how did the Universe begin?
while we still don’t have a great way to describe the singularity of the Big Bang other than saying *it happened*, we can talk about what happens mere moments after the Big Bang.
let& #39;s walk through, step by step, the beginnings of the Universe.
while we still don’t have a great way to describe the singularity of the Big Bang other than saying *it happened*, we can talk about what happens mere moments after the Big Bang.
let& #39;s walk through, step by step, the beginnings of the Universe.
right after the Big Bang, the Universe was insanely hot. since temperature (T) is related to energy (E) as E = kT, the Universe was SUPER energetic.
in these conditions, gamma rays (which are just high energy photons), combine to create "virtual particles" & vice versa.
in these conditions, gamma rays (which are just high energy photons), combine to create "virtual particles" & vice versa.
the above diagram, also known as a Feynman Diagram, shows how particle interactions progress over time. time is read from left to right, i.e. 2 photons combine to then create an electron and positron pair.
but the diagram can also be flipped! electron + positron = gamma rays
but the diagram can also be flipped! electron + positron = gamma rays
just after the Big Bang (and I’m talking, like, 10⁻⁴³ seconds afterwards!!) the forward and reverse of these processes were in equilibrium. in other words stuff was getting created and destroyed equally!
but remember what this was contingent upon: temperature.
but remember what this was contingent upon: temperature.
after the initial monumental surge of temperature and energy from the Big Bang, stuff started to cool.
after the temperature cooled by ~1 billion K, our gamma rays no longer had enough energy to create virtual particles.
in other words, they were “frozen out.”
after the temperature cooled by ~1 billion K, our gamma rays no longer had enough energy to create virtual particles.
in other words, they were “frozen out.”
the Universe has 4 distinct forces:
• strong (quarks: protons, neutrons)
• weak (leptons: electrons, neutrinos, etc)
• electromagnetic (charged particles: electrons etc)
• gravity (all!)
these forces cause particles to interact. over time, they started to freeze out, too...
• strong (quarks: protons, neutrons)
• weak (leptons: electrons, neutrinos, etc)
• electromagnetic (charged particles: electrons etc)
• gravity (all!)
these forces cause particles to interact. over time, they started to freeze out, too...
about 10⁻⁴³ seconds after the Big Bang, gravity decoupled from the other 3 forces. but the Universe continued to cool, and shortly thereafter, the remaining 3 forces separated as well.
about 10⁻⁴ seconds after the Big Bang, gamma rays lost enough of energy that they could no longer pair produce to form virtual particles.
this quark-gluon plasma soup steadily cools until baryons like protons and neutrons can form...
this quark-gluon plasma soup steadily cools until baryons like protons and neutrons can form...
finally, 1 second after the Big Bang, neutrinos decouple and zoom freely throughout the cosmos. some of the neutrinos we detect today are those from this stage in the Universe!
weee!!!!
we have a cosmic “neutrino” background— constant neutrinos from the early universe.
weee!!!!
we have a cosmic “neutrino” background— constant neutrinos from the early universe.
these cosmic neutrinos have actually been detected as minor fluctuations and imprints on the cosmic microwave background at *exactly* the temperature predicted by the Big Bang.
AND we detect 3 flavors of neutrinos, exactly what we would’ve expected.
HOW INSANELY COOL IS THAT
AND we detect 3 flavors of neutrinos, exactly what we would’ve expected.
HOW INSANELY COOL IS THAT
things get a little dicey after this. the Universe *may* then have formed primordial black holes— random fluctuations of extremely high density regions that collapse to form black holes.
2-20 minutes later, nuclear fusion occurs, creating helium, lithium, & deuterium (with some other isotopes).
we have our first elements.
the stuff that makes the Universe-- the stuff that makes us, US.
we have our first elements.
the stuff that makes the Universe-- the stuff that makes us, US.
fast forward 100,000 years. matter starts to dominate over radiation, and the first molecules form.
377,000 years after the Big Bang, we have another landmark: recombination.
now, free electrons recombine into neutral atoms, releasing photons to stream through the cosmos.
377,000 years after the Big Bang, we have another landmark: recombination.
now, free electrons recombine into neutral atoms, releasing photons to stream through the cosmos.
these free streaming photons are the cosmic microwave background radiation I talked about here: https://twitter.com/starstrickensf/status/1176308857229869056?s=21
the">https://twitter.com/starstric... wavelength of these photons is stretched SO much because it’s so long ago, that it appears as static on our old TVs!!
the">https://twitter.com/starstric... wavelength of these photons is stretched SO much because it’s so long ago, that it appears as static on our old TVs!!
after photons started to stream freely, the Universe became transparent, but there were no large scale structures to produce light!
this time is referred to as the cosmic Dark Ages. stars and galaxies have still yet to form.
this time is referred to as the cosmic Dark Ages. stars and galaxies have still yet to form.
about 1 billion years after the Big Bang, large scale structures were created. as stars and galaxies were born, their light re-lit up the Universe. this ionization broke up neutral hydrogen atoms into free electrons and protons.
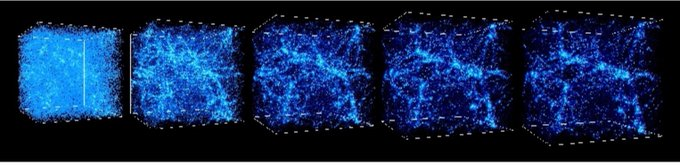
interestingly, since dark matter is unaffected by radiation, it started clumping far before ordinary matter began to clump together.
so, galaxies actually form AROUND dark matter clumps!
(img: simulation of structure over time. from UChicago’s Center for Cosmological Physics)
so, galaxies actually form AROUND dark matter clumps!
(img: simulation of structure over time. from UChicago’s Center for Cosmological Physics)
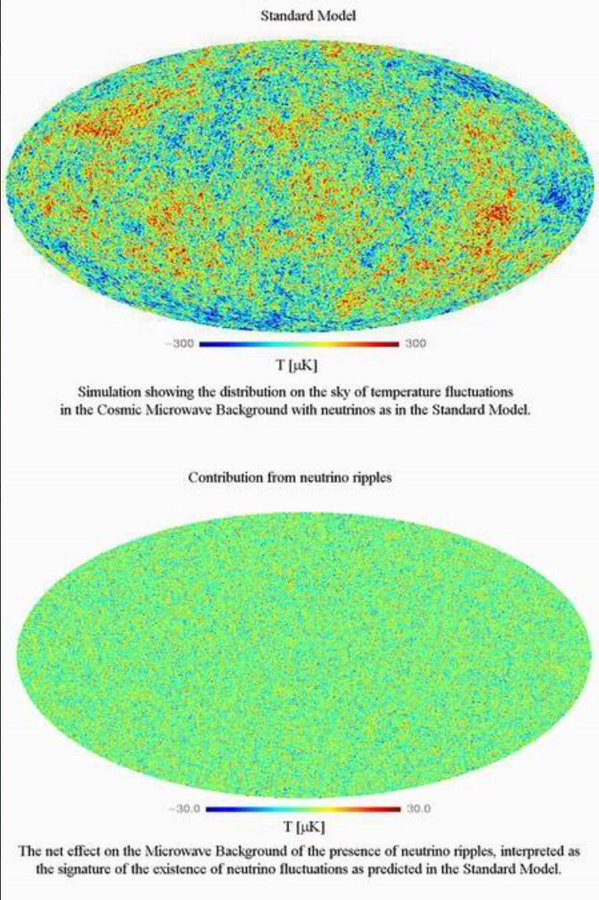
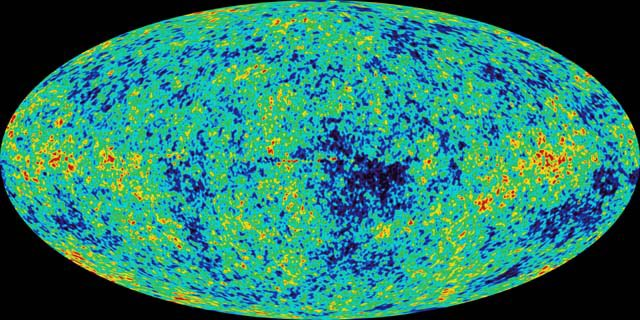
dark matter created tiny ripples in the cosmic microwave background because it interacts via gravity.
those ripples have now been OBSERVED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😍" title="Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes" aria-label="Emoji: Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes">
https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😍" title="Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes" aria-label="Emoji: Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes">
those ripples have now been OBSERVED
finally, gravity continued to pull structures together to form galaxies, clusters of galaxies and superclusters of galaxies.
the Universe starts to resemble our present day Universe.
we& #39;re home.
the Universe starts to resemble our present day Universe.
we& #39;re home.

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter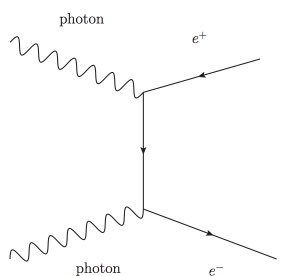
 " title="dark matter created tiny ripples in the cosmic microwave background because it interacts via gravity. those ripples have now been OBSERVED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😍" title="Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes" aria-label="Emoji: Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>
" title="dark matter created tiny ripples in the cosmic microwave background because it interacts via gravity. those ripples have now been OBSERVED https://abs.twimg.com/emoji/v2/... draggable="false" alt="😍" title="Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes" aria-label="Emoji: Smiling face with heart-shaped eyes">" class="img-responsive" style="max-width:100%;"/>


