2) Implications: “The R0 values we estimated have important implications for predicting the effects of pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions. EG, threshold for combined vaccine efficacy & herd immunity needed for disease extinction is calculated as 1 – 1/R0. #COVID19
3) “At R0 = 2.2, this threshold is only 55%. But at R0 = 5.7, this threshold rises to 82% (i.e., >82% of the population has to be immune, through either vaccination or prior infection, to achieve herd immunity to stop transmission).” #COVID19
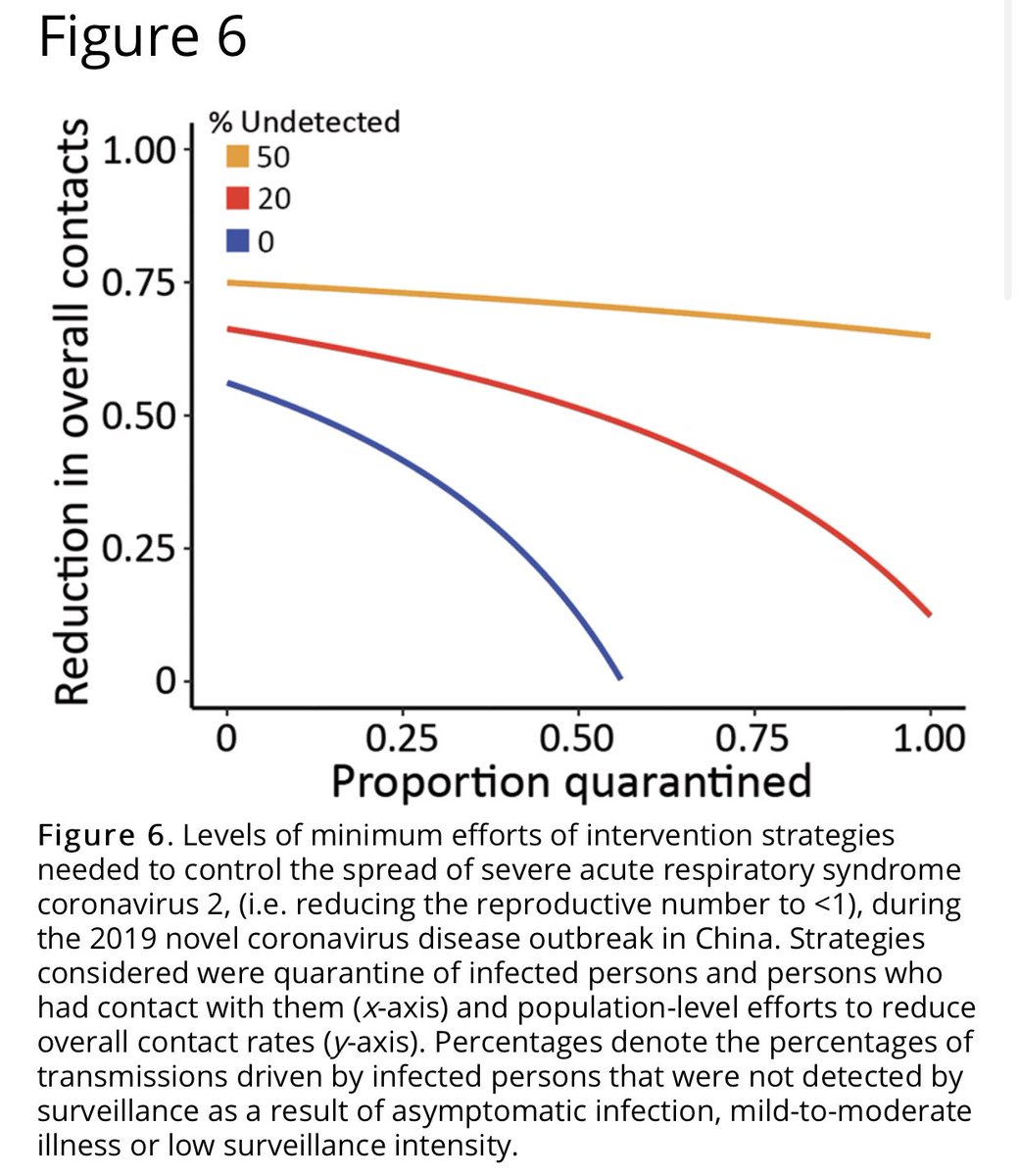
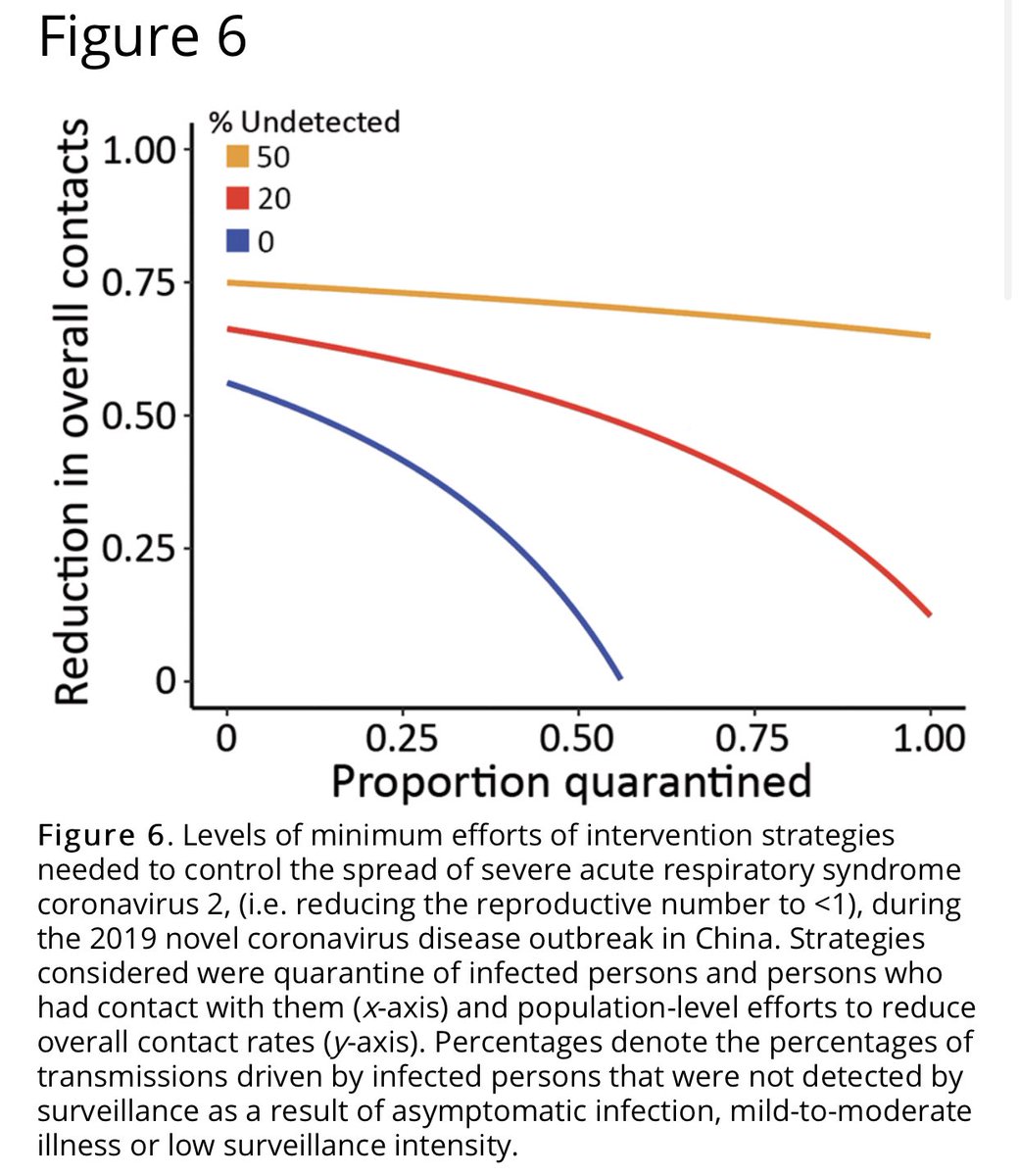
4) “Results show that quarantine and contact tracing of symptomatic persons can be effective when the fraction of unidentified persons is low. However, when 20% of transmission is driven by unidentified infected, high levels of social distancing efforts will be needed” #COVID19
5) this highlights the importance of early and effective surveillance, contact tracing, and quarantine!  https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> Translation: we need to now be even more vigilant than previously thought given the higher revised R0. #COVID19
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="➡️" title="Rightwards arrow" aria-label="Emoji: Rightwards arrow"> Translation: we need to now be even more vigilant than previously thought given the higher revised R0. #COVID19
6) “recent study based on structural analysis of the virus particles suggests SARS-CoV-2 has a much higher affinity to the receptor needed for cell entry than the 2003 SARS virus, providing a molecular basis for the high infectiousness of #SARSCoV2. #COVID19
7) Note that this R0 is much higher than the recent Imperial College review of published R0 of 3.87. Ergo, a 5.7 is on considerably different level of infectiousness. #COVID19 https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/sph/ide/gida-fellowships/Imperial-College-COVID19-Europe-estimates-and-NPI-impact-30-03-2020.pdf">https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imp...
8) clarifying that this is from a Los Alamos group’s reanalysis. But posted on CDC’s journal Emerging Infectious Diseases.
9) And to be clear, R0 is the R reproductive number at time 0 before countermeasures. So this is not the R(effective) at current time under mitigation like distancing and testing+tracing+quarantine.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter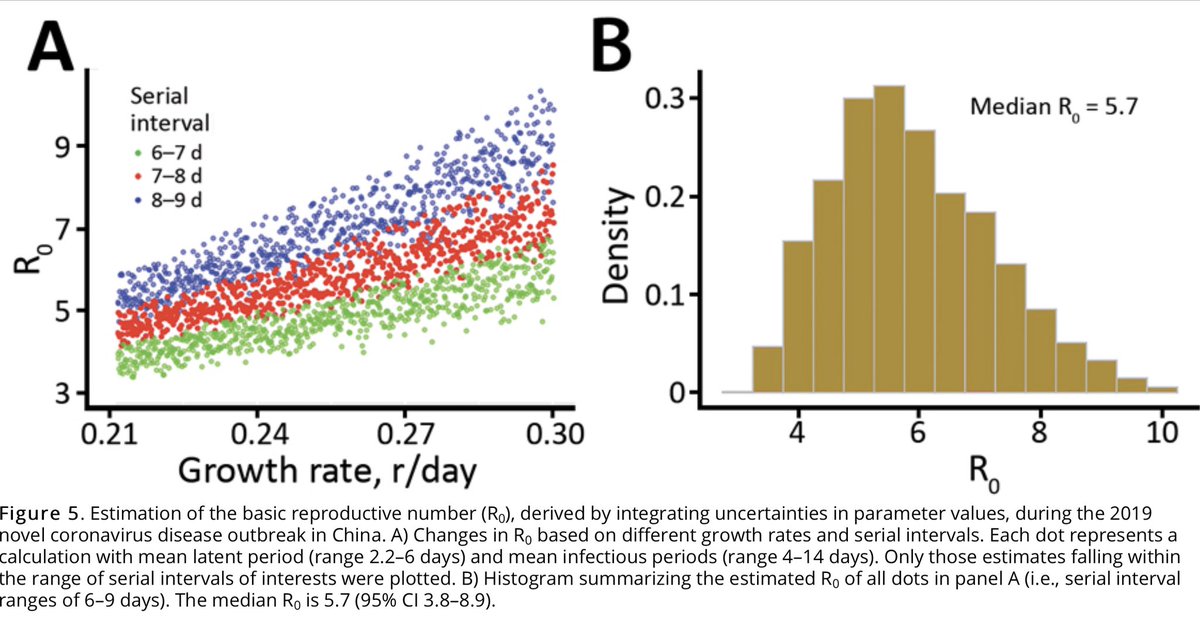 New higher R0 from CDC reanalysis... it’s a 5.7!https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Police cars revolving light" aria-label="Emoji: Police cars revolving light">(95% Confidence Interval: 3.8–8.9). Wowzers. This much higher #SARSCoV2 R0 value carries lot of implications for vaccines and treatments and containment measures needed. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Pushpin" aria-label="Emoji: Pushpin">Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> #COVID19 https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/artic..." title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Police cars revolving light" aria-label="Emoji: Police cars revolving light">New higher R0 from CDC reanalysis... it’s a 5.7!https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Police cars revolving light" aria-label="Emoji: Police cars revolving light">(95% Confidence Interval: 3.8–8.9). Wowzers. This much higher #SARSCoV2 R0 value carries lot of implications for vaccines and treatments and containment measures needed. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Pushpin" aria-label="Emoji: Pushpin">Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> #COVID19 https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/artic..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
New higher R0 from CDC reanalysis... it’s a 5.7!https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Police cars revolving light" aria-label="Emoji: Police cars revolving light">(95% Confidence Interval: 3.8–8.9). Wowzers. This much higher #SARSCoV2 R0 value carries lot of implications for vaccines and treatments and containment measures needed. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Pushpin" aria-label="Emoji: Pushpin">Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> #COVID19 https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/artic..." title="https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Police cars revolving light" aria-label="Emoji: Police cars revolving light">New higher R0 from CDC reanalysis... it’s a 5.7!https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🚨" title="Police cars revolving light" aria-label="Emoji: Police cars revolving light">(95% Confidence Interval: 3.8–8.9). Wowzers. This much higher #SARSCoV2 R0 value carries lot of implications for vaccines and treatments and containment measures needed. https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="📌" title="Pushpin" aria-label="Emoji: Pushpin">Thread https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="🧵" title="Thread" aria-label="Emoji: Thread"> #COVID19 https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/artic..." class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>