Coronavirus might spread much farther than 6 feet in the air.
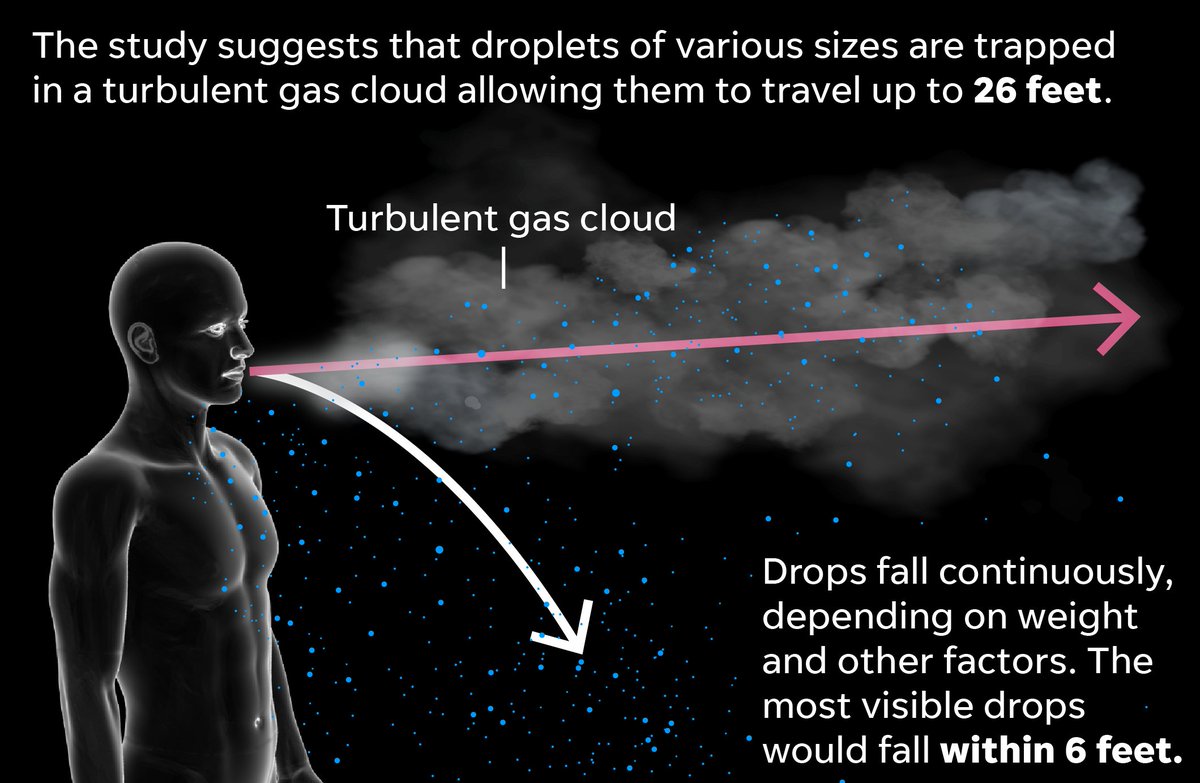
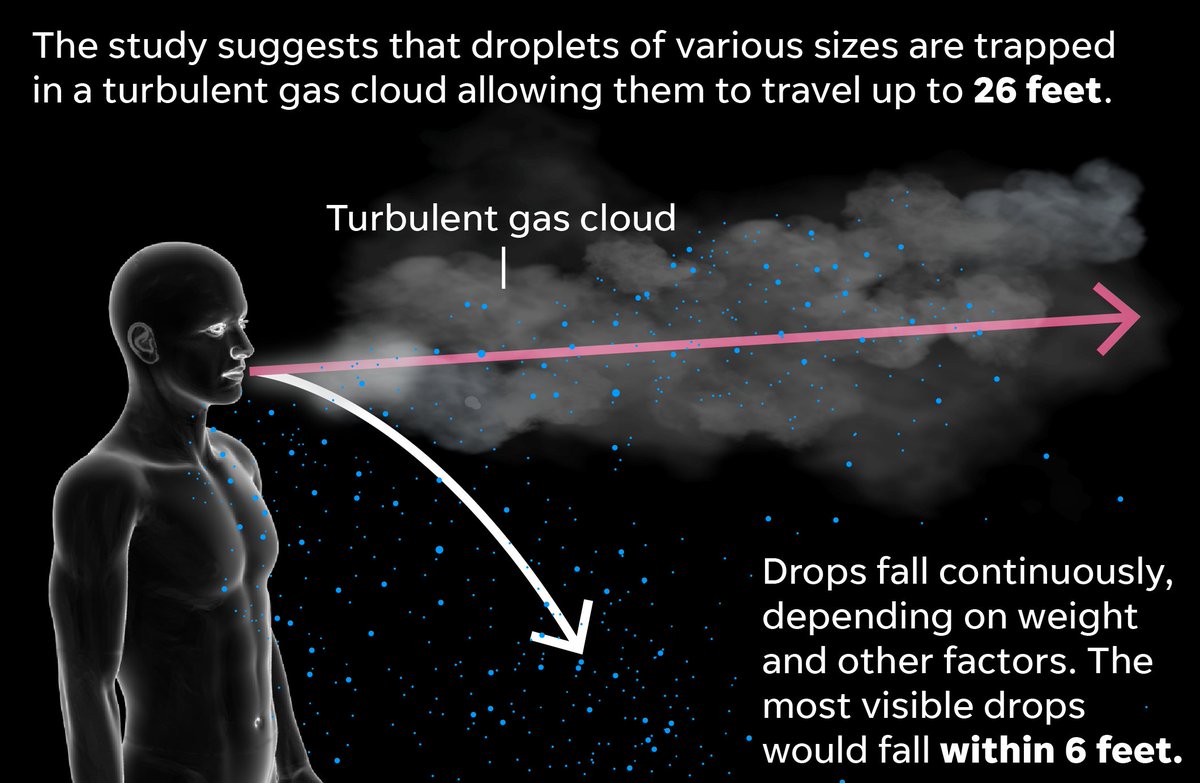
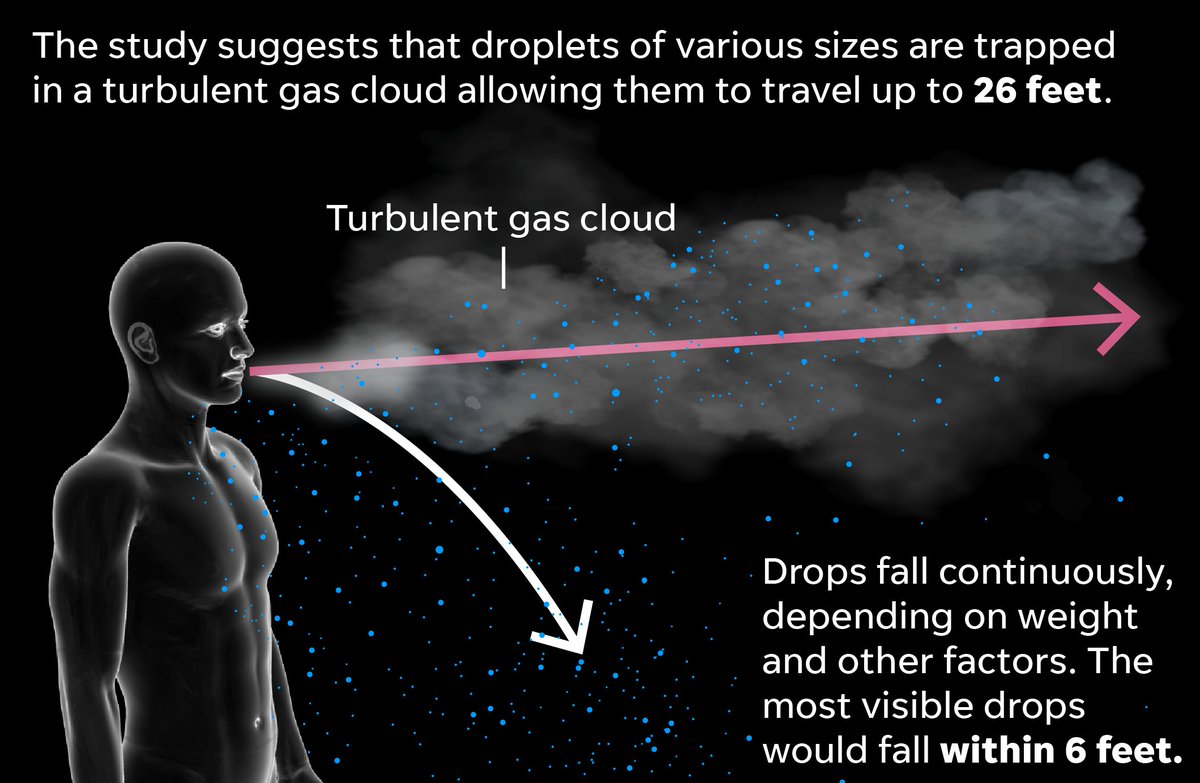
New research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association shows that droplets in our coughs could travel as much as 26 feet.
CDC says wear a mask in public.
New research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association shows that droplets in our coughs could travel as much as 26 feet.
CDC says wear a mask in public.
As seen in this video, shot from different views and posted with the report, the invisible cloud can travel up to 26 feet.
Findings such as these may have some bearing on the CDC& #39;s recommendation on Friday that Americans wear non-surgical face masks in public — especially in places where other social distancing measures are difficult to maintain.
Much into how far the cloud and its droplets travel: physiology, the environment, humidity and temperature.
The cloud can reach up to 26 feet for sneezes and less than that for coughs; about 16 to 19 feet.
Floating droplets can stay suspended long enough for to inhale a virus.
The cloud can reach up to 26 feet for sneezes and less than that for coughs; about 16 to 19 feet.
Floating droplets can stay suspended long enough for to inhale a virus.
According to a 2009 World Health Organization report, when someone coughs, they can spray up to 3,000 droplets. A sneeze could yield 40,000.
Droplets can be very small; as small and invisible as micron size to the ones that you can see that are on the order of the millimeter.
Droplets can be very small; as small and invisible as micron size to the ones that you can see that are on the order of the millimeter.
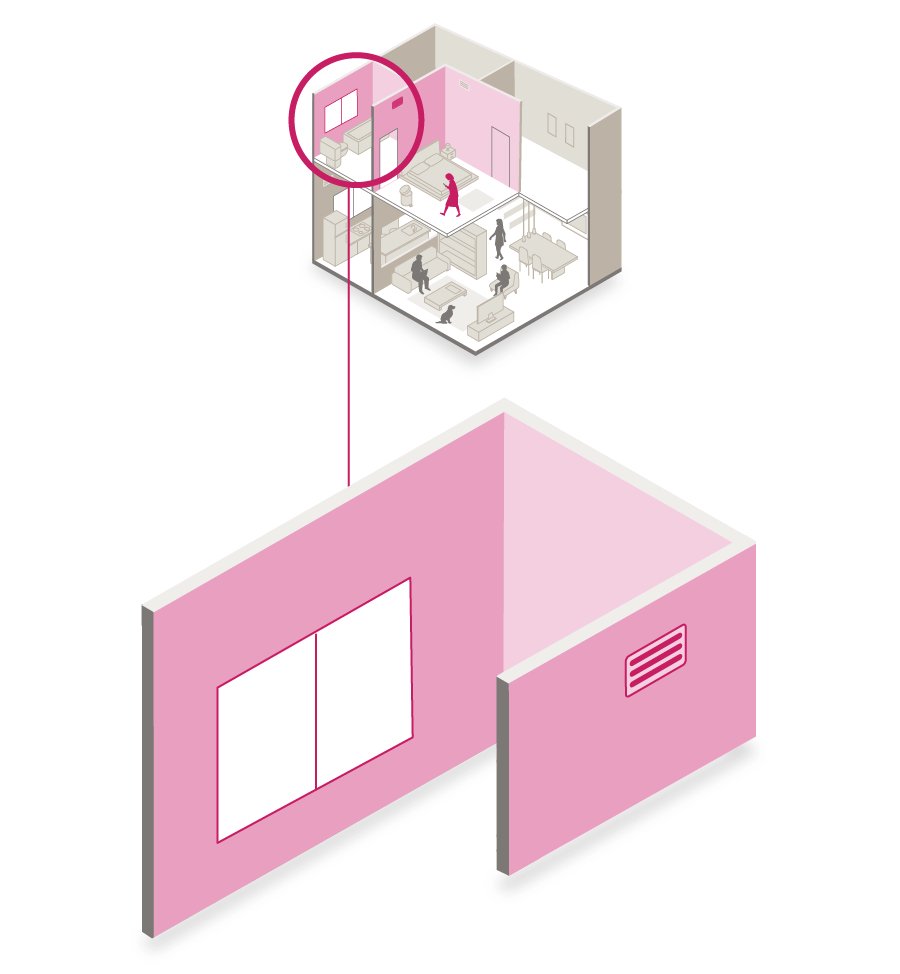
Pathogens in the cloud could potentially reach air circulation systems inside buildings, according to the study& #39;s author, Lydia Bourouiba of Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Though, there are questions about whether the detected virus particles are still live.
This heightens dangers for those caring for COVID-19 patients. Without sufficient air circulation droplets can linger in hospitals and homes.
The best defenses are the outdoors and open windows which dissipate the clouds or droplets.
Learn more here: https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/news/2020/03/21/coronavirus-how-safely-take-care-someone-sick-covid-19/2866984001/">https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/...
The best defenses are the outdoors and open windows which dissipate the clouds or droplets.
Learn more here: https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/news/2020/03/21/coronavirus-how-safely-take-care-someone-sick-covid-19/2866984001/">https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/...
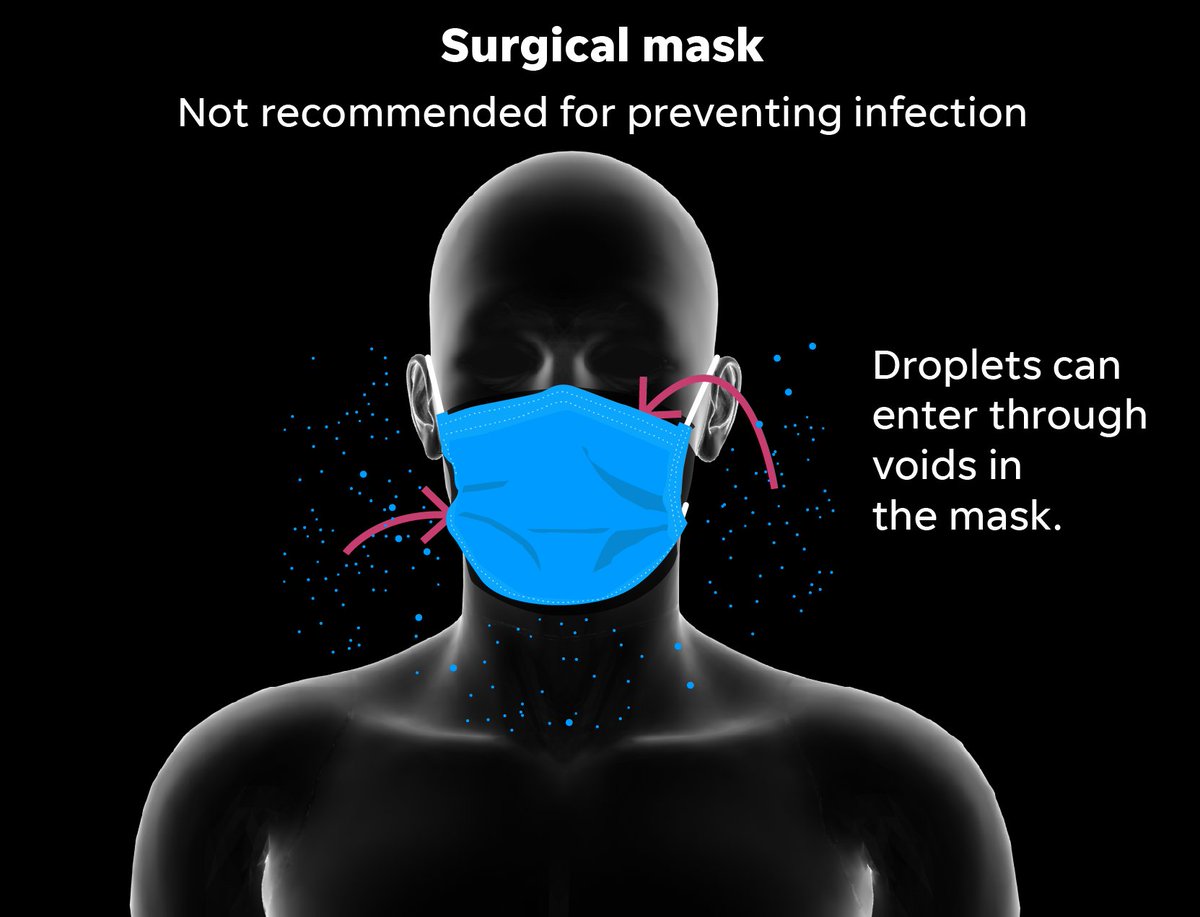
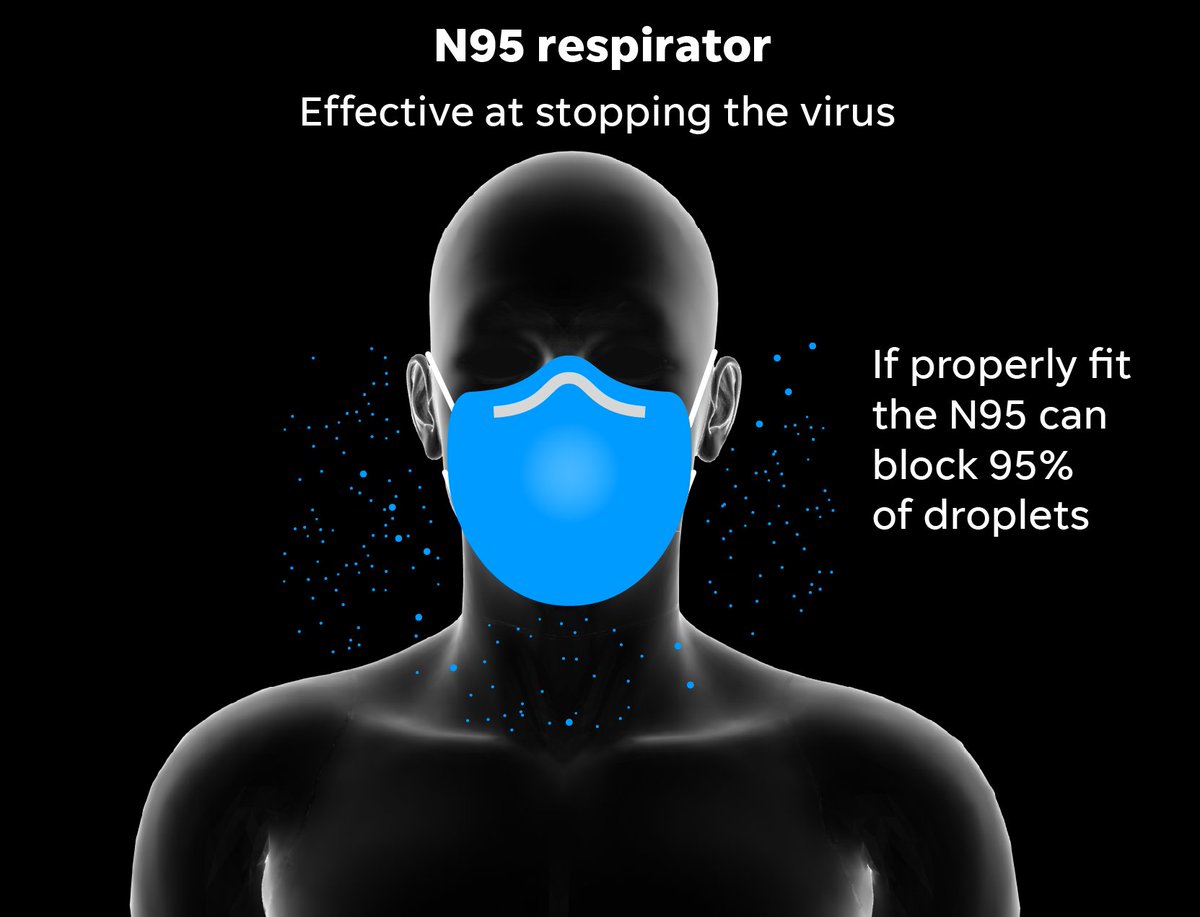
Surgical masks are helpful at blocking large droplets, but unlike respirators they do not provide a reliable level of protection from inhaling smaller airborne particles, according to the CDC.
N95 respirators are tight-fitting and filter out at least 95% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns. They have a protection factor (APF) of 10.
That means the N95 reduces the aerosol concentration to 1/10 of that in the room, blocking 90% of airborne particles.
That means the N95 reduces the aerosol concentration to 1/10 of that in the room, blocking 90% of airborne particles.
The CDC now recommends Americans wear cloth face coverings in public settings where its difficult to stay at least 6 feet apart such as grocery stores and pharmacies.
Get the whole story here: https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/news/2020/04/03/coronavirus-protection-how-masks-might-stop-spread-through-coughs/5086553002/">https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/...
Get the whole story here: https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/news/2020/04/03/coronavirus-protection-how-masks-might-stop-spread-through-coughs/5086553002/">https://www.usatoday.com/in-depth/...
Oops, we forgot a word in an above tweet, here it is again:

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter