Fundoscopy  got you down? See clearly into the
got you down? See clearly into the  with #POCUS!
with #POCUS!
 Learn How to Perform Ocular Ultrasound
Learn How to Perform Ocular Ultrasound
 Recognize Retinal Detachment, PVD,
Recognize Retinal Detachment, PVD,  ICP, + MORE!
ICP, + MORE!
 Free Ocular Ultrasound PDF Pocket Card!
Free Ocular Ultrasound PDF Pocket Card!
 New Blog Post!
New Blog Post! 
 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
#medtweetorial (1/21)
(1/21)
 got you down? See clearly into the
got you down? See clearly into the  with #POCUS!
with #POCUS! Learn How to Perform Ocular Ultrasound
Learn How to Perform Ocular Ultrasound Recognize Retinal Detachment, PVD,
Recognize Retinal Detachment, PVD,  ICP, + MORE!
ICP, + MORE! Free Ocular Ultrasound PDF Pocket Card!
Free Ocular Ultrasound PDF Pocket Card! New Blog Post!
New Blog Post! 
 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular #medtweetorial
 (1/21)
(1/21)
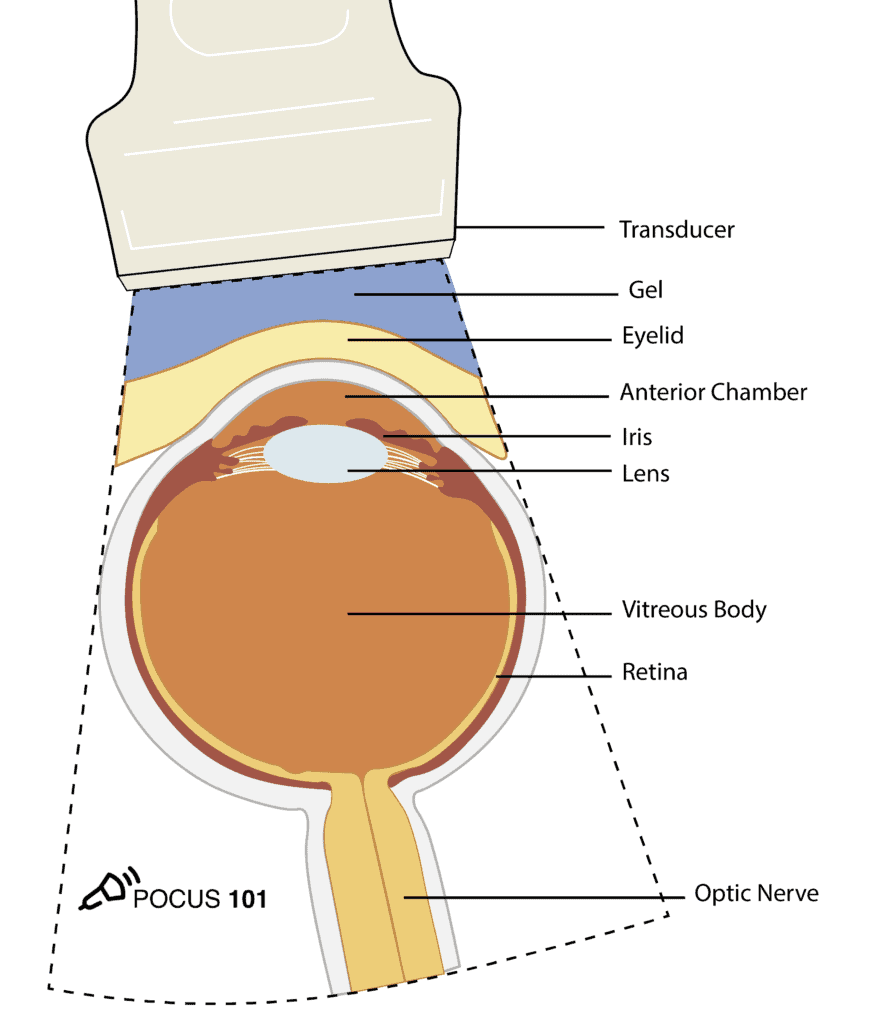
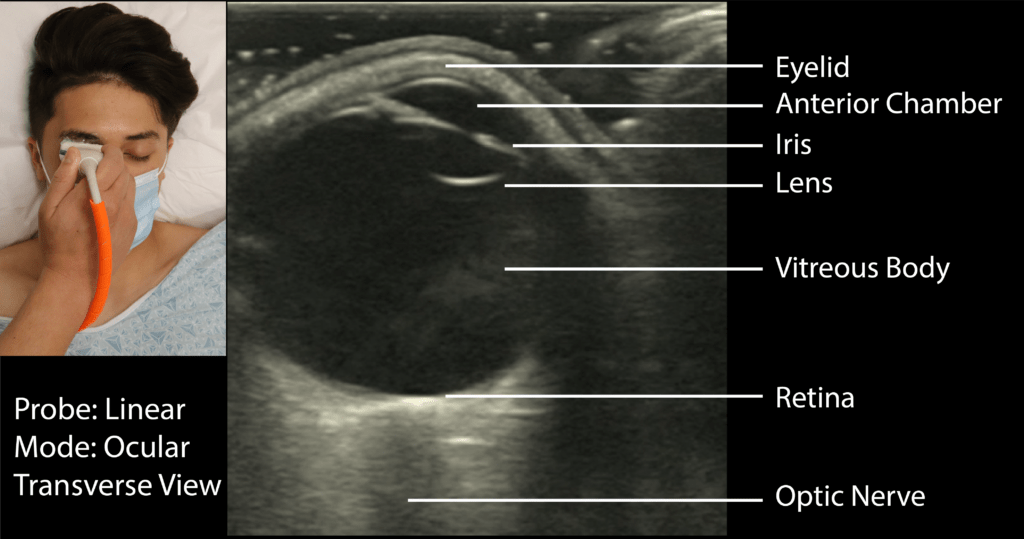
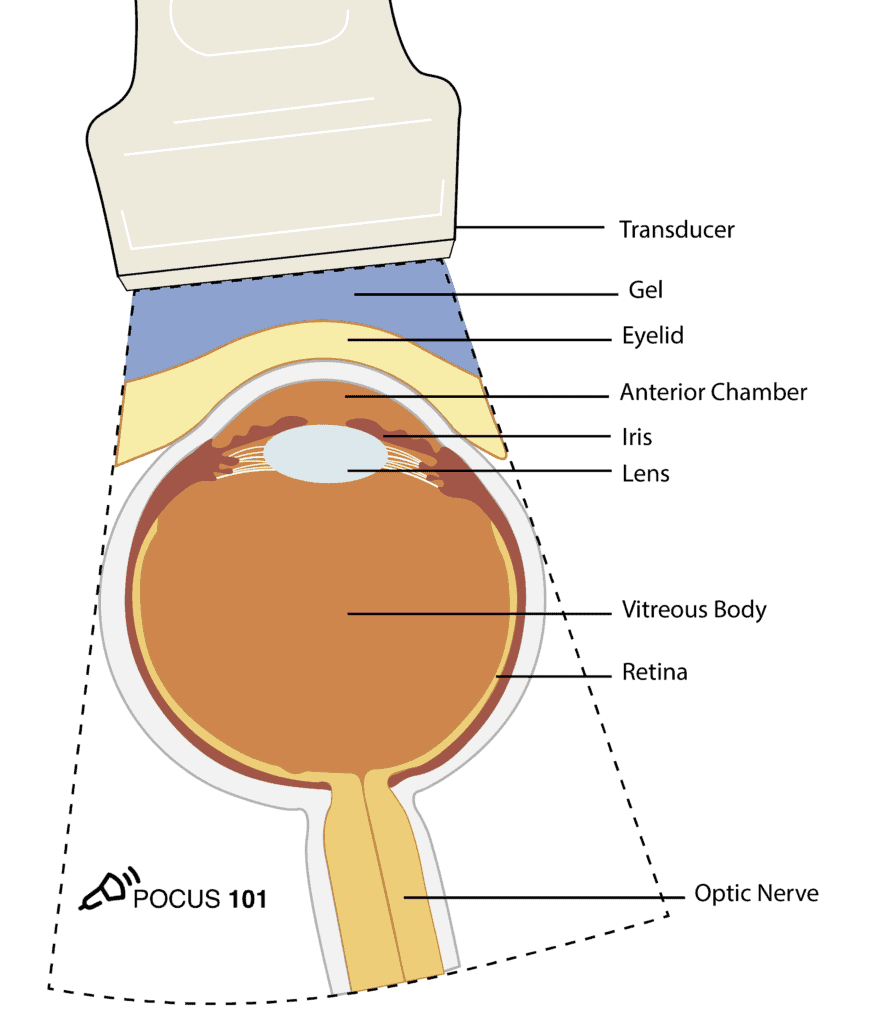
(3) Obtain the Transverse View:
Place the probe lightly on the gel covering the patient’s eye with the probe indicator pointed towards the patient’s right to obtain a transverse view.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Place the probe lightly on the gel covering the patient’s eye with the probe indicator pointed towards the patient’s right to obtain a transverse view.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
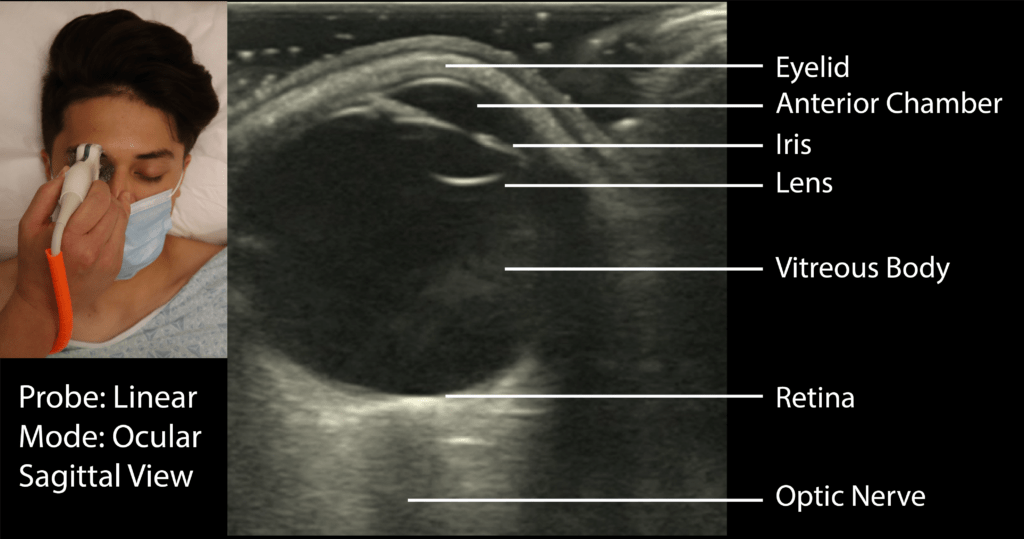
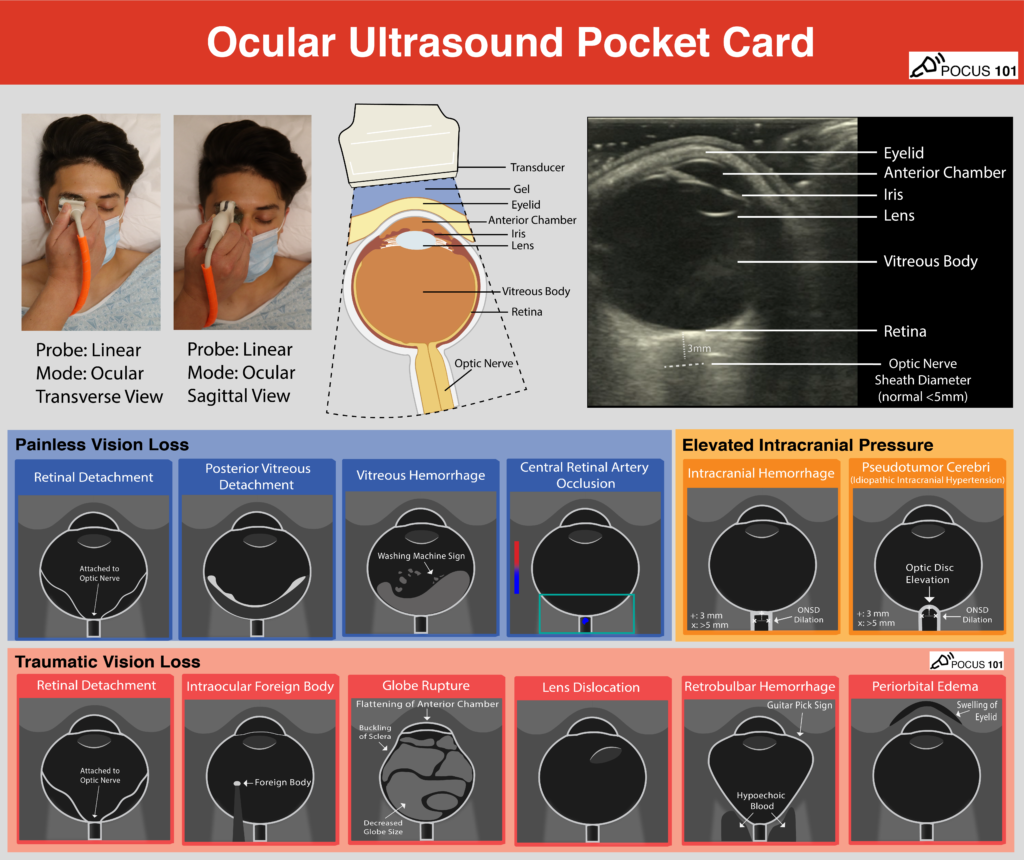
(4) Identify the Following Structures
•Eyelid
•Anterior Chamber
•Lens
•Iris
•Vitreous Body
•Retina
•Optic Nerve
•*Make sure to tilt/fan through the entire eye

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
•Eyelid
•Anterior Chamber
•Lens
•Iris
•Vitreous Body
•Retina
•Optic Nerve
•*Make sure to tilt/fan through the entire eye

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
(5) Obtain TheSagittal View
Next, turn the probe 90° clockwise so the indicator points superiorly towards the patient’s head to obtain a sagittal view. Identify the same structures you found in the transverse view.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Next, turn the probe 90° clockwise so the indicator points superiorly towards the patient’s head to obtain a sagittal view. Identify the same structures you found in the transverse view.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
(6) Assess extraocular Movements
Evaluate for extraocular movements. This is important when patients have severe periorbital edema from facial trauma.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Evaluate for extraocular movements. This is important when patients have severe periorbital edema from facial trauma.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
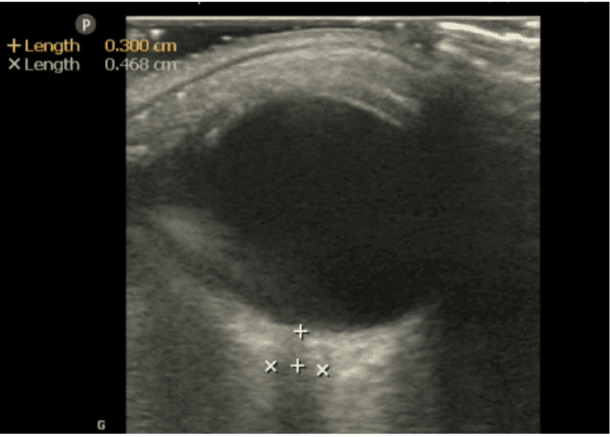
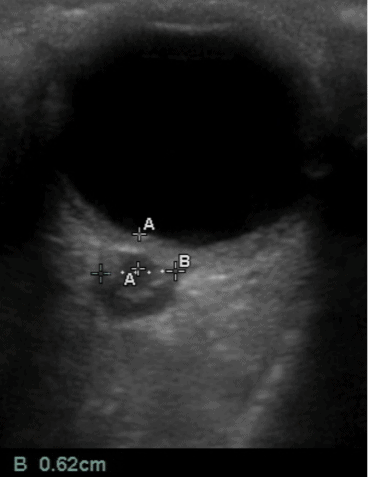
(7) Obtain Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD)
Measure 3 mm (.3cm) posterior to where the optic nerve sheath attaches to the retina. This is the location where you will use to measure your optic nerve sheath diameter.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Measure 3 mm (.3cm) posterior to where the optic nerve sheath attaches to the retina. This is the location where you will use to measure your optic nerve sheath diameter.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
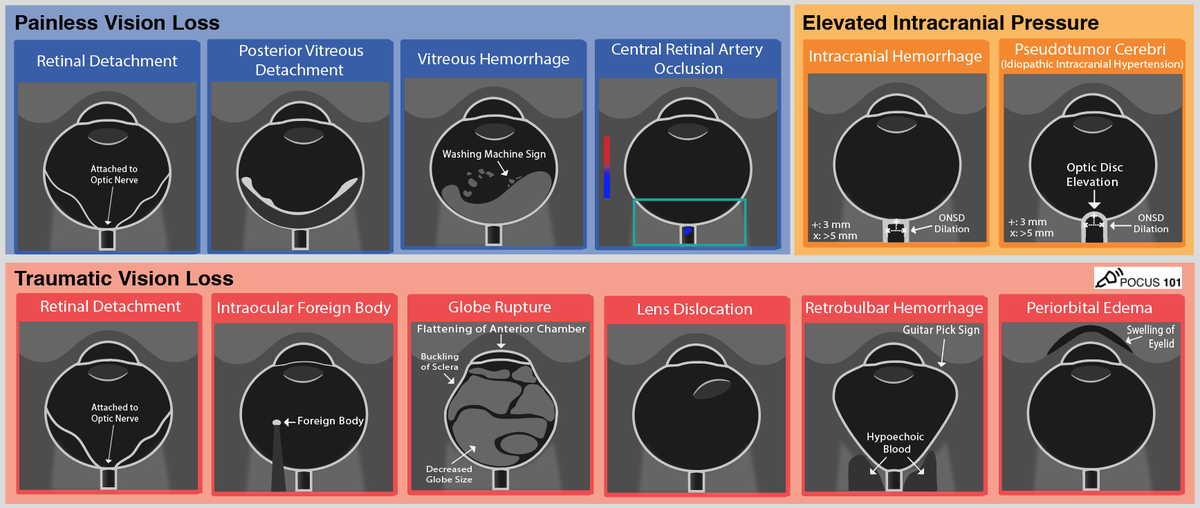
(8) Let's look at the different types of Ocular Ultrasound Pathology:
Download the Ocular Ultrasound Pathology PDF Pocket Card here for Reference.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Download the Ocular Ultrasound Pathology PDF Pocket Card here for Reference.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
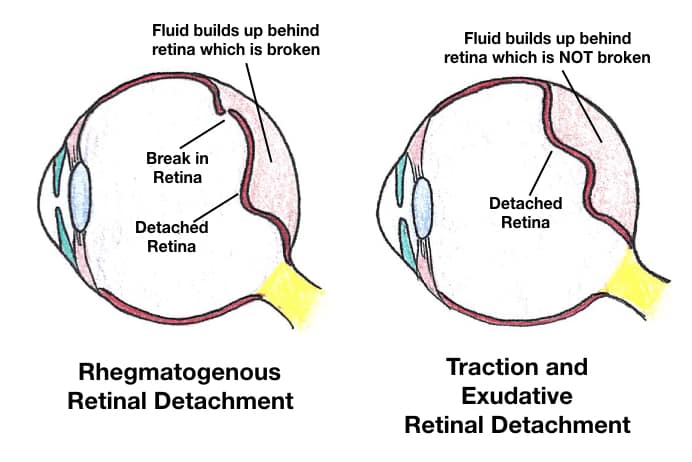
(9) There are three types of Retinal Detachments:
Rhegmatogenous, Traction, and Exudative.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Rhegmatogenous, Traction, and Exudative.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
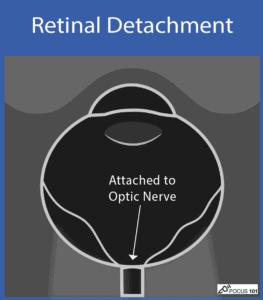
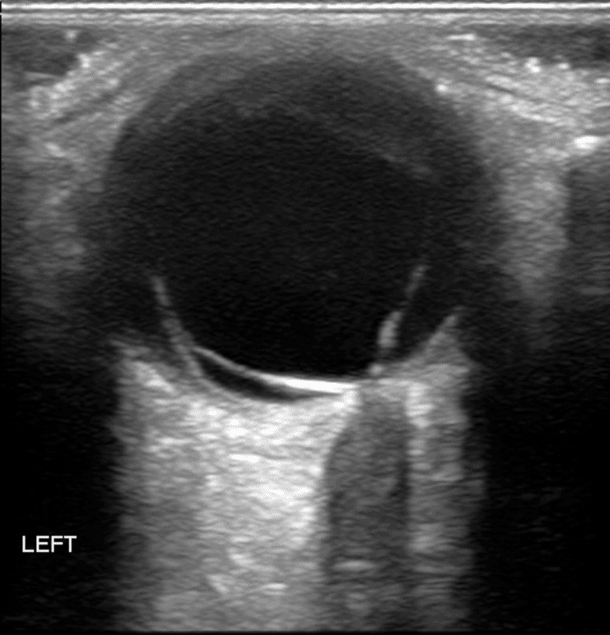
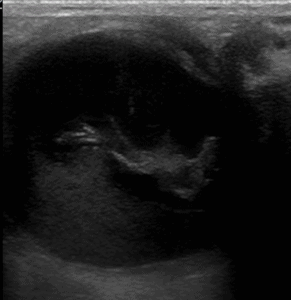
(10) Retinal Detachment: The defining characteristic is that a retinal detachment is tethered to the optic nerve and moves with the optic nerve.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Retinal Detachment Video (notice attachment to optic nerve)
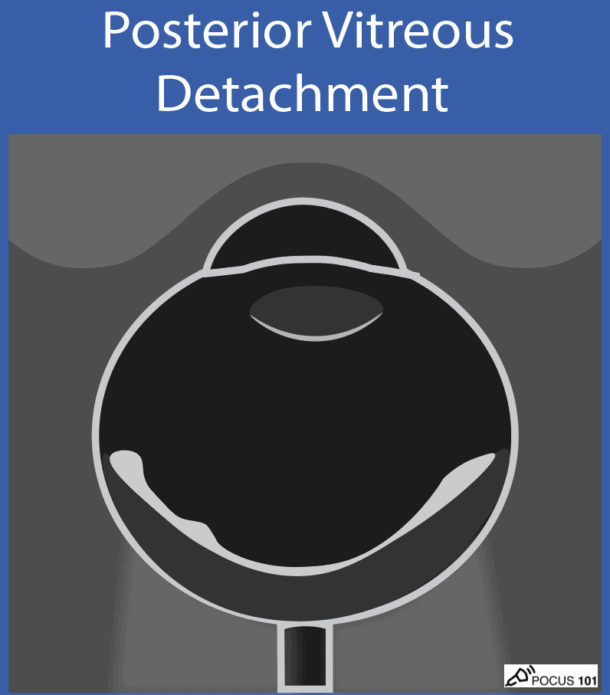
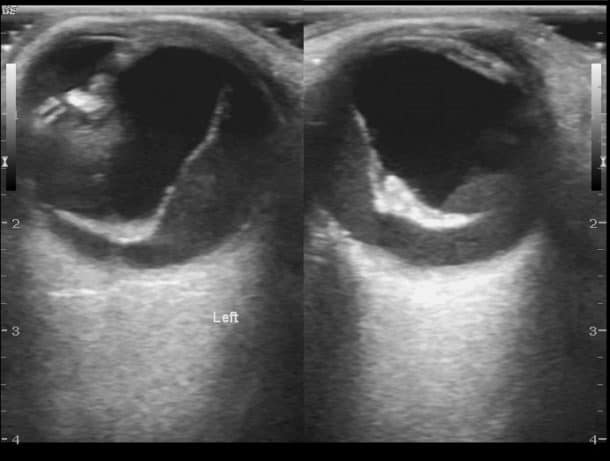
(11) Posterior Vitreous Detachment looks like a thin, hyperechoic membrane lifted off the posterior surface of the globe that is NOT tethered to the optic nerve.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
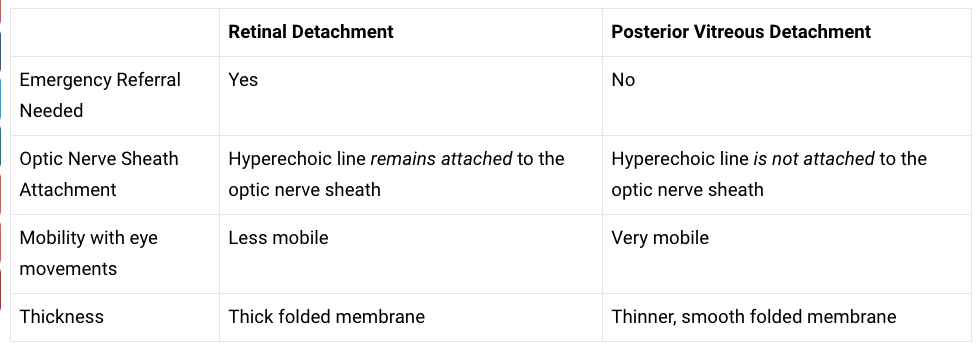
(12) Here is a table to help differentiate Retinal Detachment from Posterior Vitreous Detachment

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
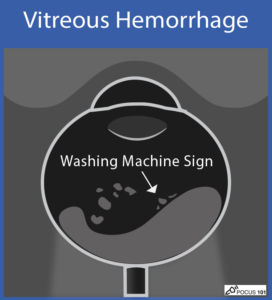
(13) Vitreous Hemorrhage: looks like echogenic material in the posterior chamber. If you ask the patient to move their eye side-to-side, you may see the washing machine sign

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
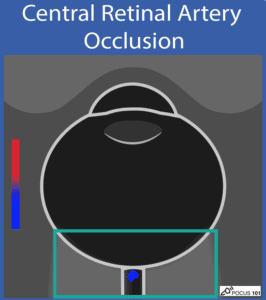
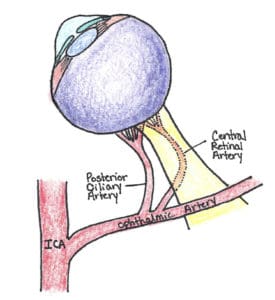
(14) Central Retinal Artery Occlusion: is a rare finding and color Doppler mode can be used to diagnose it with ocular ultrasound. You may find diminished or absent flow of the central retinal artery.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
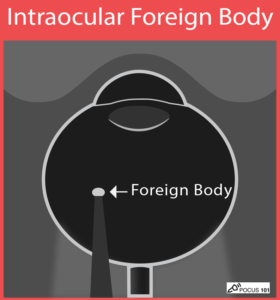
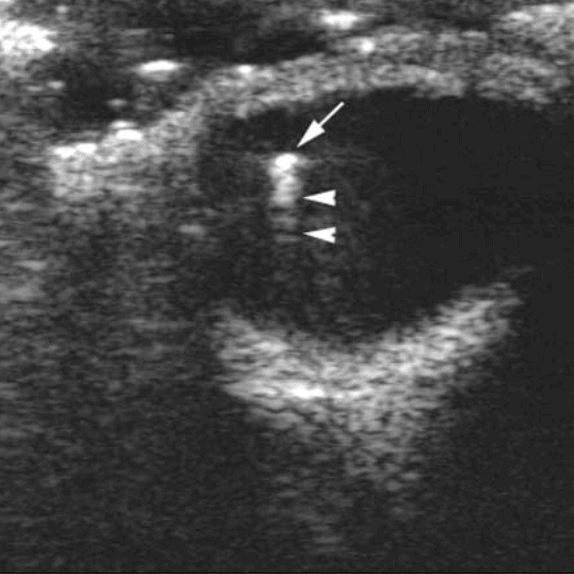
(15) Ocular Foreign Body: you can find a bright, hyperechoic object with an associated reverberation artifact (if the object is metallic).

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
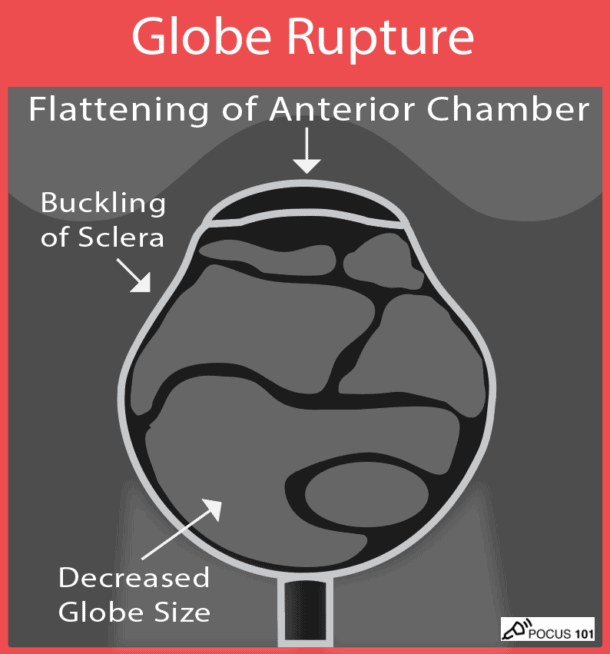
(16) Globe Rupture: you may find buckling of the sclera, asymmetric loss of the normal spherical shape of the globe, decreased size of globe, flattening or compression of the anterior chamber, or vitreous hemorrhage

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
Globe Rupture Video:
(17) Lens Dislocation: you will see the lens as a bi-convex structure with hyperechoic borders floating posteriorly in the vitreous body.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
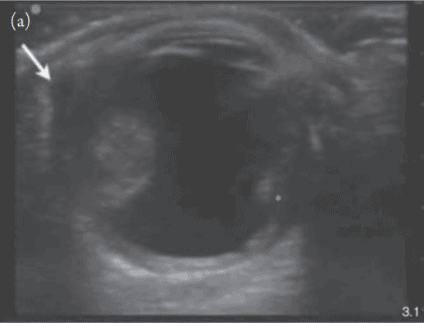
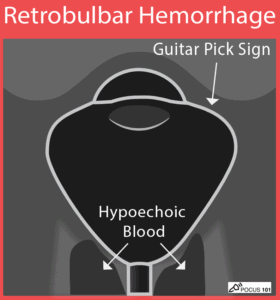
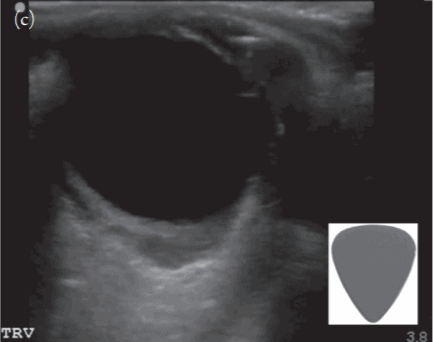
(18) Retrobulbar Hemorrhage: you may see a “Guitar Pick Sign” where the increased pressure from the retrobulbar hematoma distorts the spherical globe into a conical shape

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
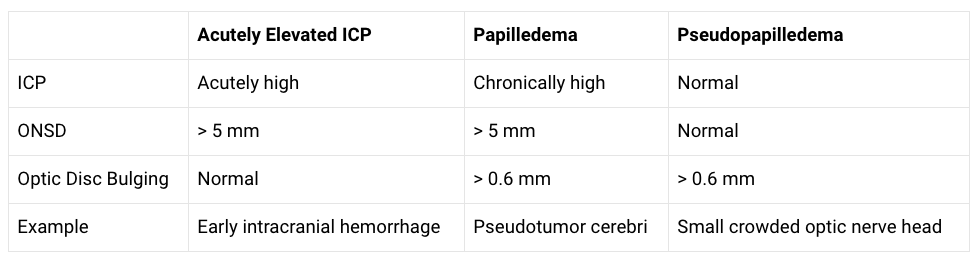
(19) Learn differences between Elevated ICP, Papilledema, and Pseudopapilledema

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
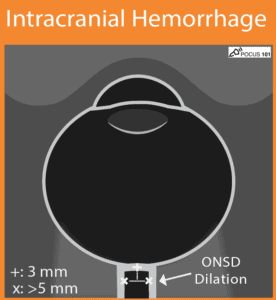
(20) Intracranial Hemorrhage with Increased ICP: you will find elevated ONSD measurements > 5 mm.

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular
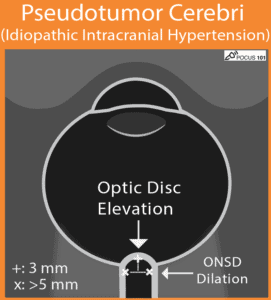
(21) Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension): you will find dilated ONSD measurements > 5 mm (increased ICP) and signs of Papilledema (optic disc bulging/elevation).

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 https://pocus101.com/Ocular
https://pocus101.com/Ocular

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter