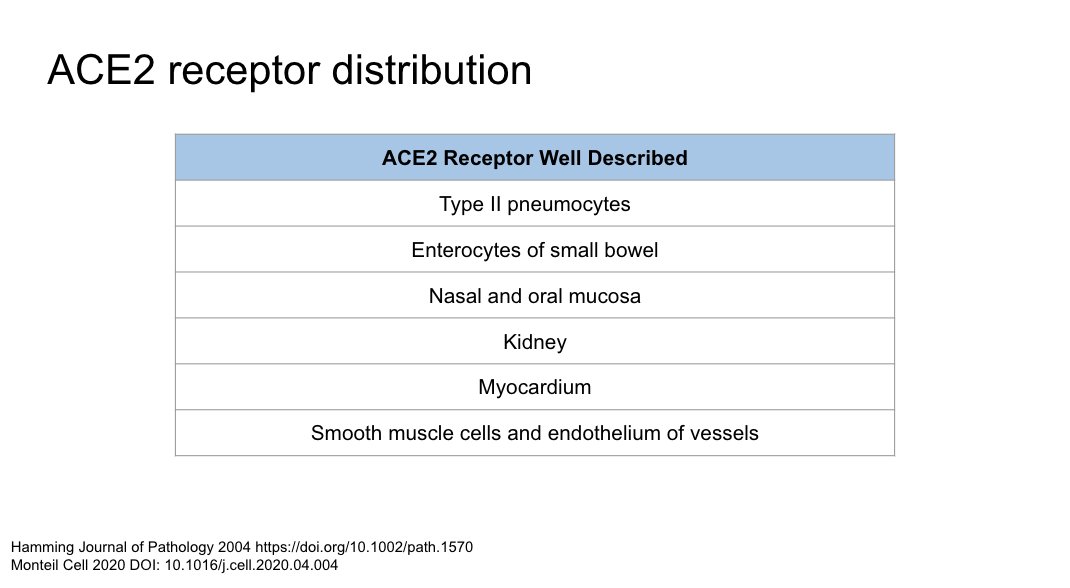
ACE2 receptor distribution within humans
https://www.cell.com/pb-assets/products/coronavirus/CELL_CELL-D-20-00739.pdf">https://www.cell.com/pb-assets...
https://www.cell.com/pb-assets/products/coronavirus/CELL_CELL-D-20-00739.pdf">https://www.cell.com/pb-assets...
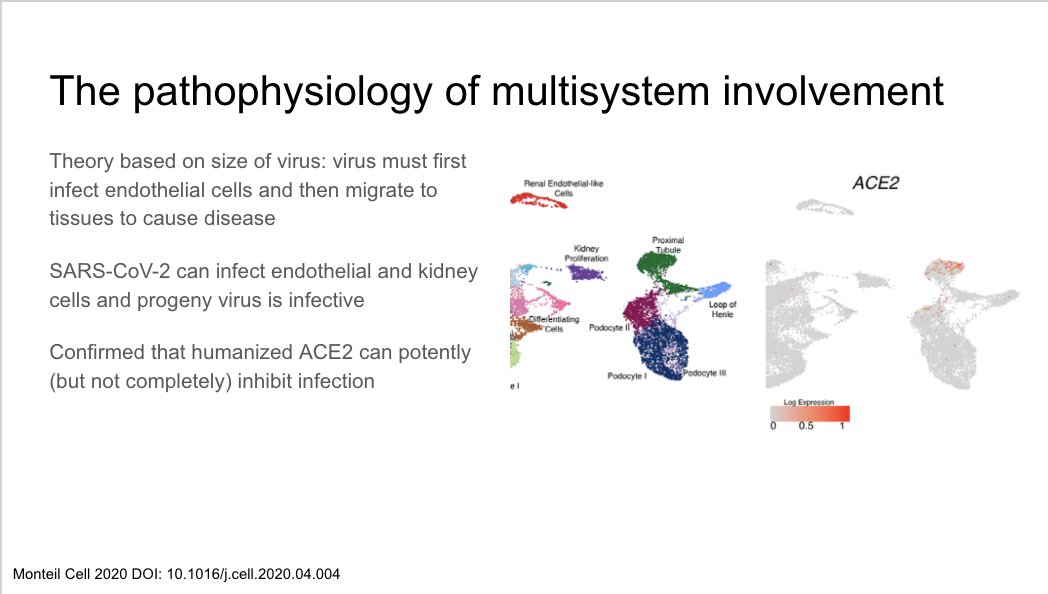
Theorized that because of virus size, it first infects endothelial cells before migrating to other tissues to cause disease. Paper shows SARS-CoV-2 can infect endothelial and kidney cells. humanized ACE2 can inhibit
https://www.cell.com/pb-assets/products/coronavirus/CELL_CELL-D-20-00739.pdf">https://www.cell.com/pb-assets...
https://www.cell.com/pb-assets/products/coronavirus/CELL_CELL-D-20-00739.pdf">https://www.cell.com/pb-assets...
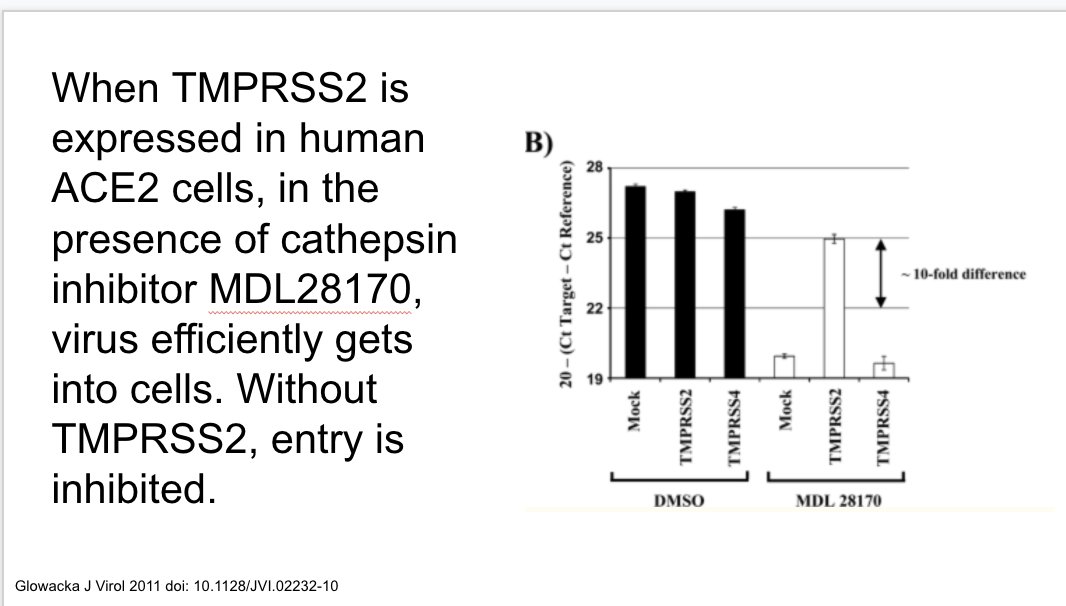
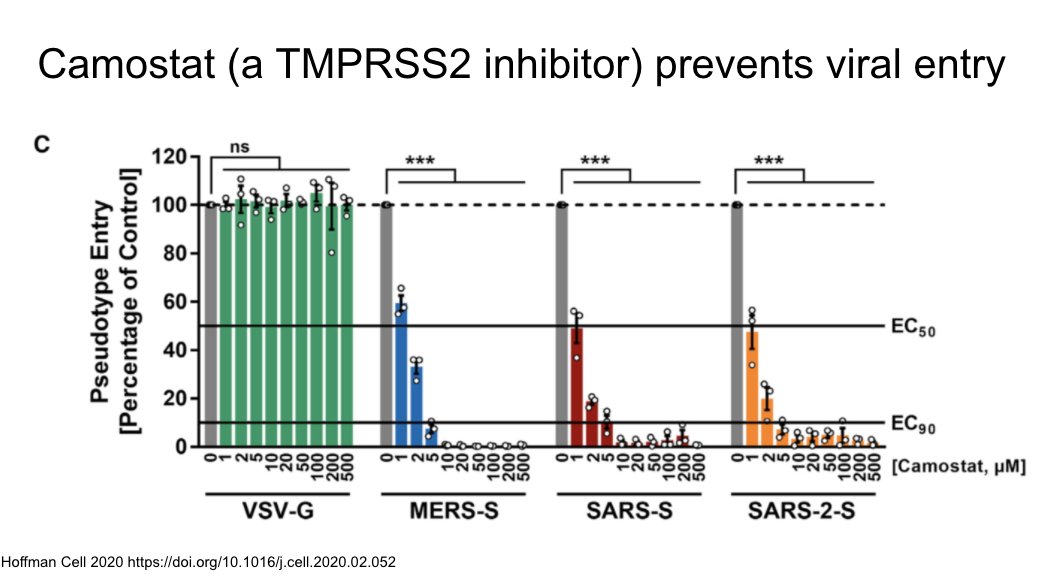
Camostat is a TMPRSS2 inhibitor and in experimental conditions prevents viral entry. Being studied clinically now.
https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302294">https://sciencedirect.com/science/a...
https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867420302294">https://sciencedirect.com/science/a...
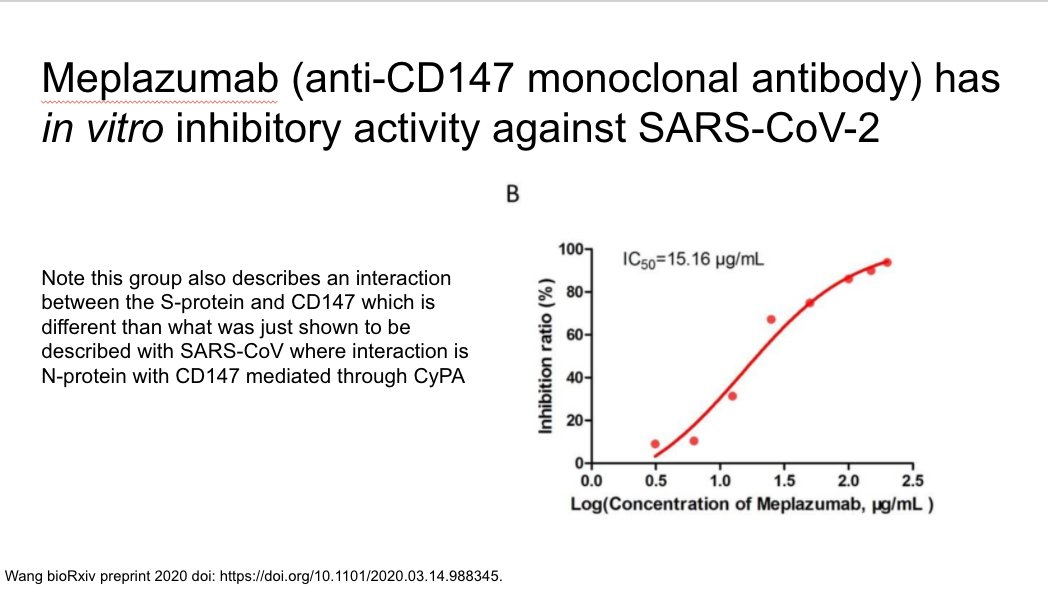
meplazumab is an anti-CD147 antibody that has in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.14.988345v1.full.pdf">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.14.988345v1.full.pdf">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
A non-randomized study of meplazumab suggests higher rates of discharge and viral clearance. Hypothesis-generating, hopefully RCT to follow.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.21.20040691v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.21.20040691v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
RAAS update: great review of RAAS and COVID interactions in NEJM, but highlights that really very little is known. worth a read
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsr2005760">https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/...
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsr2005760">https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/...
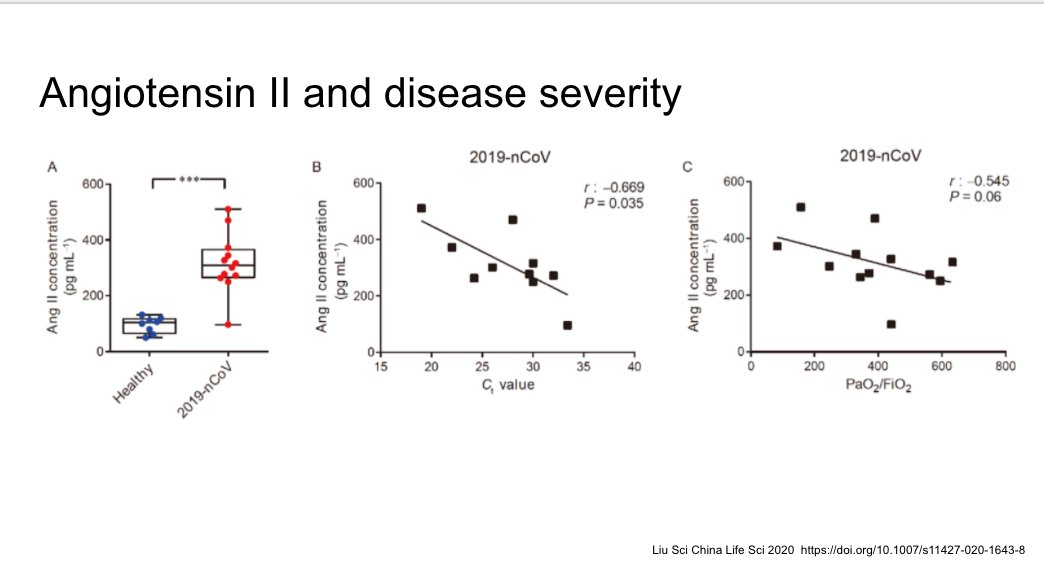
That said, angiotensin II in the blood associated with disease severity, as in some other ARDS. Authors hypothesize this is related to downregulation of ACE2 from infection.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11427-020-1643-8">https://link.springer.com/article/1...
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11427-020-1643-8">https://link.springer.com/article/1...
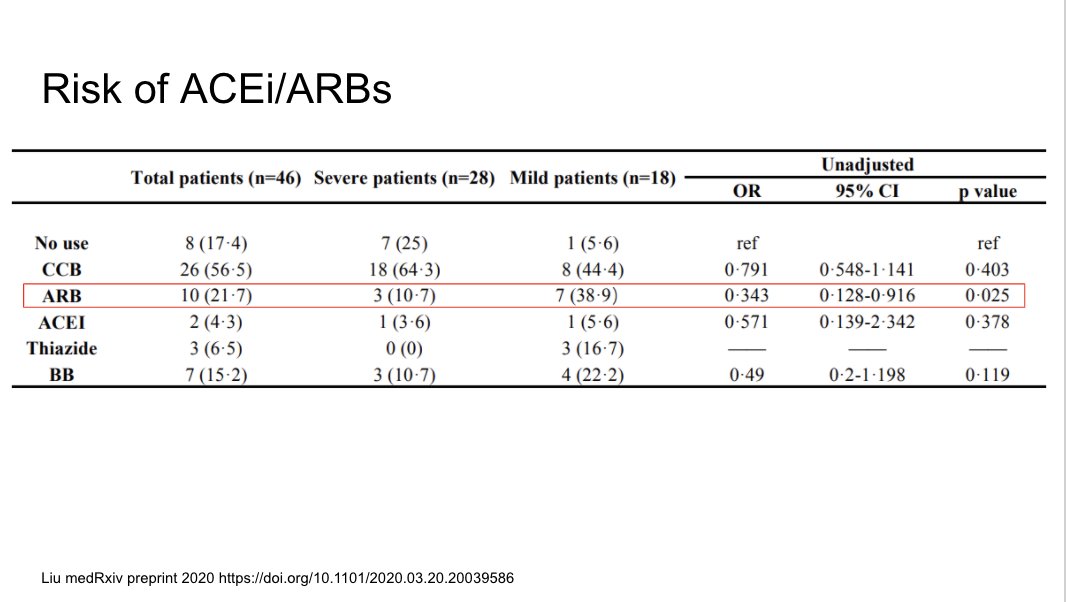
We don& #39;t have good data on whether ACEi and ARBS increase risk, or decrease risk. This is a very confounded study.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.20.20039586v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.20.20039586v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
Some slides on antibodies and immunity.
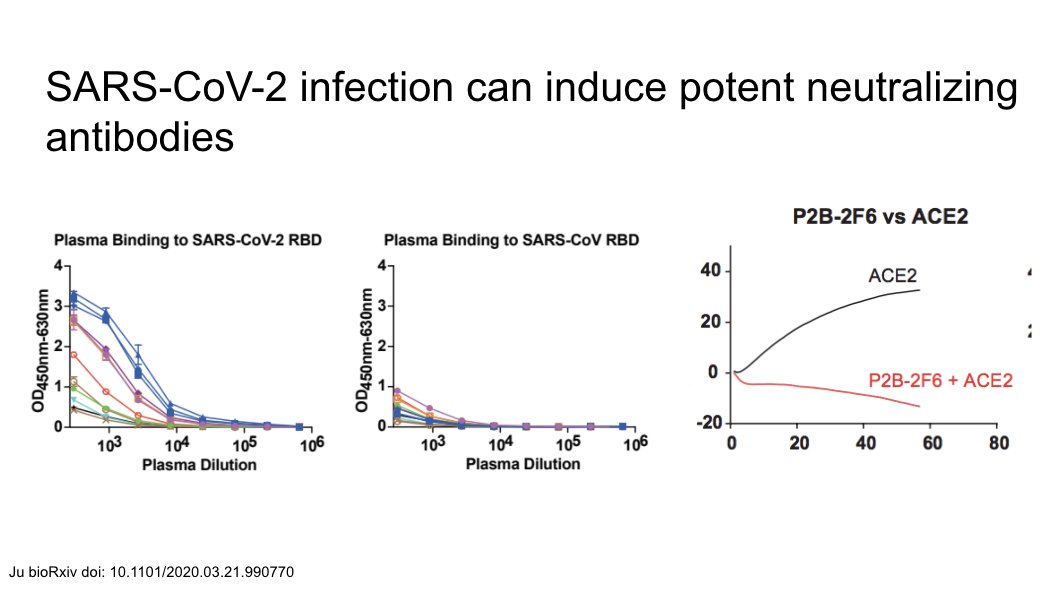
Here is a study showing development of potent neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.21.990770v2">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
Here is a study showing development of potent neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.21.990770v2">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
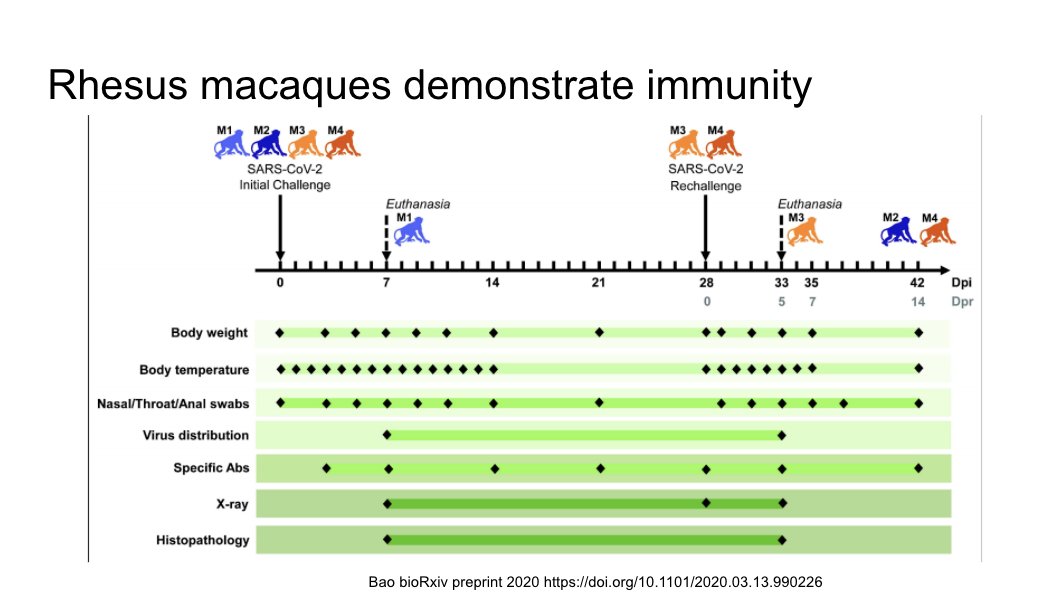
Rhesus macaques demonstrated short term immunity in this pre-print, but we don& #39;t know about long term and how this translated to humans.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.13.990226v1">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.13.990226v1">https://www.biorxiv.org/content/1...
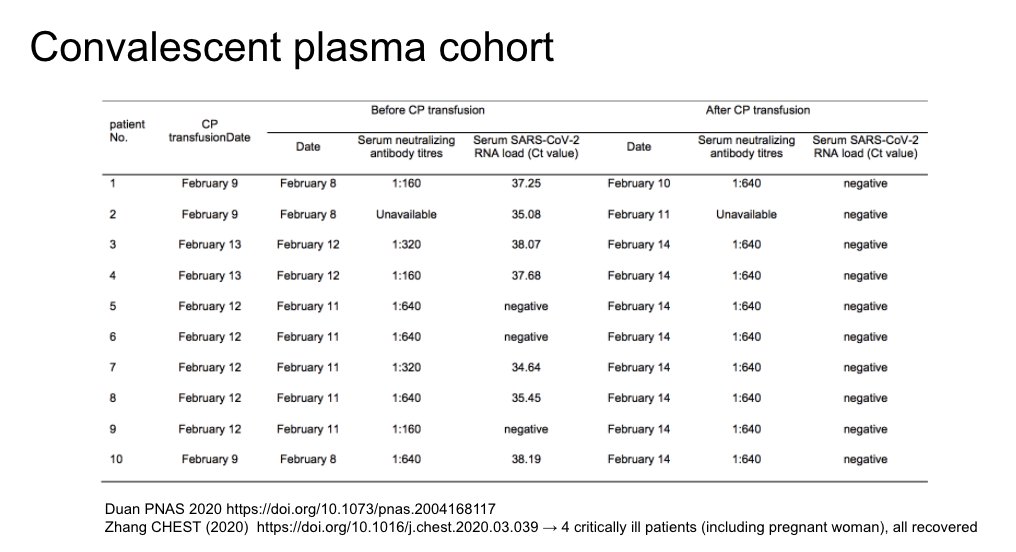
Some new series of convalescent plasma that are non-controlled. Efficacy and context for use remain uncertain.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012369220305717
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/a... href=" https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2020/04/02/2004168117
https://www.pnas.org/content/e... href=" https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2763983">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012369220305717
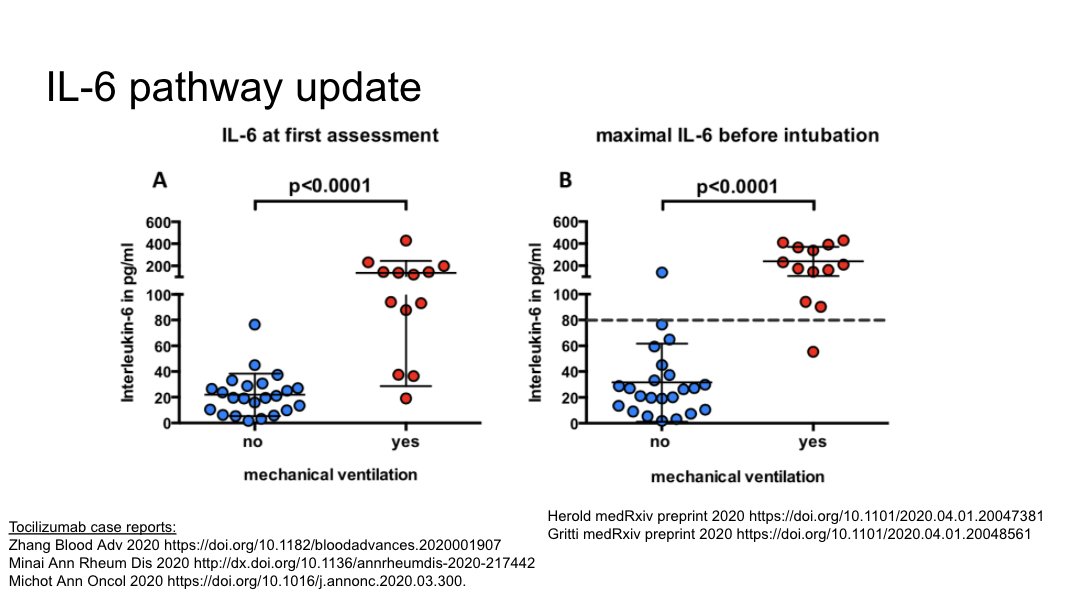
Continued interest in IL-6 pathway and role of therapeutics targeting this pathway. A number of reports referenced in the slide.
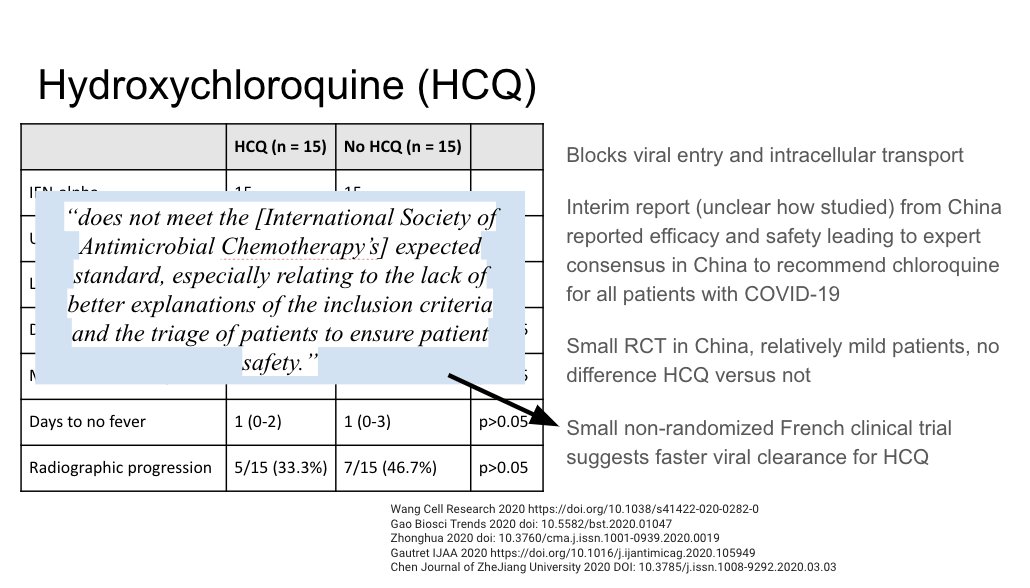
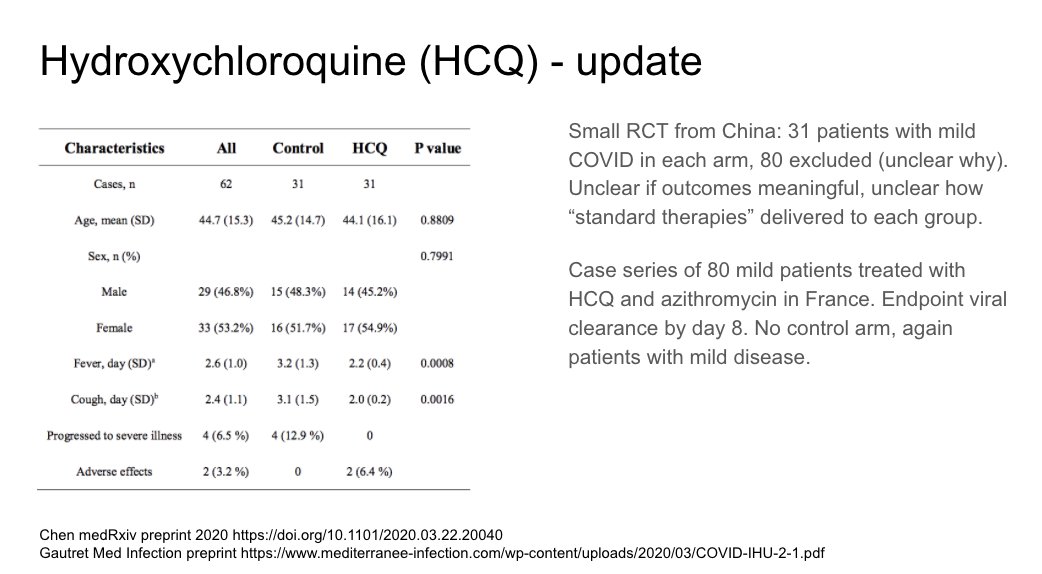
Additional HCQ data, in particular a small RCT in China with soft outcomes and a lot missing in the report. Fairly uninterpretable
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.20040">https://doi.org/10.1101/2...
https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.20040">https://doi.org/10.1101/2...
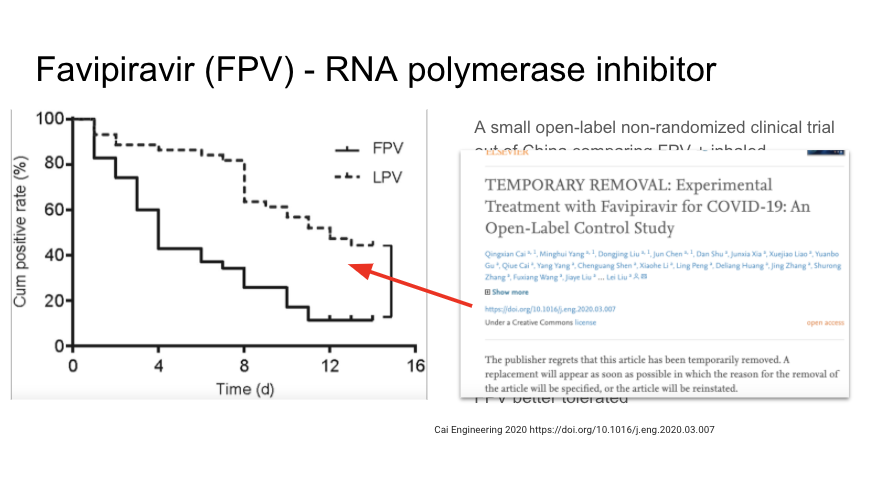
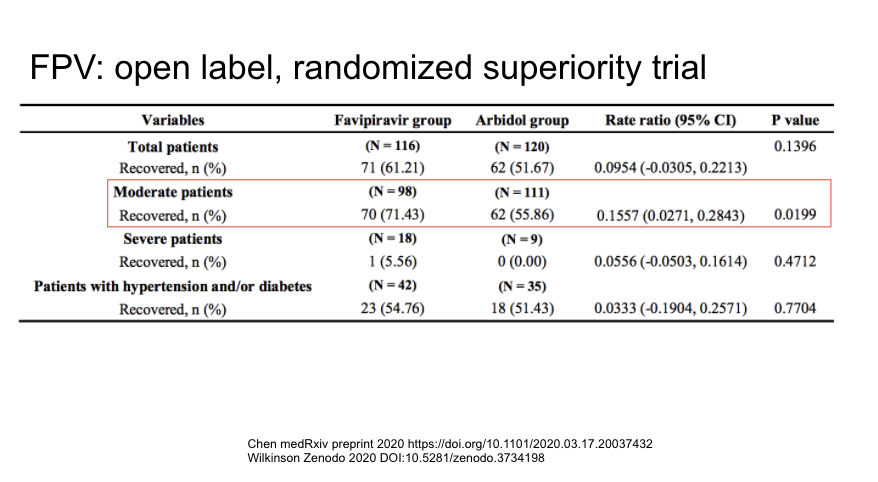
A new open-label RCT of favipiravir vs arbidol (another anti-viral) found a questionable benefit in a non-specified sub group. Provocative but need additional data....
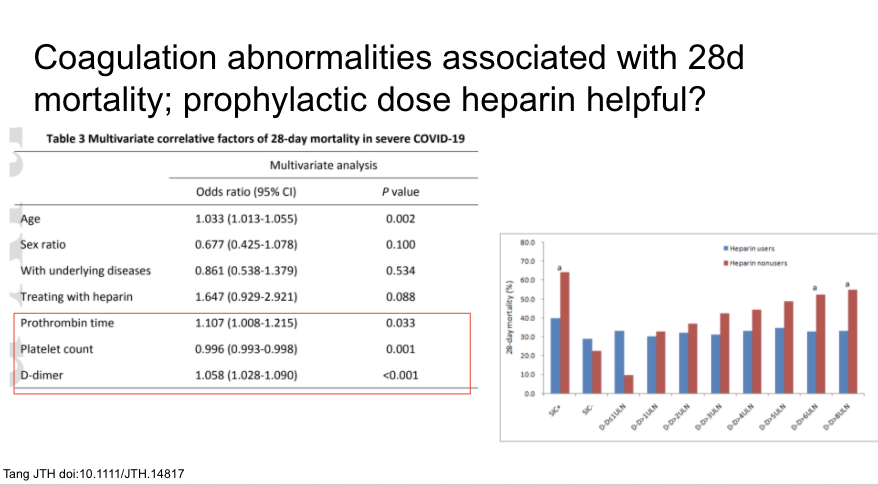
Coagulation abnormalities are associated with 28d mortality in this pretty flawed study that also suggested ppx dosing AC may be important with high d-dimer. Need a lot more good data on this question which comes up again and again clinically.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jth.14817">https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.11...
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jth.14817">https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.11...
In keeping with the previous slide, microthrombi have been reported in a couple autopsy studies
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339984522_A_pathological_report_of_three_COVID-19_cases_by_minimally_invasive_autopsies">https://www.researchgate.net/publicati...
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339984522_A_pathological_report_of_three_COVID-19_cases_by_minimally_invasive_autopsies">https://www.researchgate.net/publicati...
A few new studies on cardiac injury.
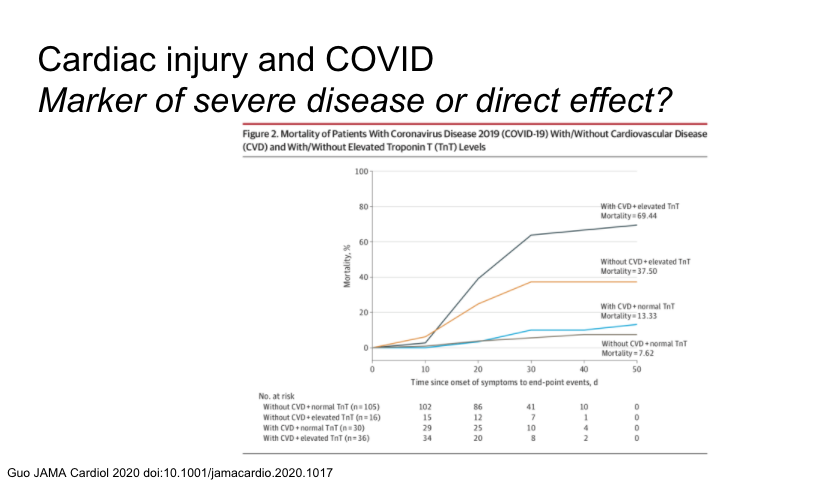
the first was of 187 patients receiving care at one hospital in Wuhan. Troponin T elevation associated with co-morbidity, ARDS, VT/VF, coagulopathy. In hospital mortality 60% in cardiac injury and 9% without. Most prominent in those with CVD
the first was of 187 patients receiving care at one hospital in Wuhan. Troponin T elevation associated with co-morbidity, ARDS, VT/VF, coagulopathy. In hospital mortality 60% in cardiac injury and 9% without. Most prominent in those with CVD
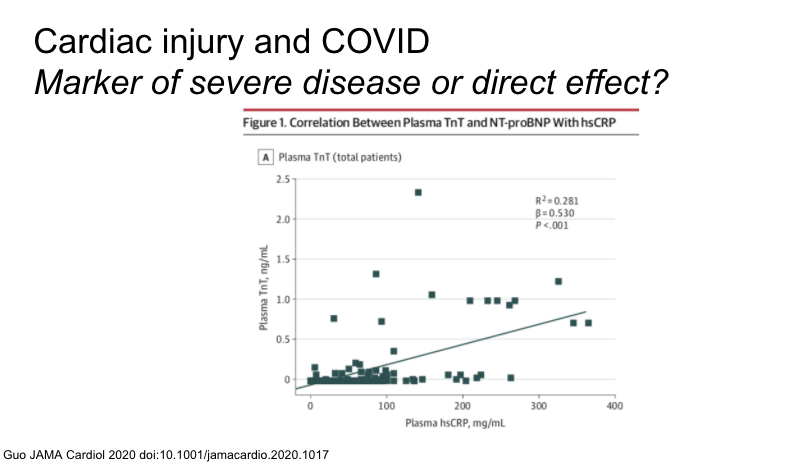
Same study, troponin elevation was associated with CRP. inflammatory association?
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2763845">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2763845">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
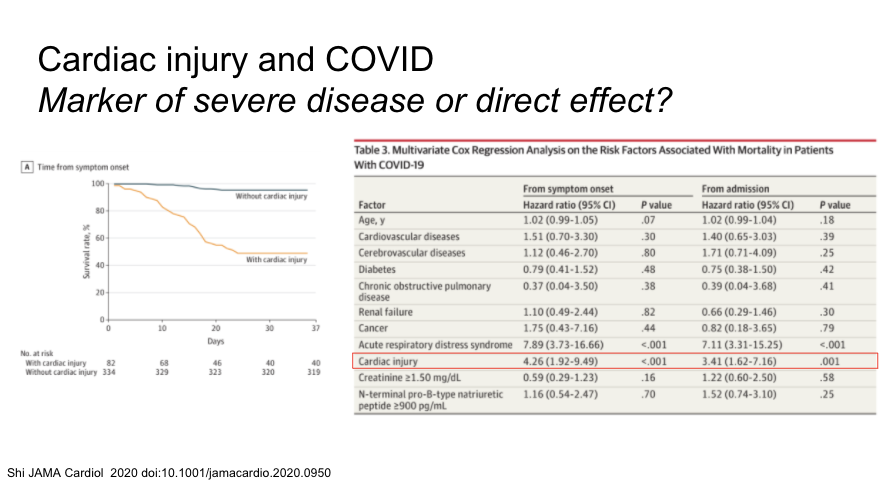
Another study of 416 patients with 20% having cardiac injury. Multivariable cox regression found adjusted hazard ratio for death with cardiac injury of 3.41.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2763524">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2763524">https://jamanetwork.com/journals/...
Interesting case report with MR findings suggestive of COVID-19 myocarditis.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32219357 ">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32219357 ">https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32...
Again, autopsy studies showing myocyte damage with some inflammatory cell infiltration - pathological correlate of cardiac injury?
https://www.thelancet.com/lanres/article/s2213-2600(20)30076-x">https://www.thelancet.com/lanres/ar... https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339984522_A_pathological_report_of_three_COVID-19_cases_by_minimally_invasive_autopsies">https://www.researchgate.net/publicati...
https://www.thelancet.com/lanres/article/s2213-2600(20)30076-x">https://www.thelancet.com/lanres/ar... https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339984522_A_pathological_report_of_three_COVID-19_cases_by_minimally_invasive_autopsies">https://www.researchgate.net/publicati...
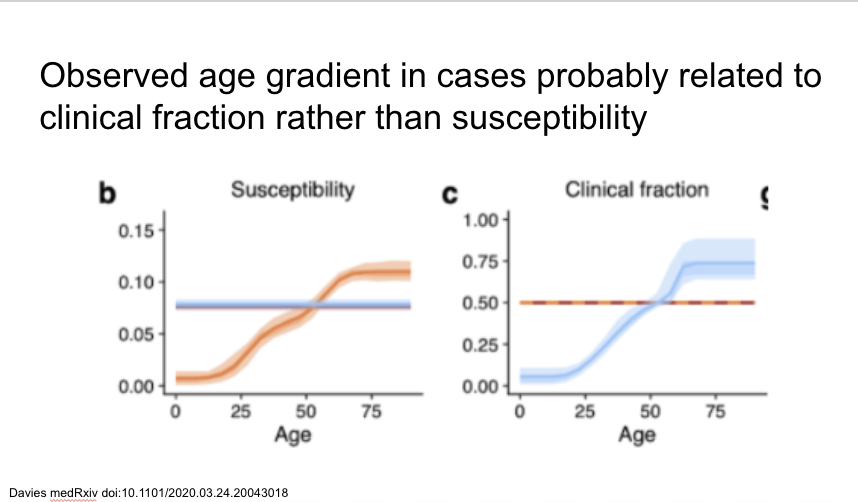
Interesting modeling study suggests age distribution more likely to be explained by differential clinical fraction by age rather than differing susceptibility (orange lines on figures). Implications for population control.
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.24.20043018v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.24.20043018v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
This suggests that clinical fraction in the young is 10% and over 70% after age 70
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.24.20043018v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.24.20043018v1">https://www.medrxiv.org/content/1...
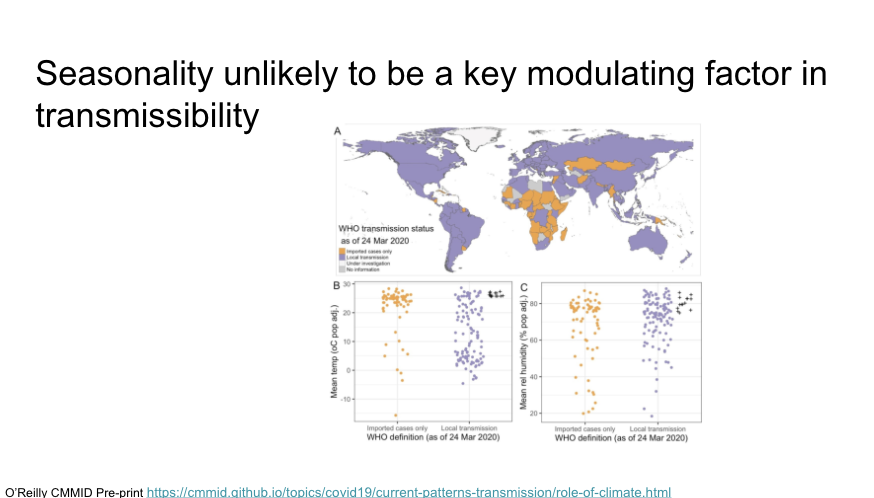
Seasonality is unlikely to be a key modulating factor in transmissability
https://cmmid.github.io/topics/covid19/current-patterns-transmission/role-of-climate.html">https://cmmid.github.io/topics/co...
https://cmmid.github.io/topics/covid19/current-patterns-transmission/role-of-climate.html">https://cmmid.github.io/topics/co...
A number of good reports from the last few weeks highlighting the role of sentinel surveillance
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2764137
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/... href=" https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/69/wr/mm6914e3.htm?s_cid=mm6914e3_x
https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volu... href=" https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.12.2000334">https://www.eurosurveillance.org/content/1...
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2764137
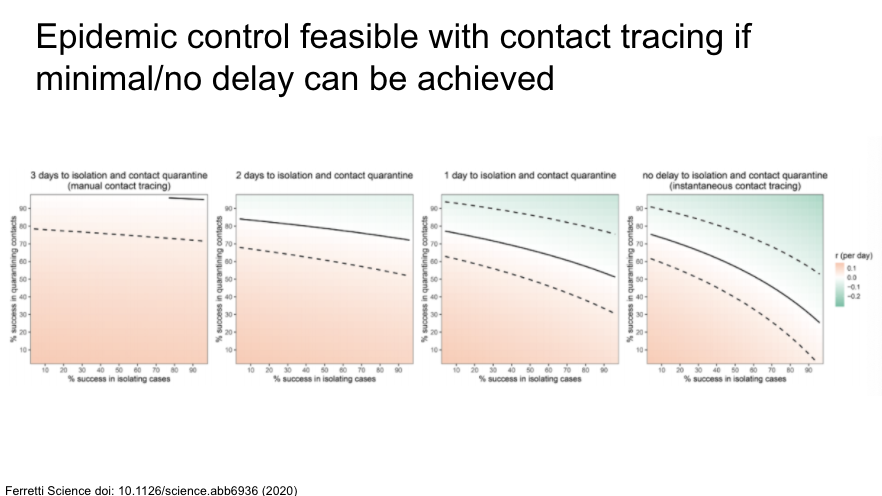
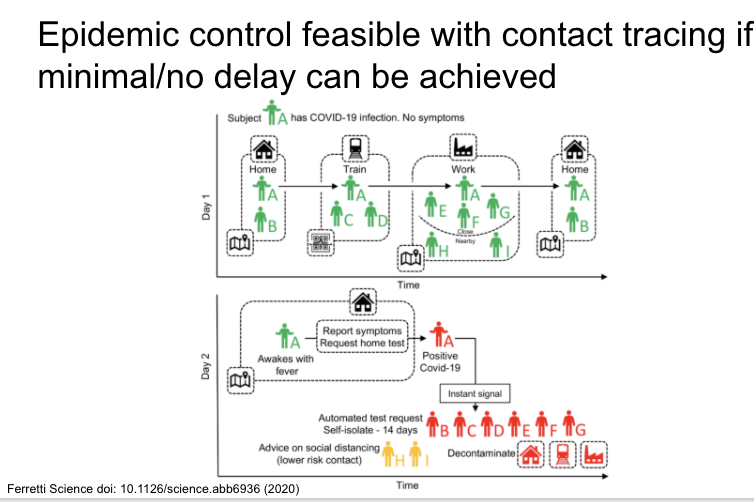
Very nice modeling study showing that rapid contact tracing with minimal delay is needed for isolation of symptomatic people and contact tracing of asymptomatic cases.
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2020/03/30/science.abb6936">https://science.sciencemag.org/content/e...
https://science.sciencemag.org/content/early/2020/03/30/science.abb6936">https://science.sciencemag.org/content/e...
They propose using a cell phone app that keeps a temporary record of proximity events between individuals. Obvious issues for data protection and privacy. Authors note it would not need to be coercive because don& #39;t need full uptake for large impacts.
/end
/end

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter